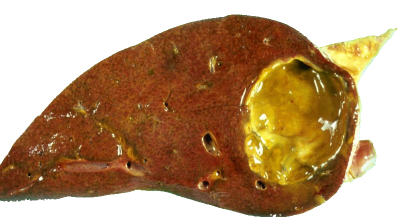
Pyogene leverabces
Pyogene leverabces
Auteur: J. Sprakel, MD - Laatste update: 31-08-2017
Pyogene leverabces
Epidemiologie
- - Incidentie: 5-20 per 100.000
- - Mortaliteit: 6-30% 1
- - Vroeger bij "foi appendiculaire" - portaal abcederende hepatitis na appendicitis 2
- - Huidige oorzak: galwegpathologie
- Etiologie
- 1. Opstijgende infectie vanuit de galwegen 3-9
- 2. Hematogene verspreidingsroute 10
- 3. Directe uitbreiding van een intra-abdominale infectie zoals bij fistelvorming (bijvoorbeeld subfrenisch abces of maagulcus) en necrose van het leverparenchym 2,6,8,9,11
- 4. Cryptogeen: in circa 40% van de leverabcessen - onduidelijke ethiologie 1,12
- Microbiologie:
- - Galwegpathologie: gramnegatieve aerobe bacteriën en enterokokken vooral E. Coli 13
- - Hematogene verspreiding: grampositieve, facultatief anaerobe kokken 14-15
- - Intraperitoneale infectiebron: facultatief aeroben en anaeroben (Bacteroides fragilis)
- - Bij immuungecompromitteerden: Candida albicans 16-18
Anamnese
- - Aspecifieke klachten
- - Vermoeidheid
- - Misselijkheid
- - Overgeven
- - Gewichtsverlies
- - Nachtzweten
- - Verminderde eetlust
- - Uitstralende pijn naar de rechterschouder, pijn bij het ademhalen en droge hoest bij diafragmaprikkeling
- - ERCP
- - Reizen (cave: amoebe leverabces - E. histolytica)
- - Bloederige ontlasting bij amoebendysenterie
- - Icterus
Diagnostiek
- Laboratorium
- - Verhoogde ontstekingsparameters
- - Leukocytose zonder eosinofilie
- - Gestoorde leverfuncties met name alkalisch fosfatase
- - Hypoalbuminemie 19
- - Indirecte hemagglutinatie (IHA) en latexagglutinatie (LA) - bij amoebeabces 20-22
- - Parasitologisch onderzoek van de feces bij verdenking amoebeabces
- - Bloedkweken
- Echo abdomen
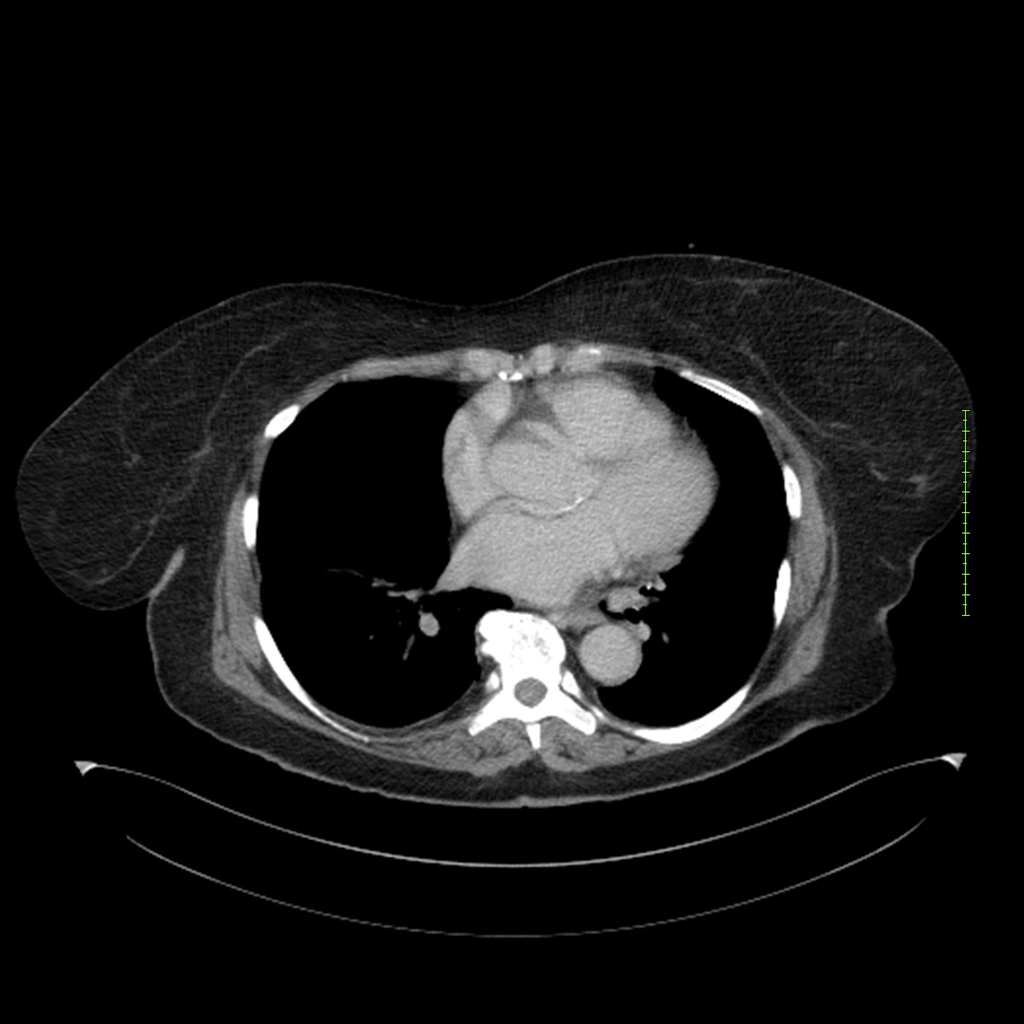
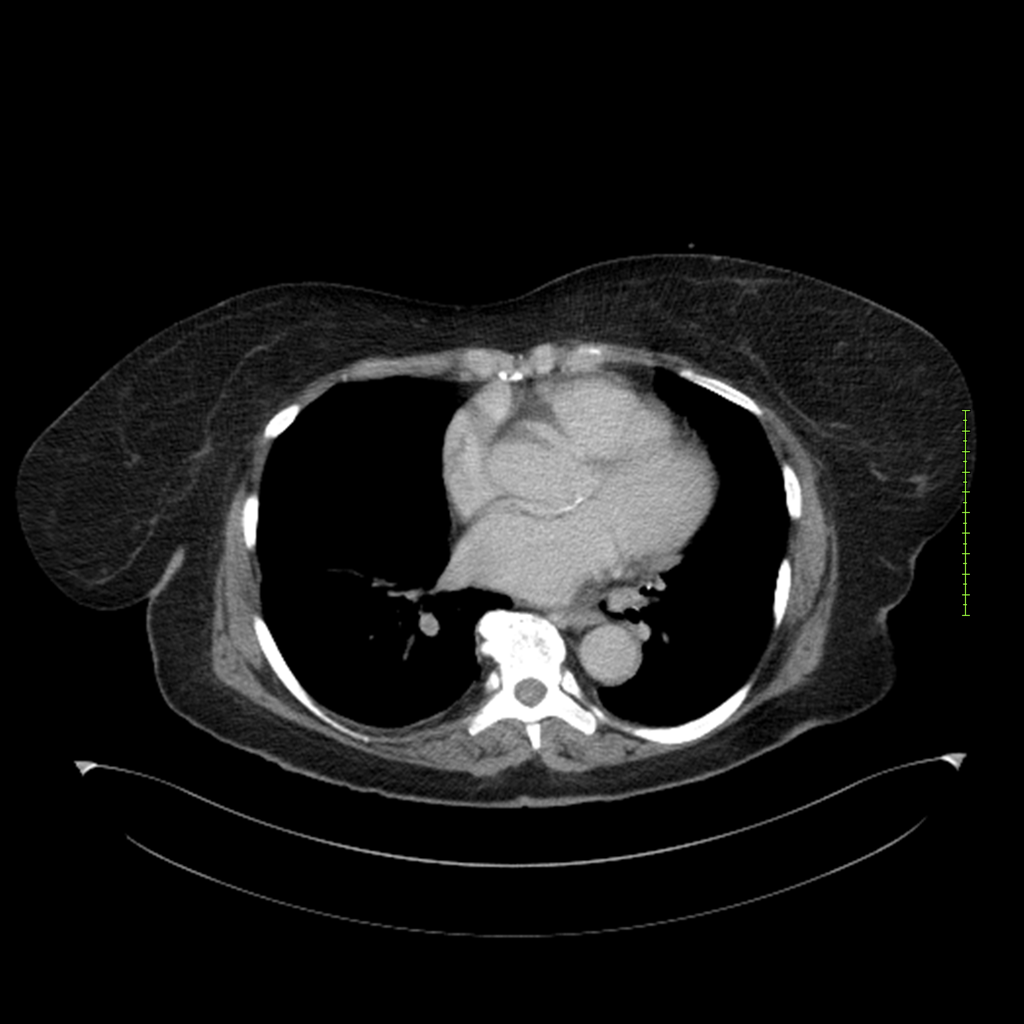
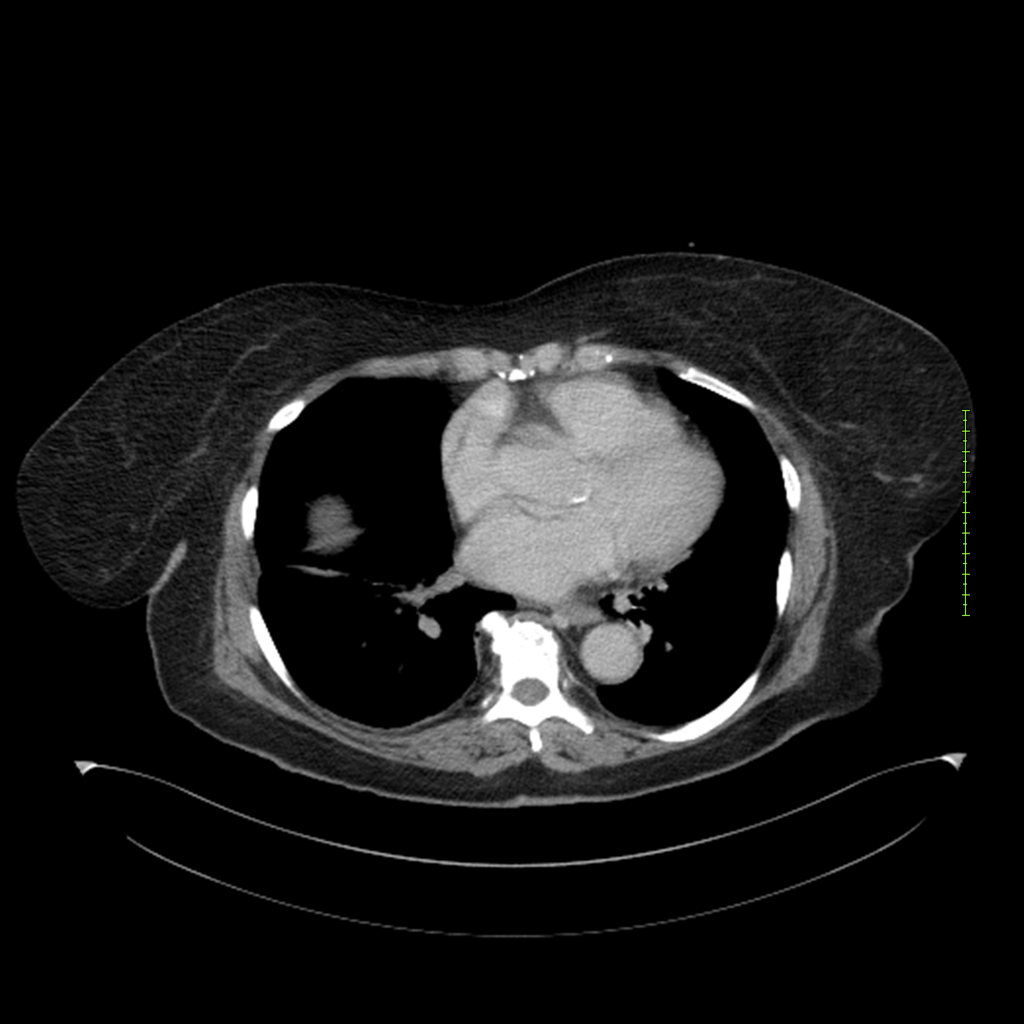
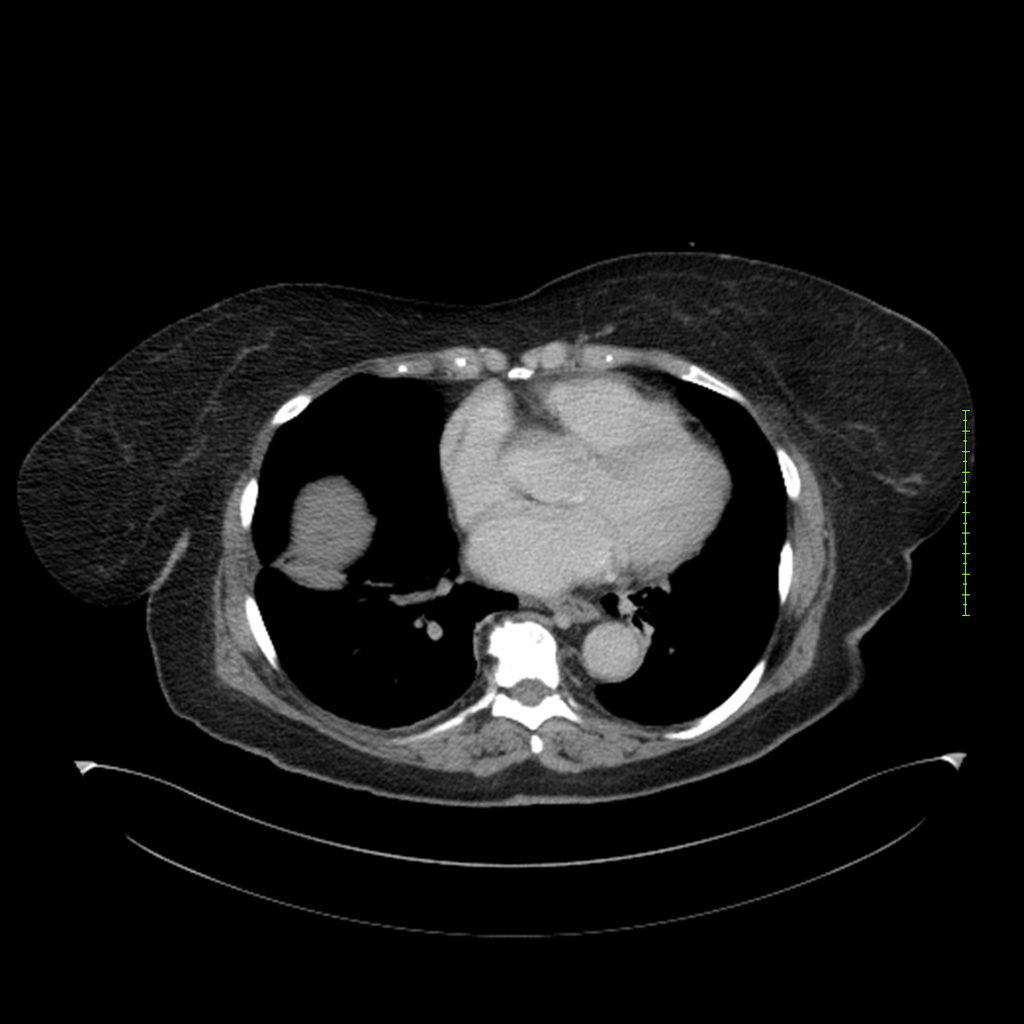
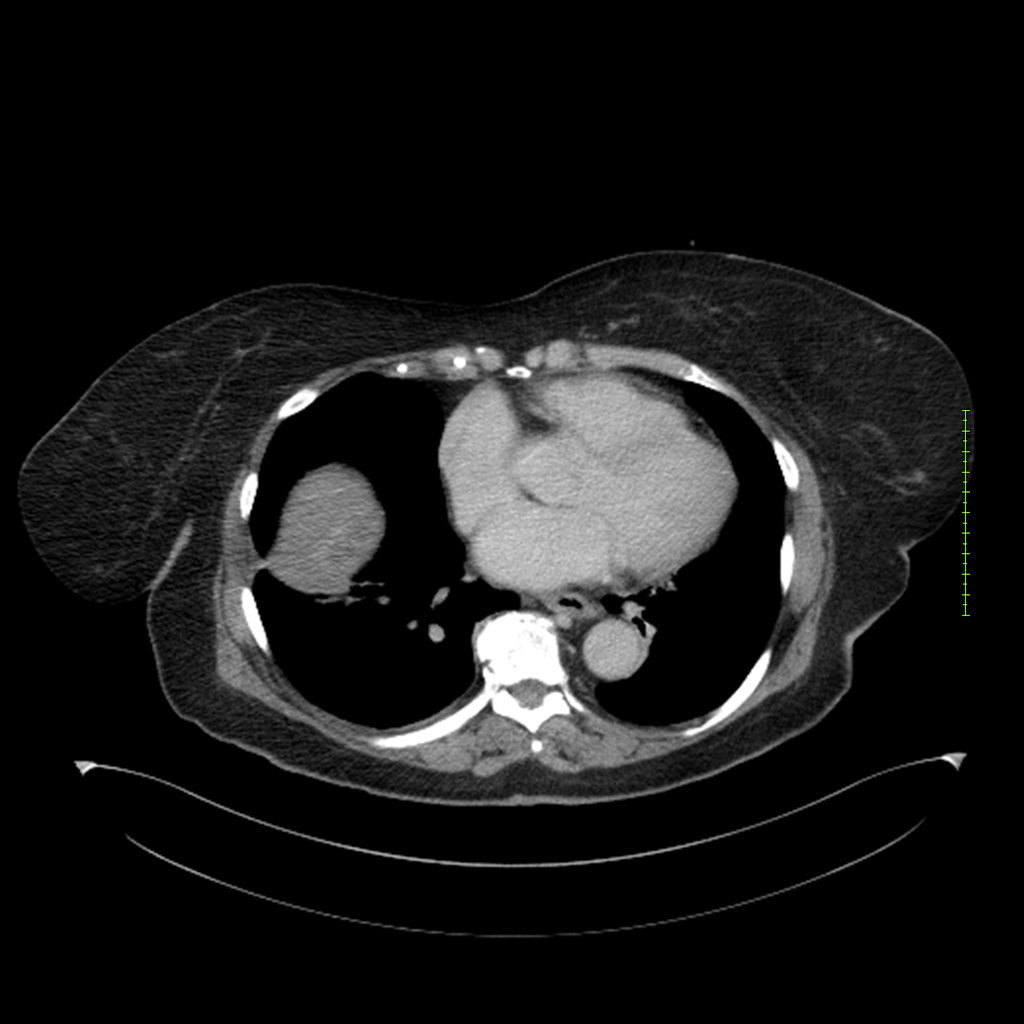
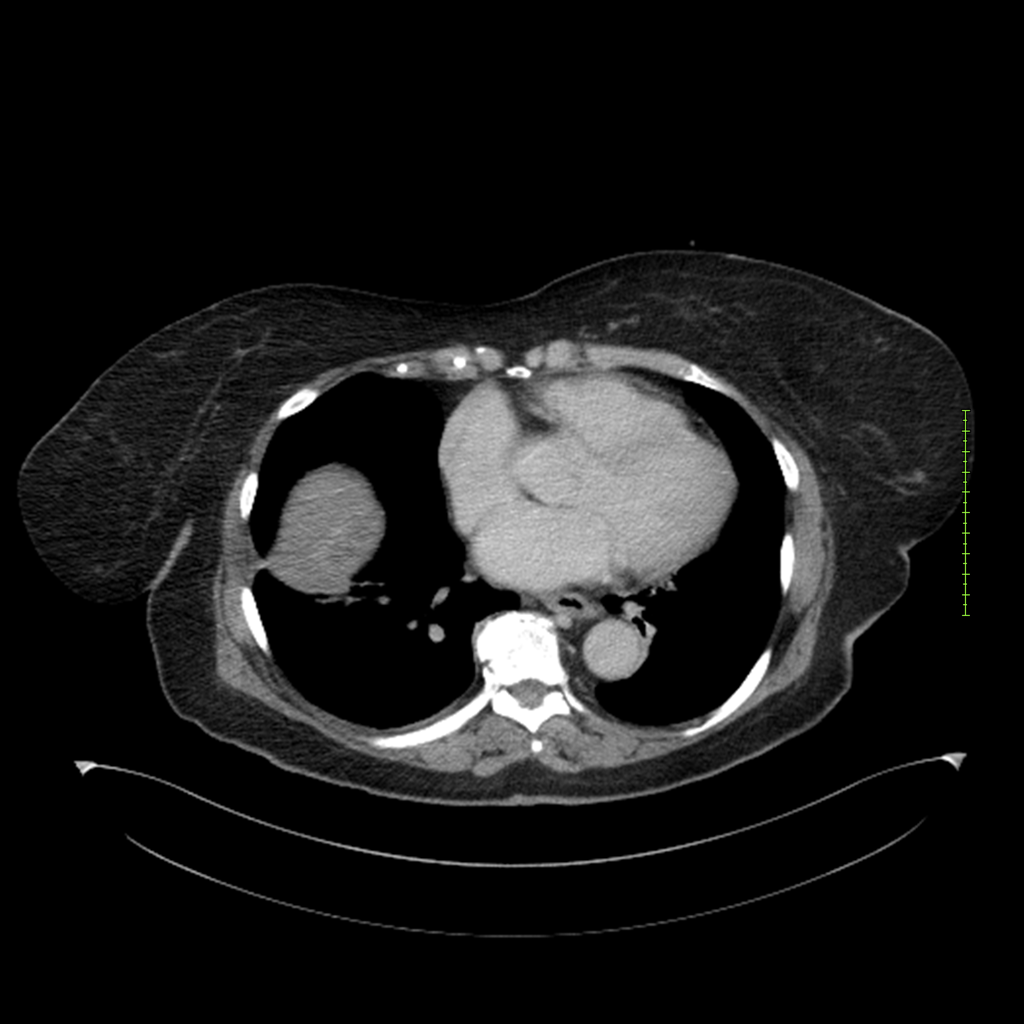
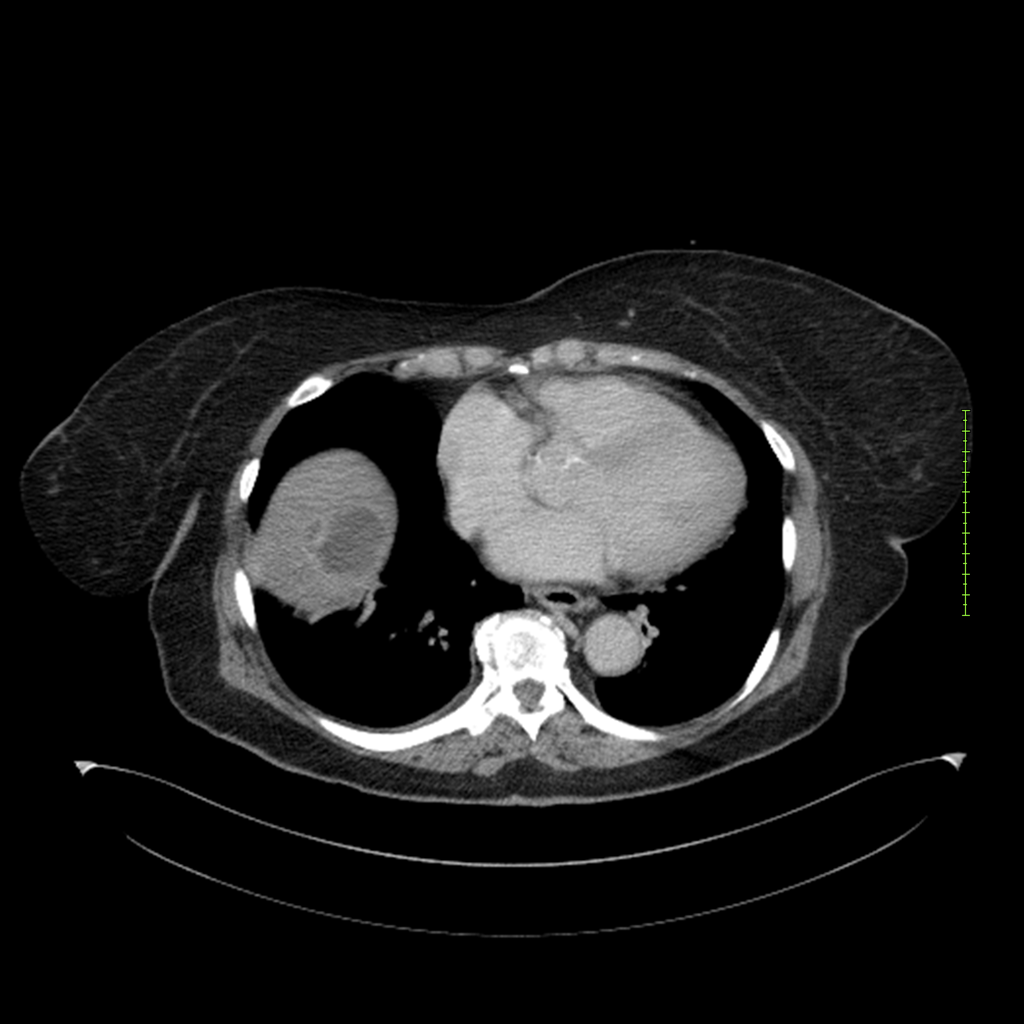
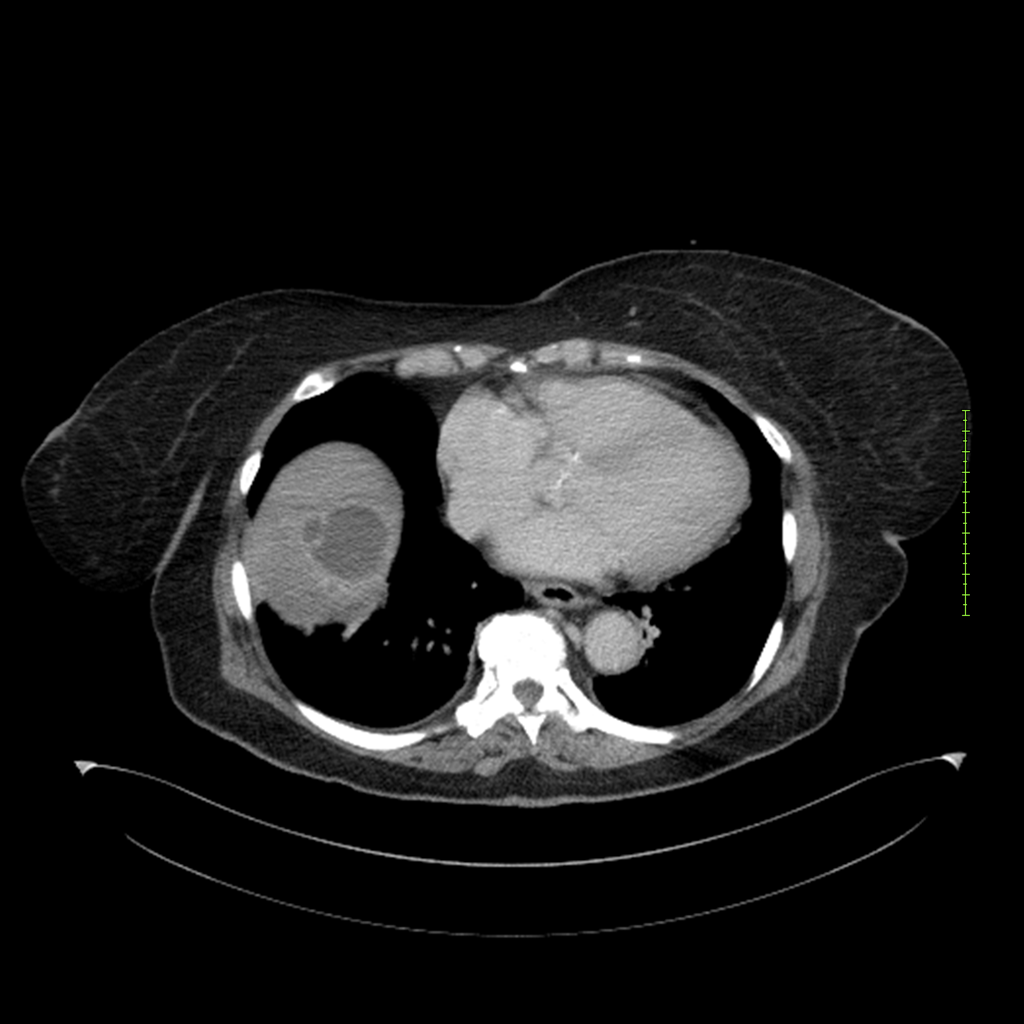
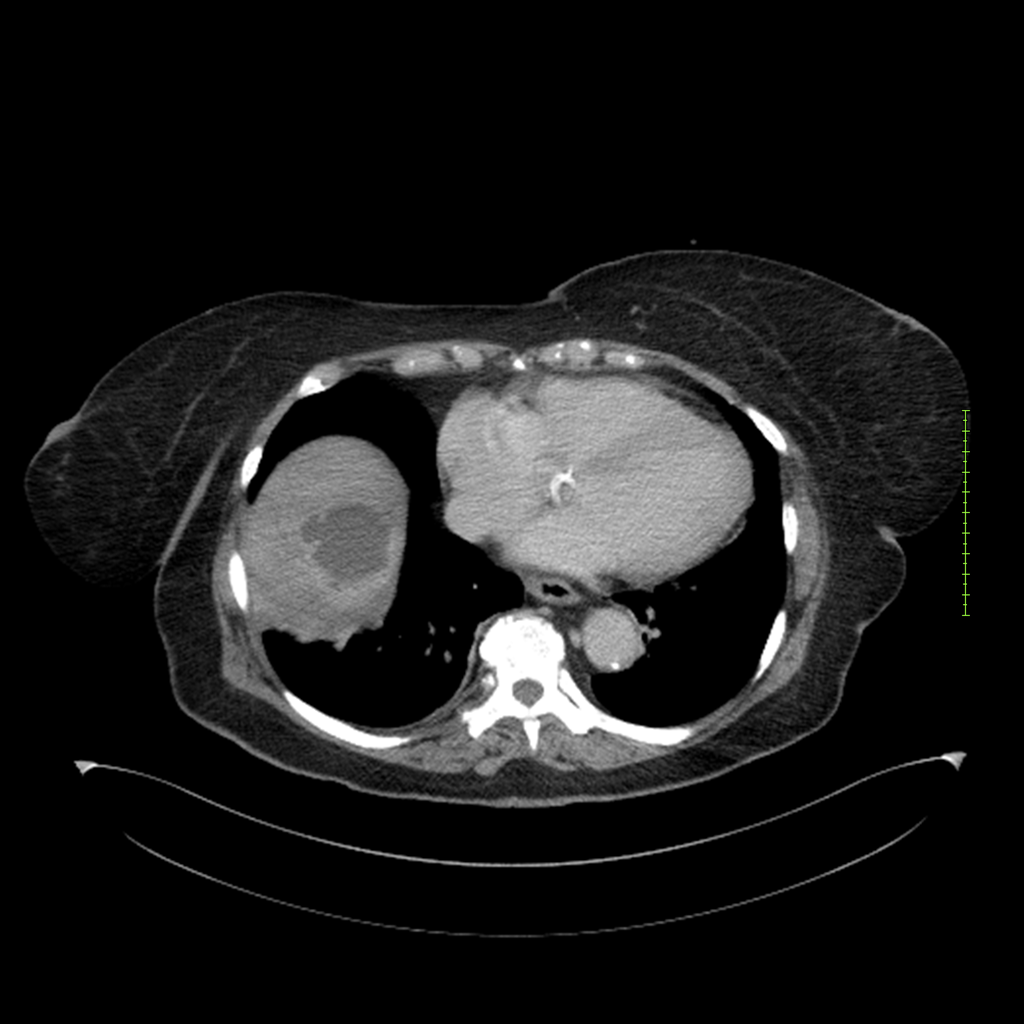
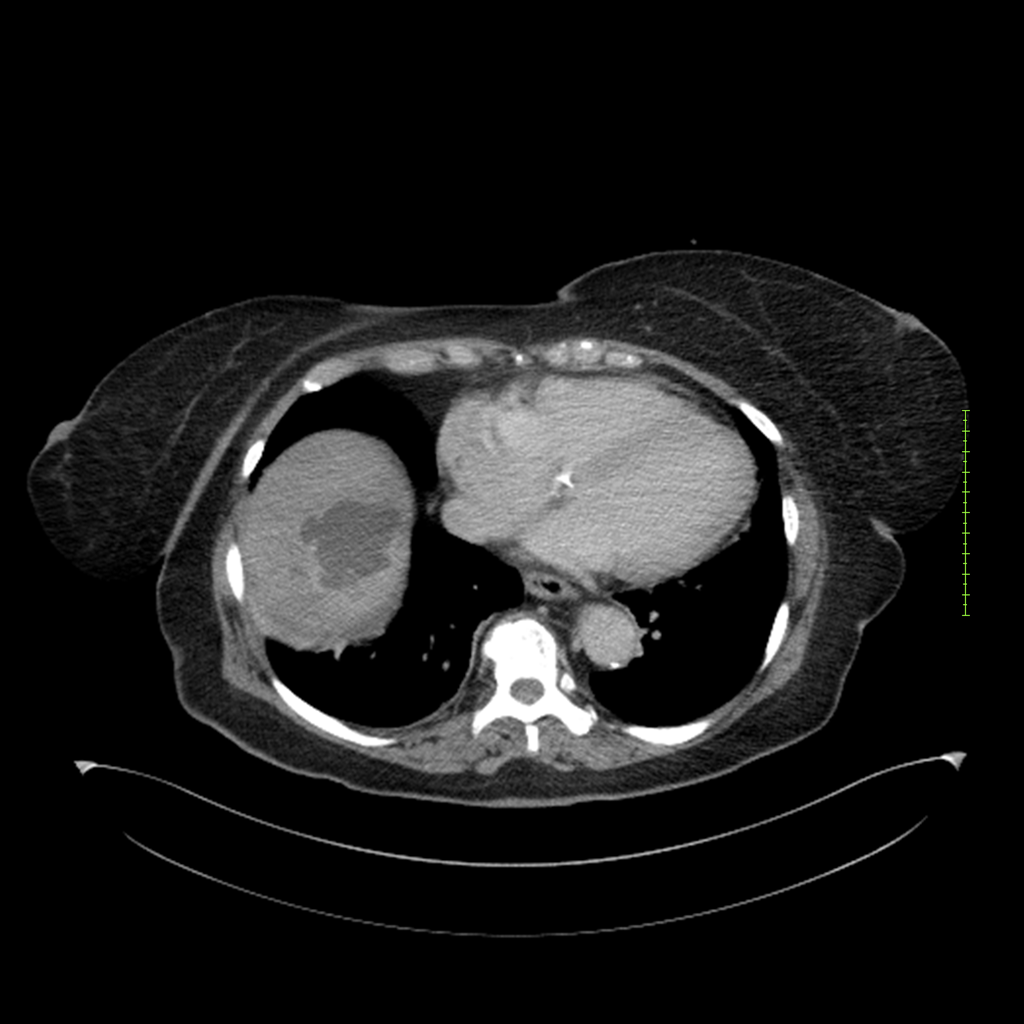
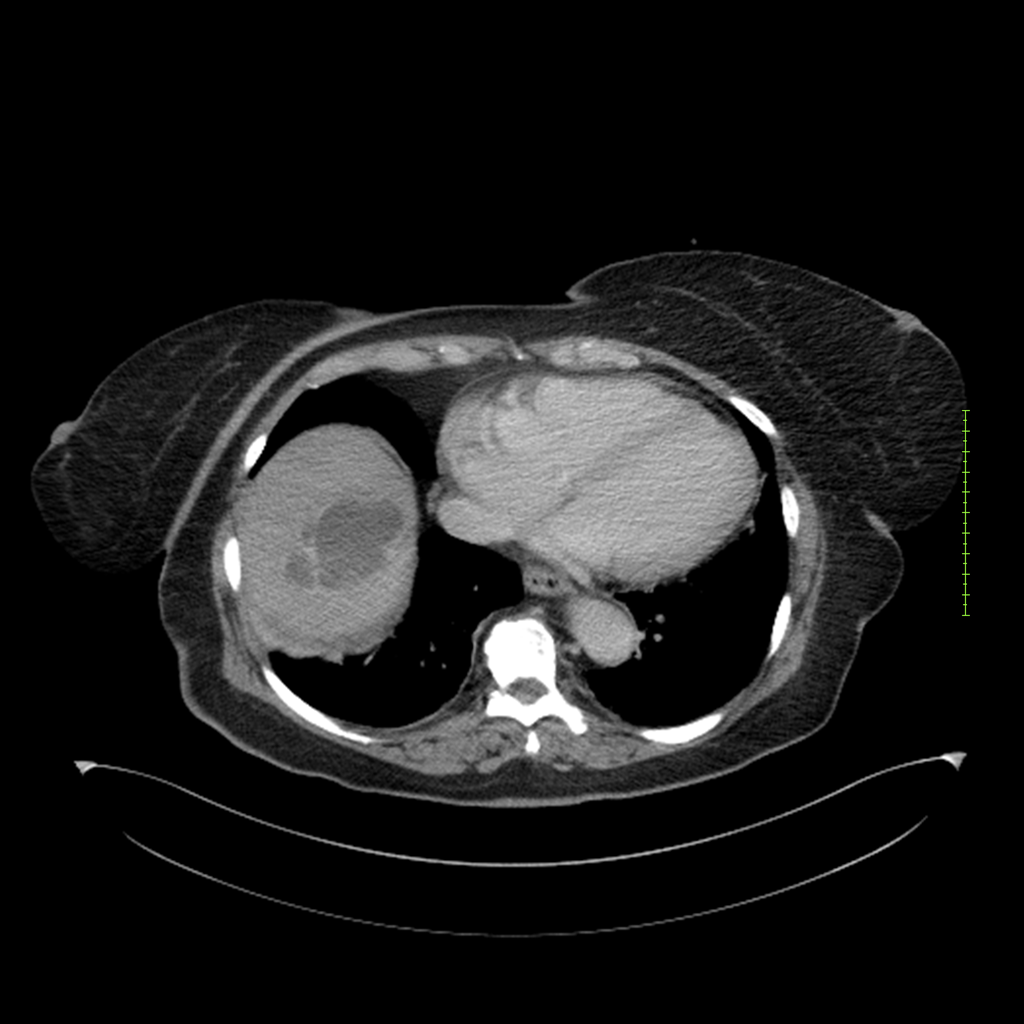
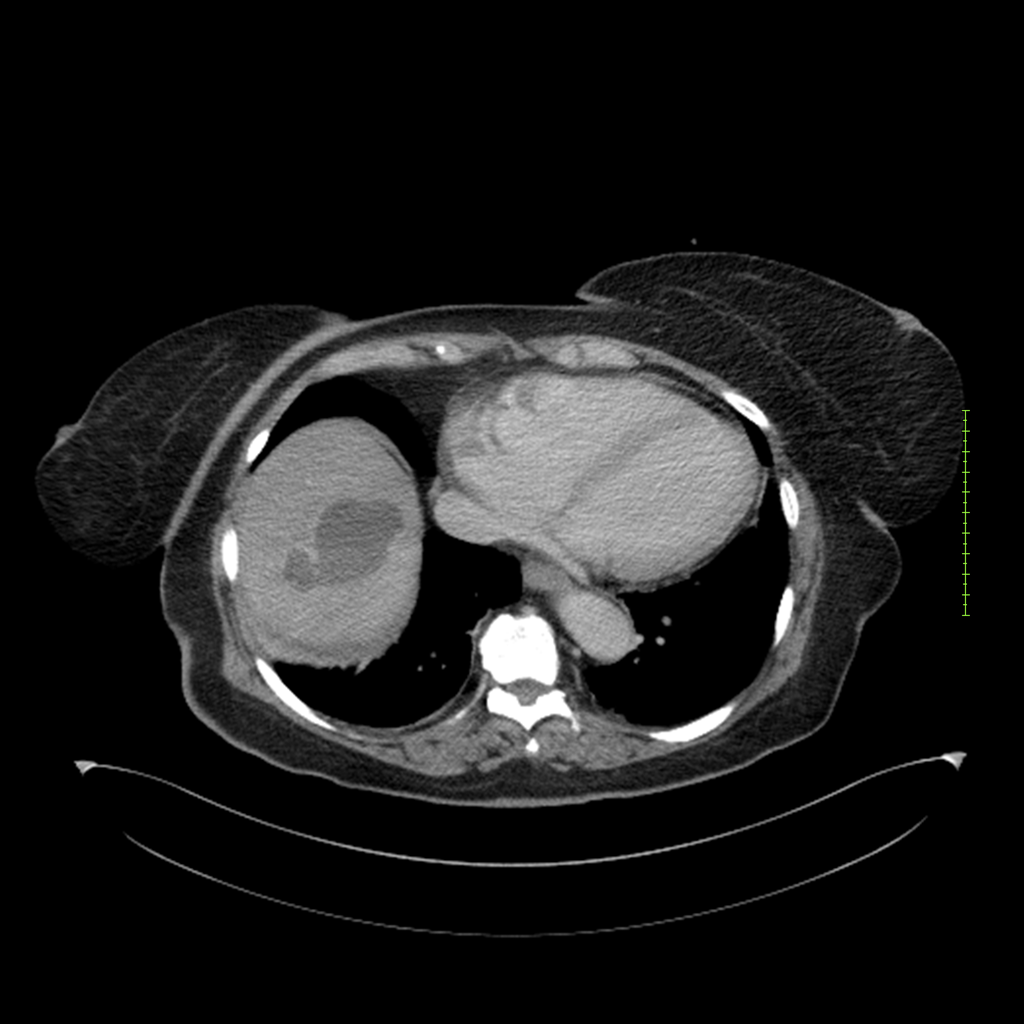
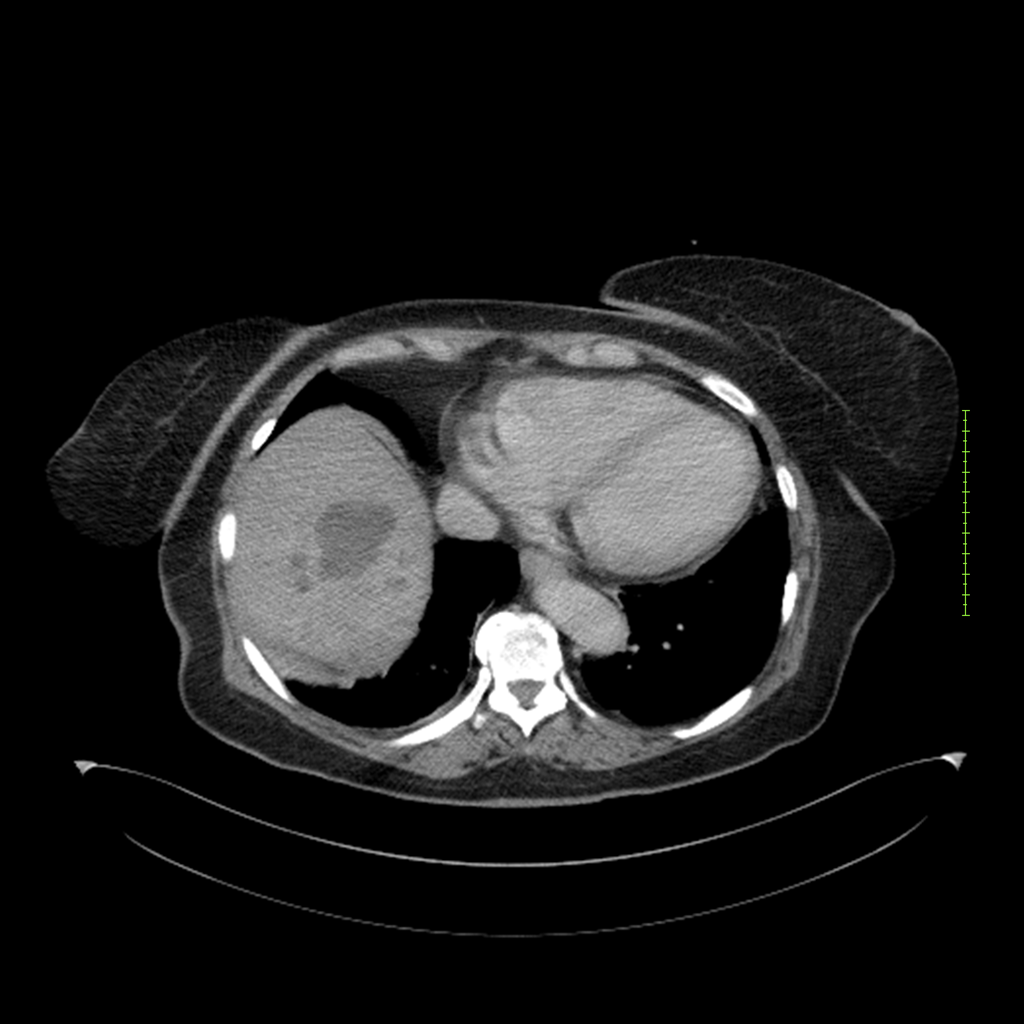
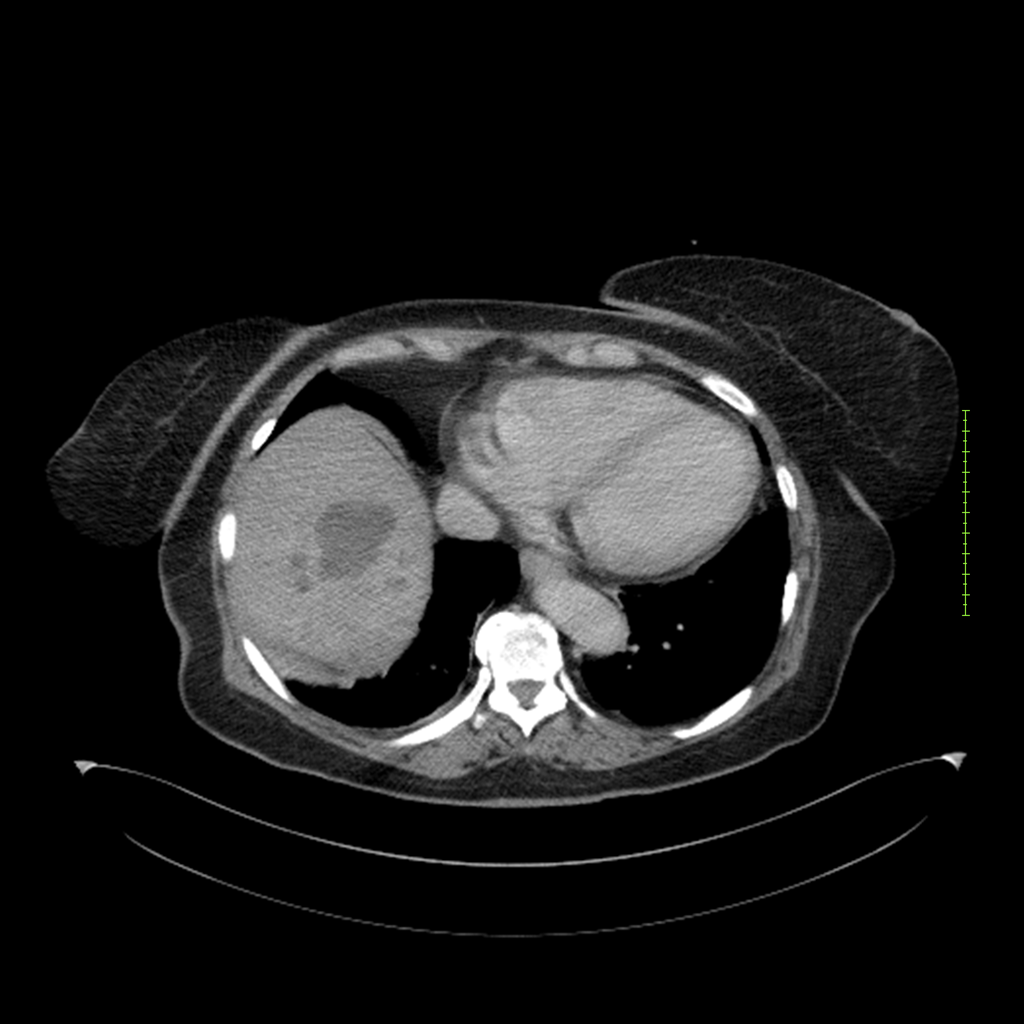
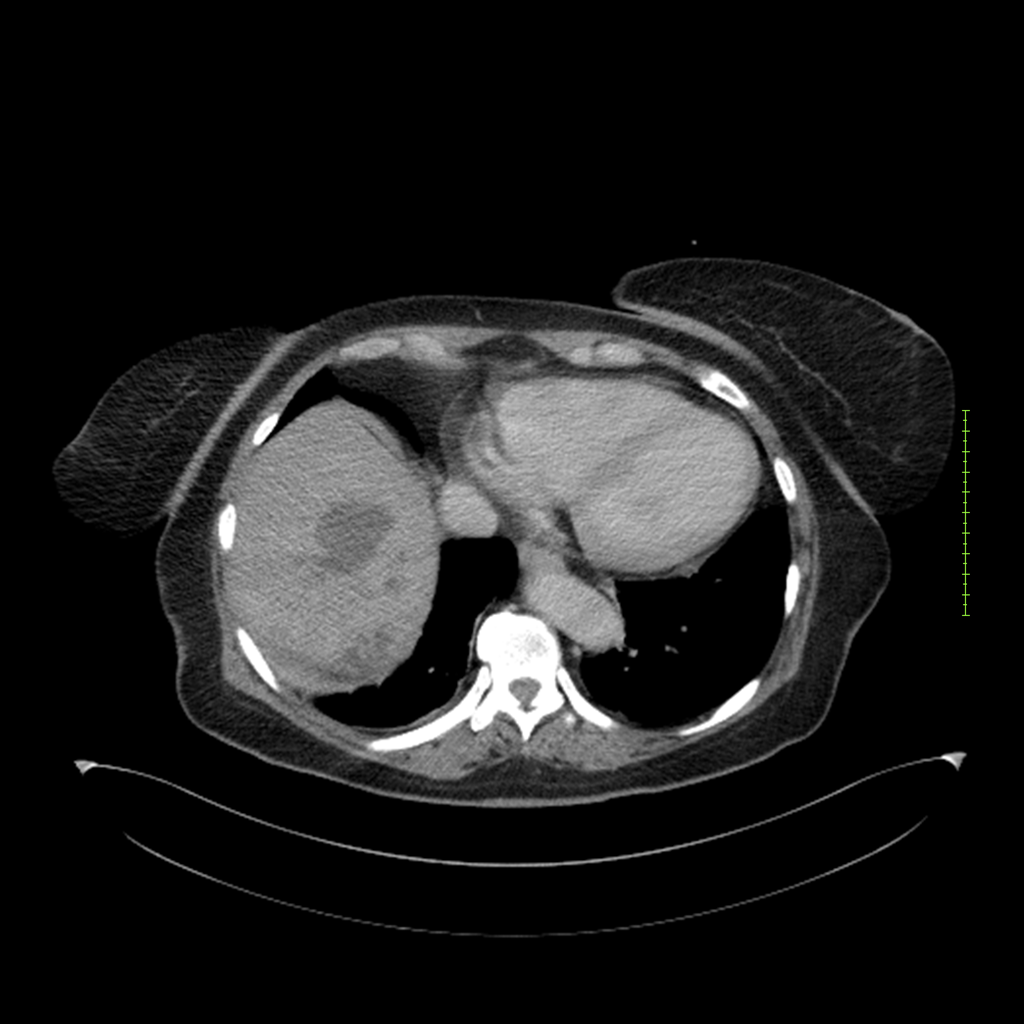
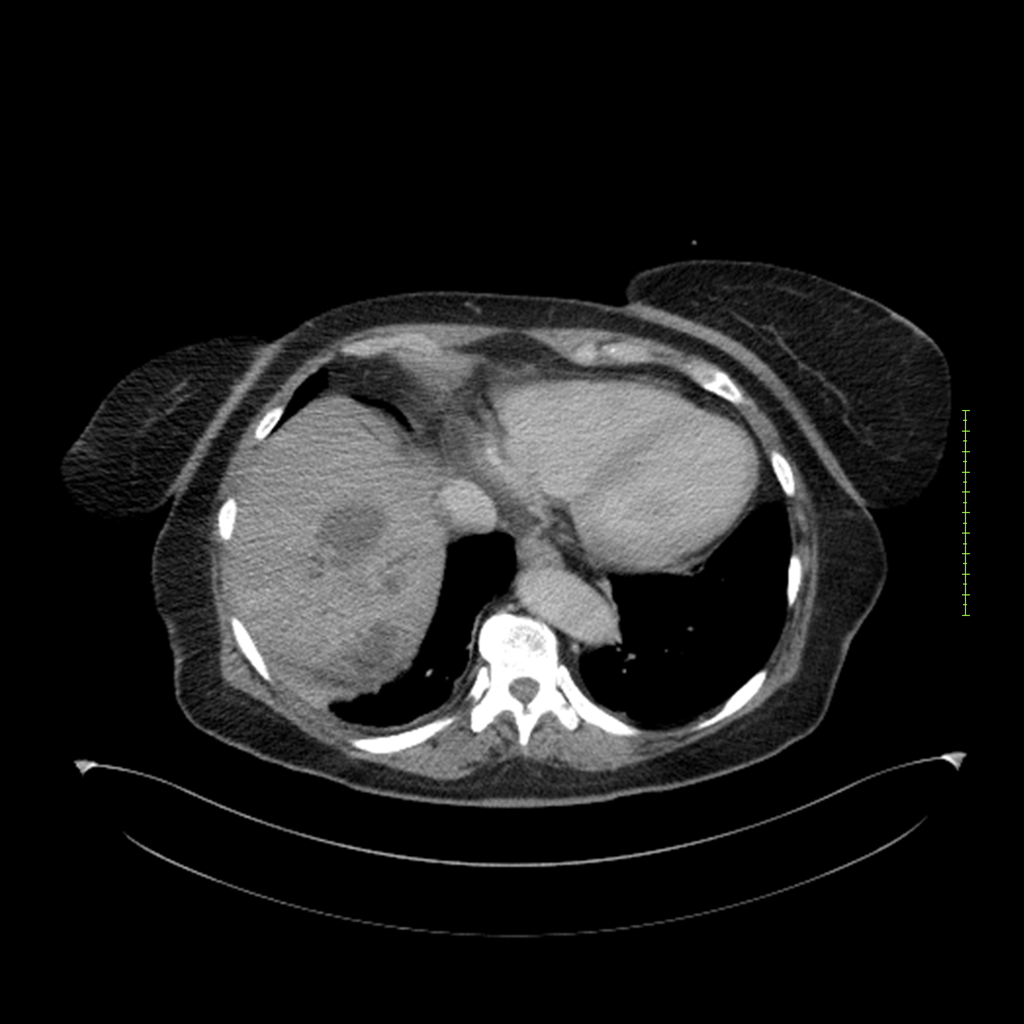
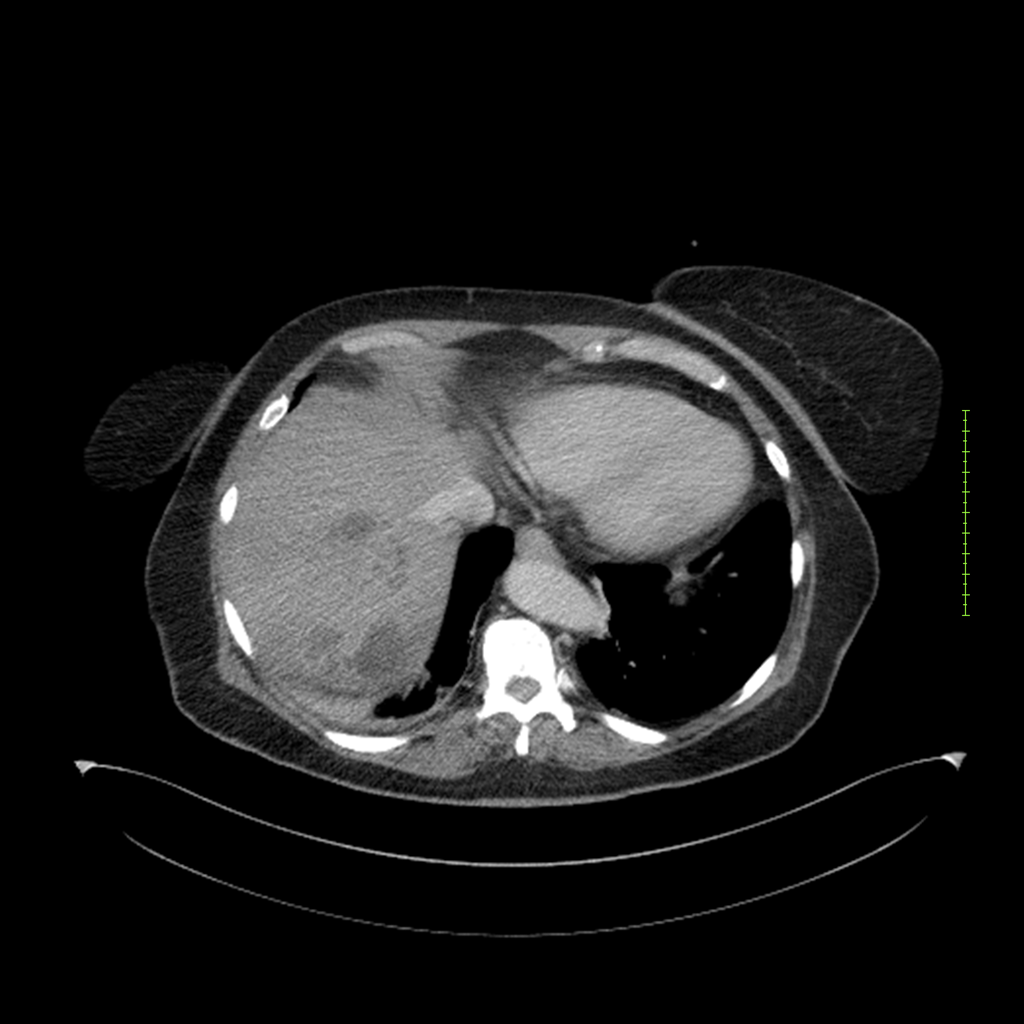
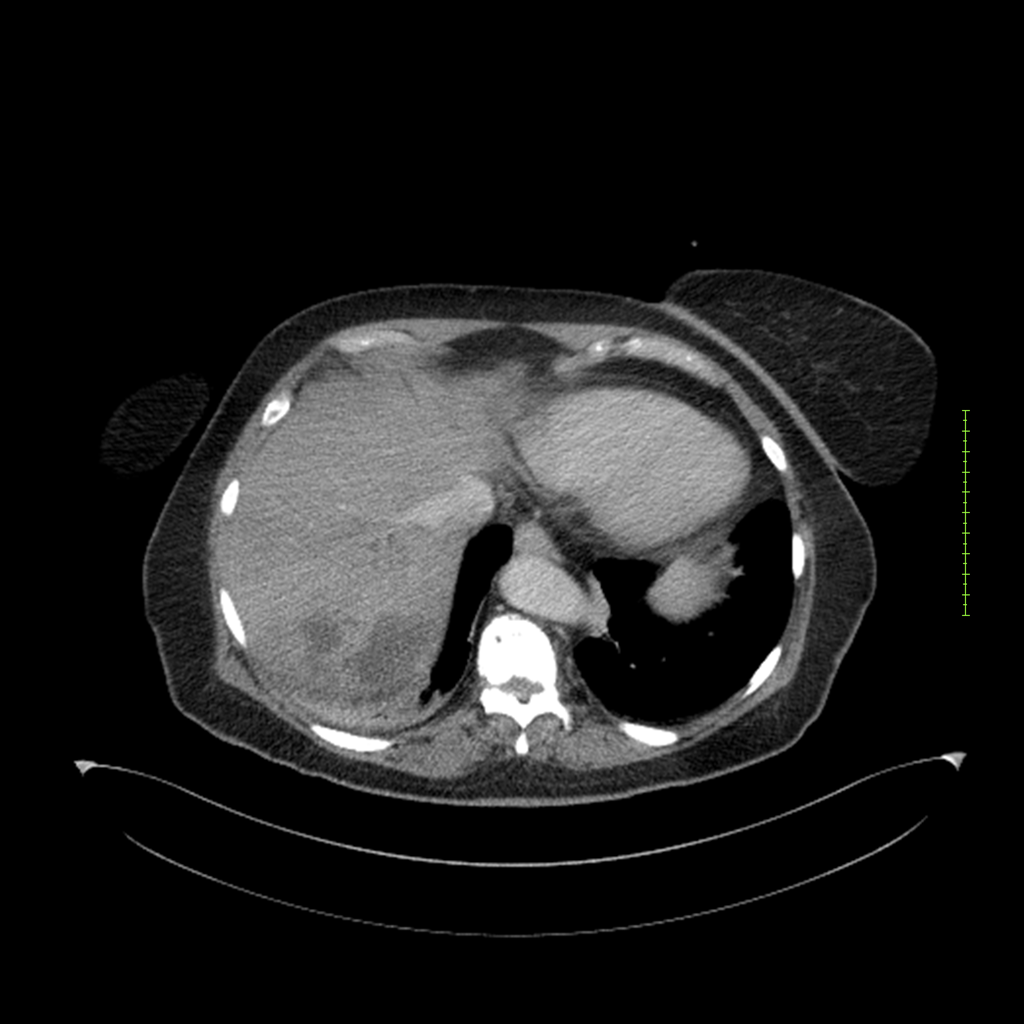
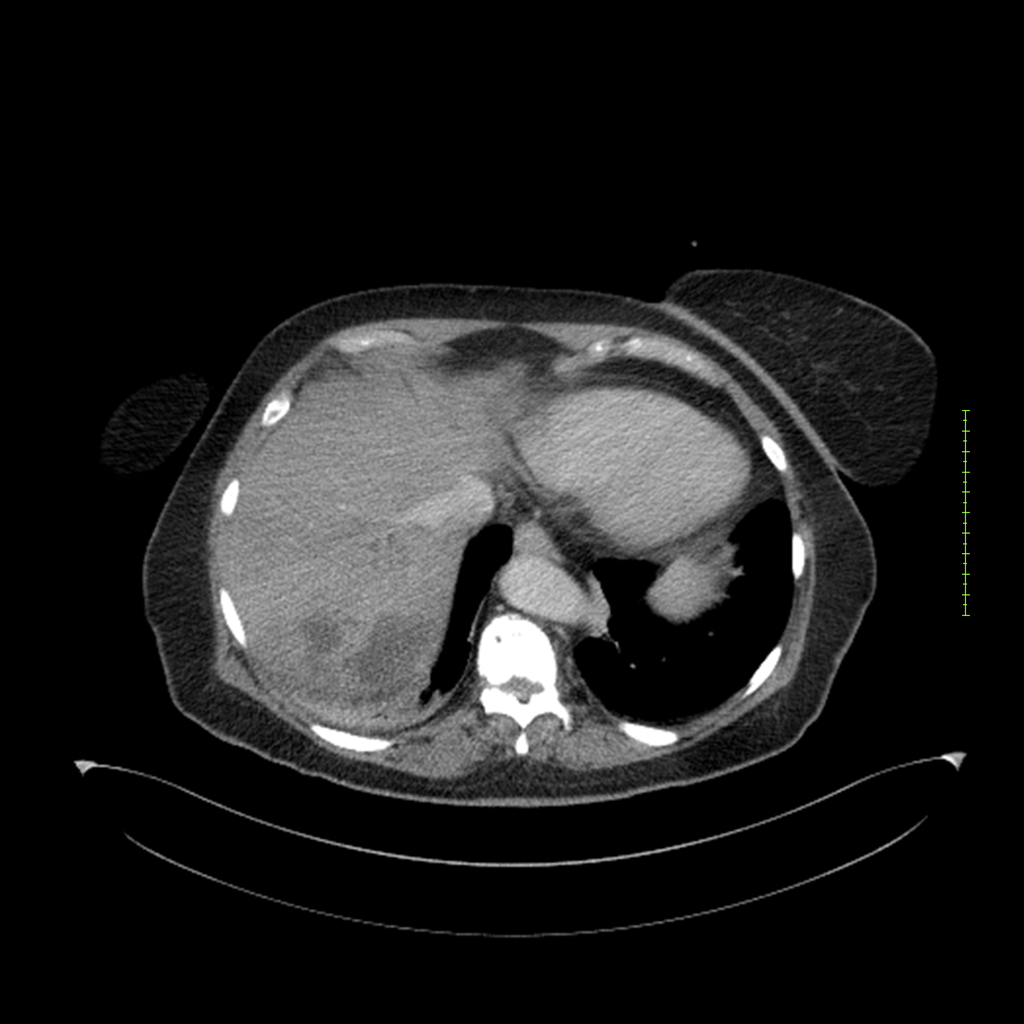
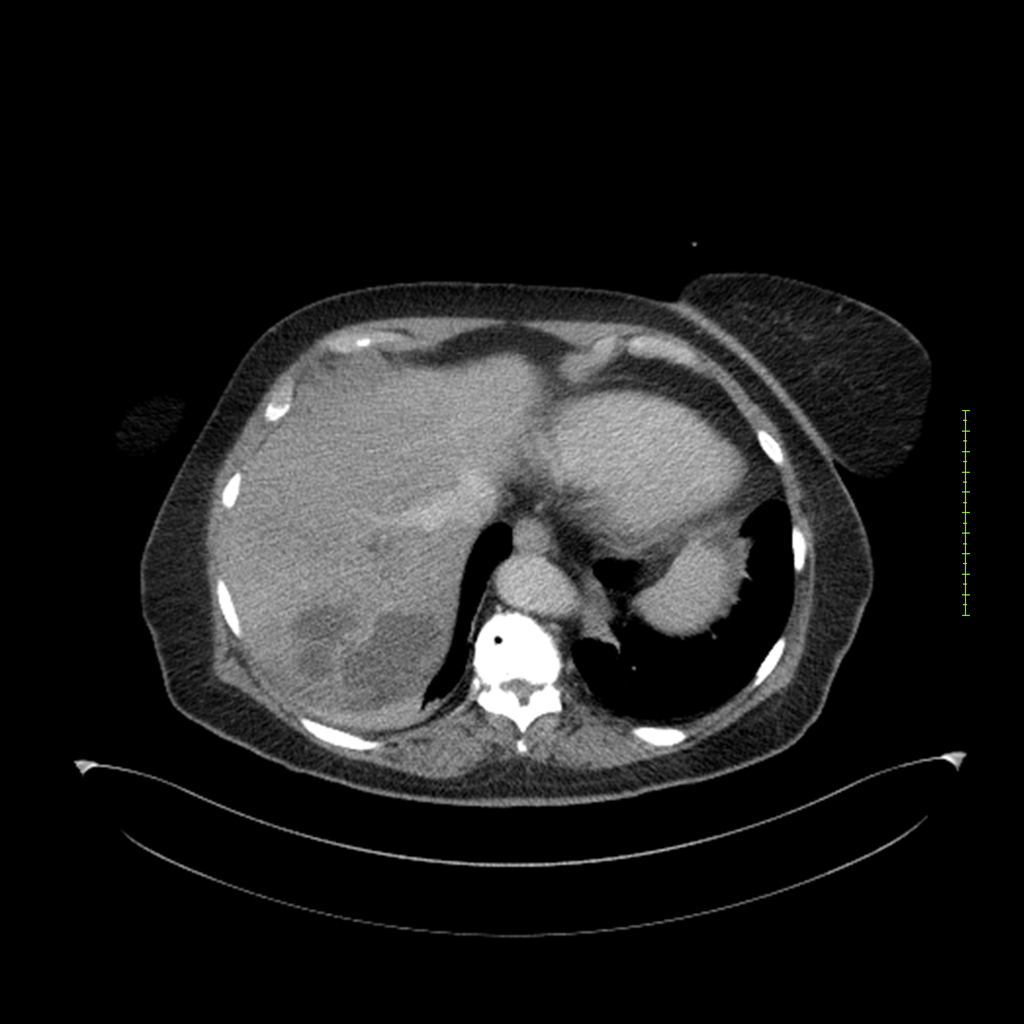
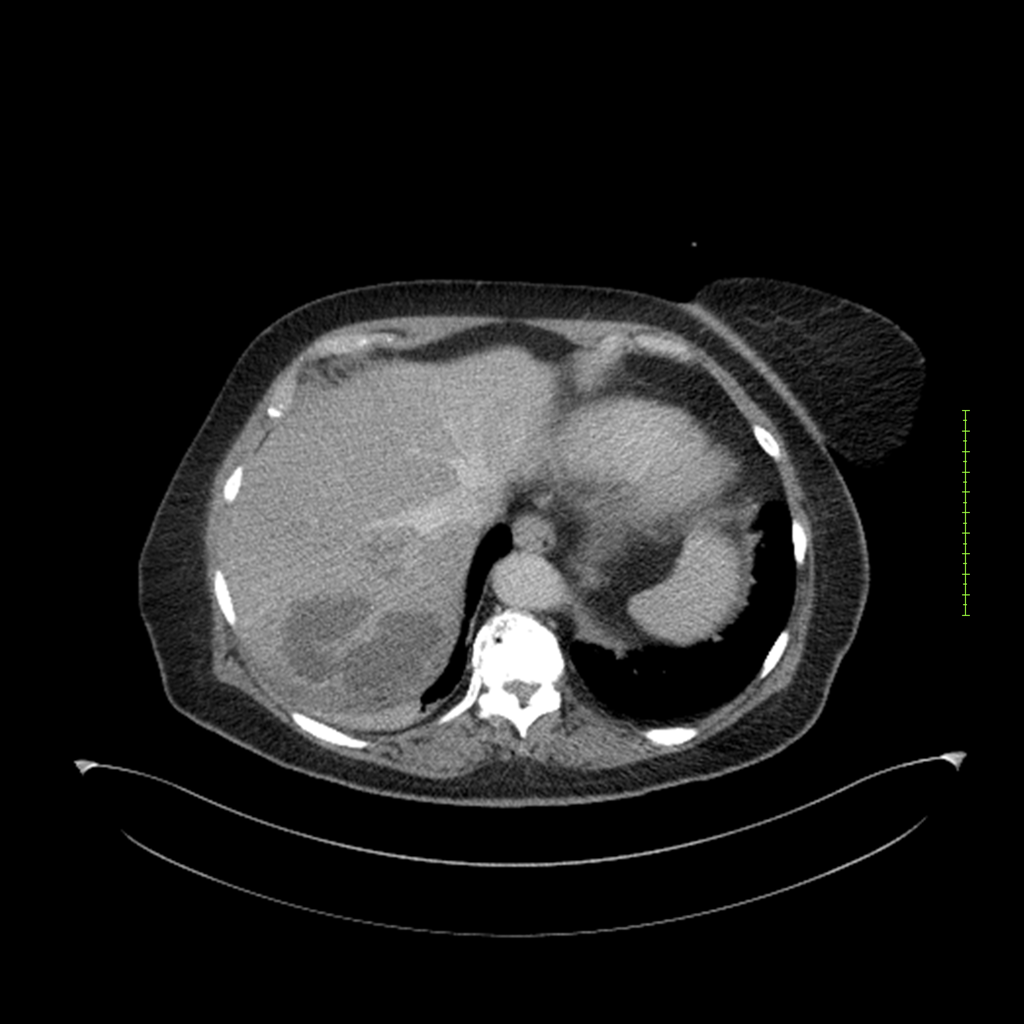
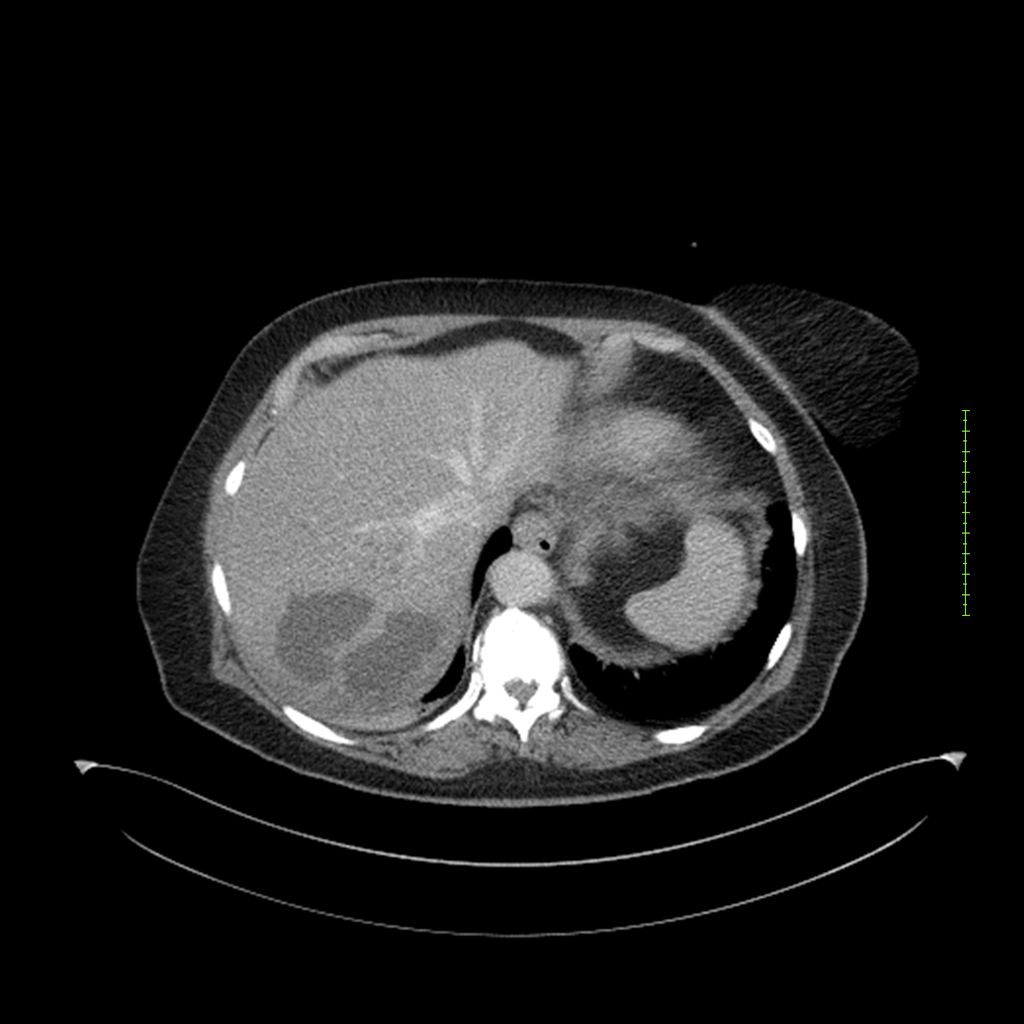
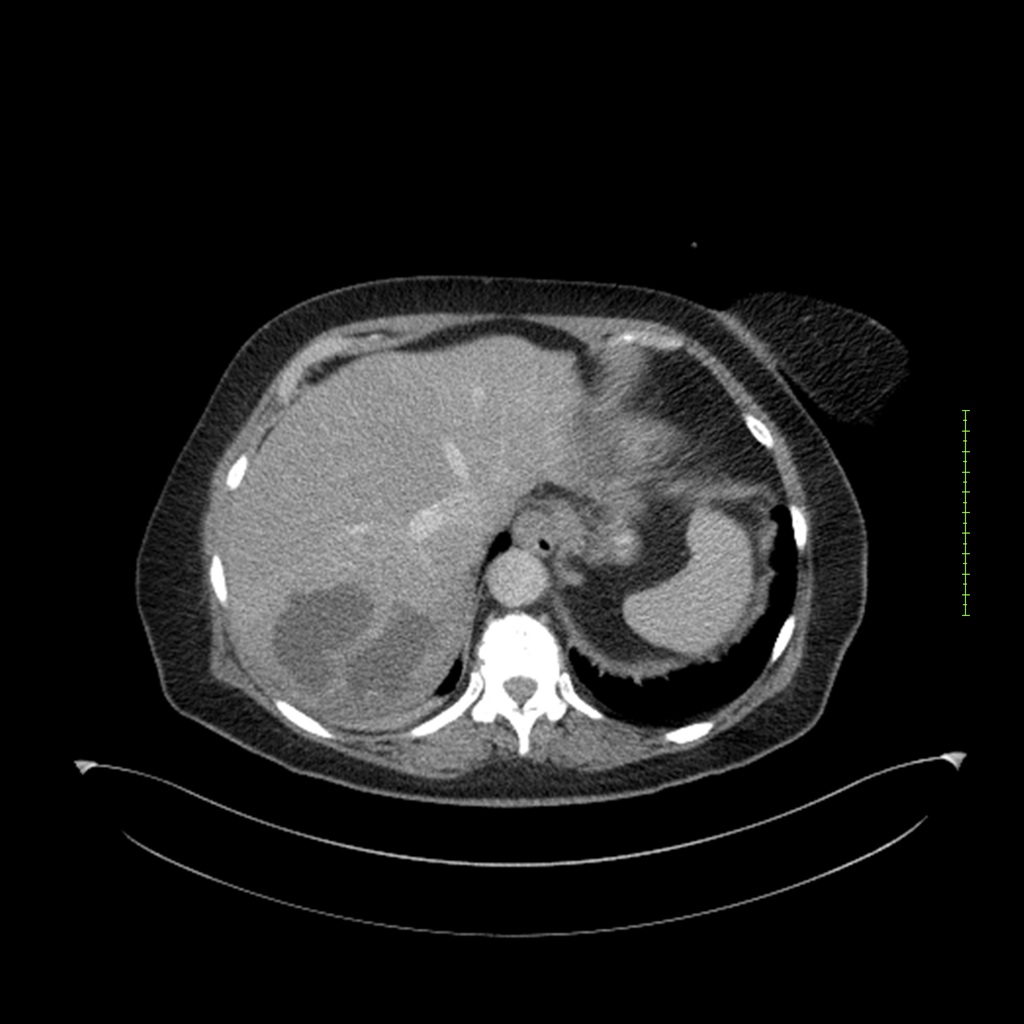
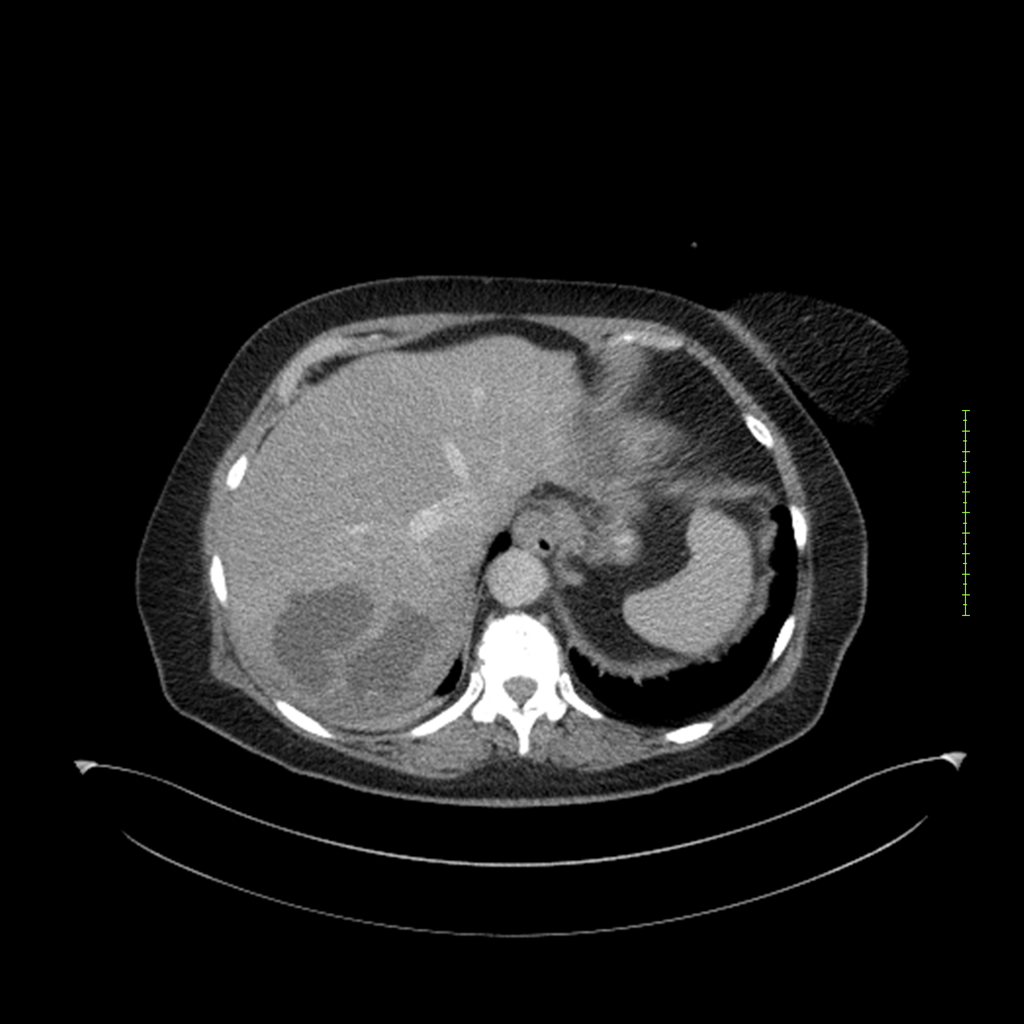
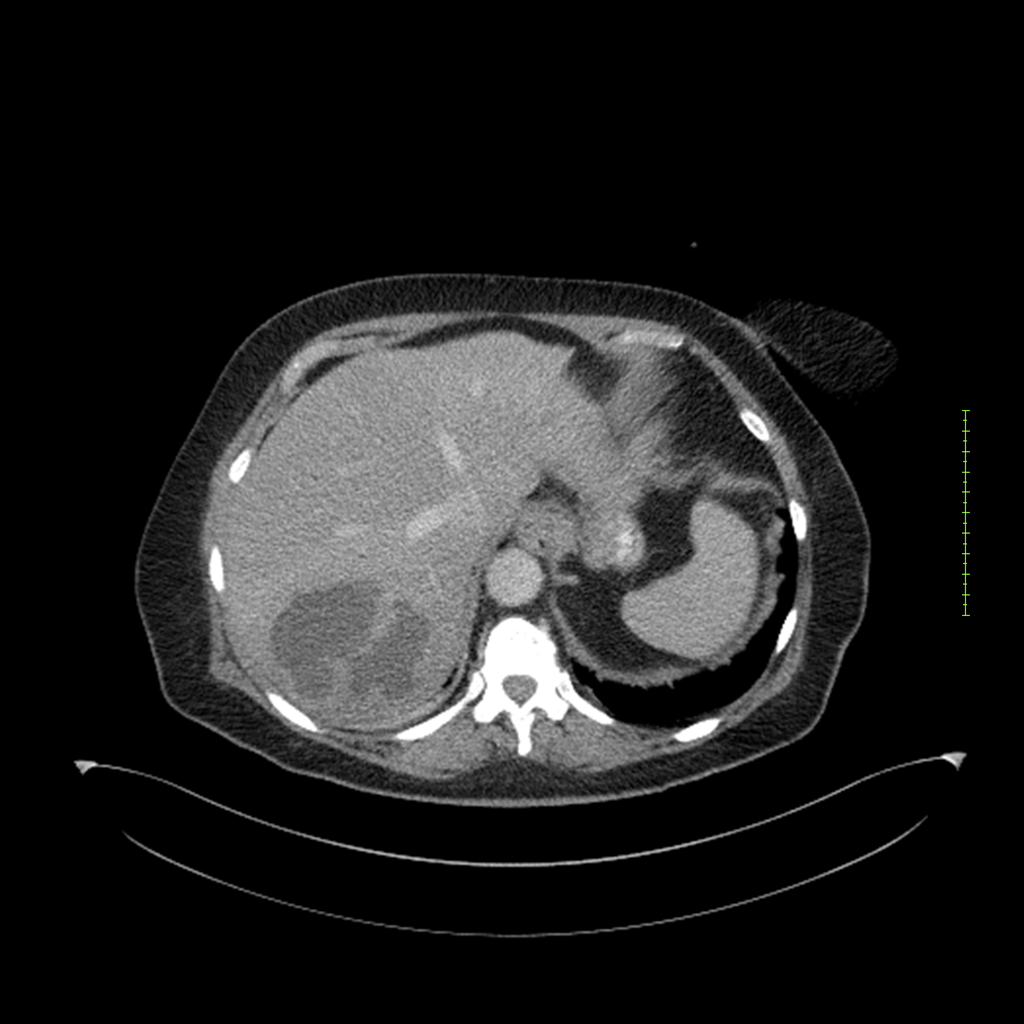
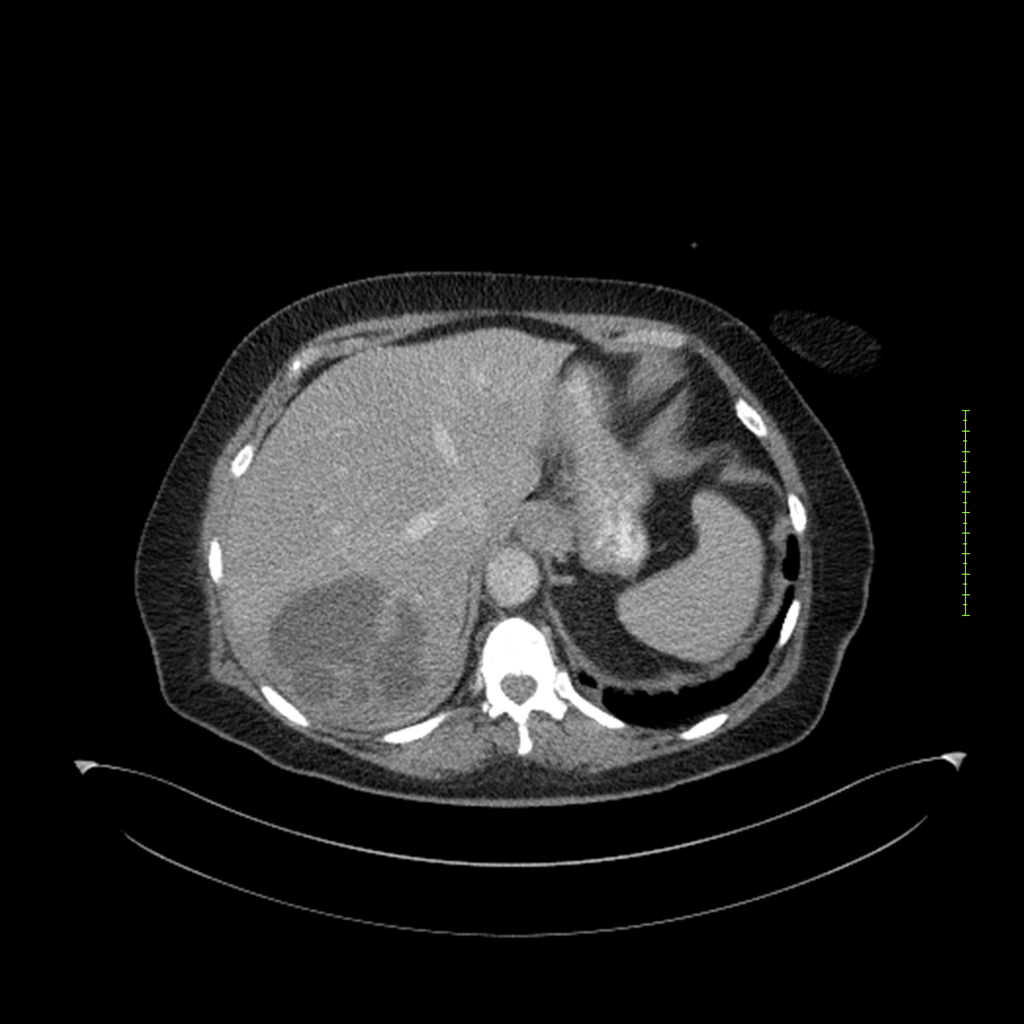
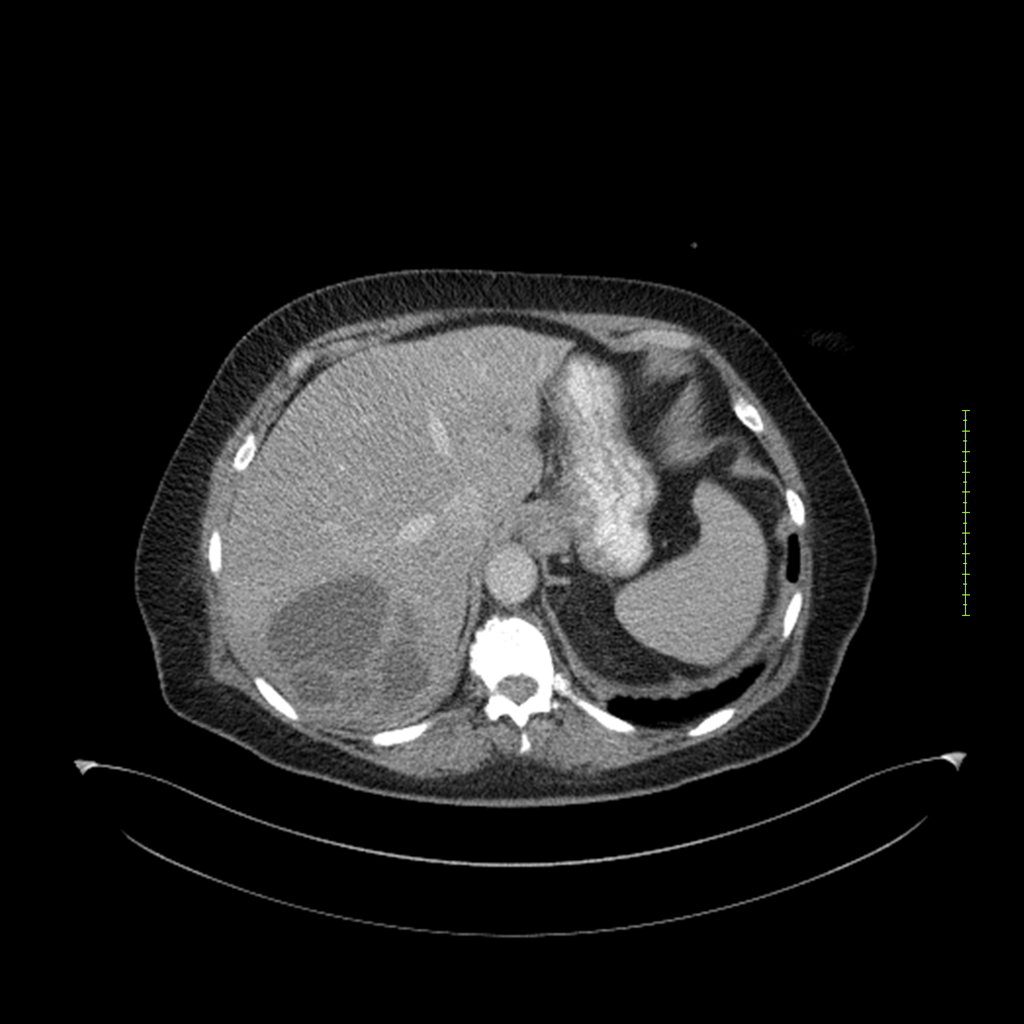
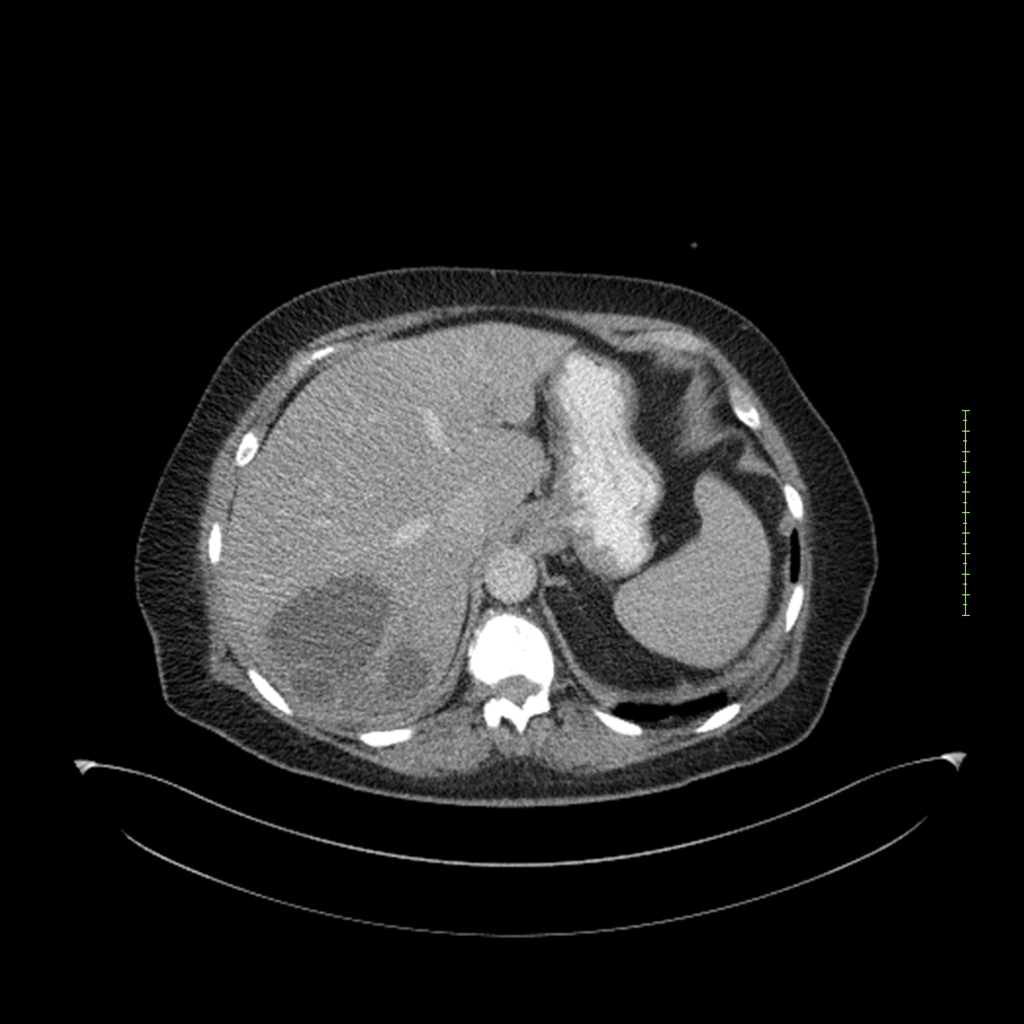
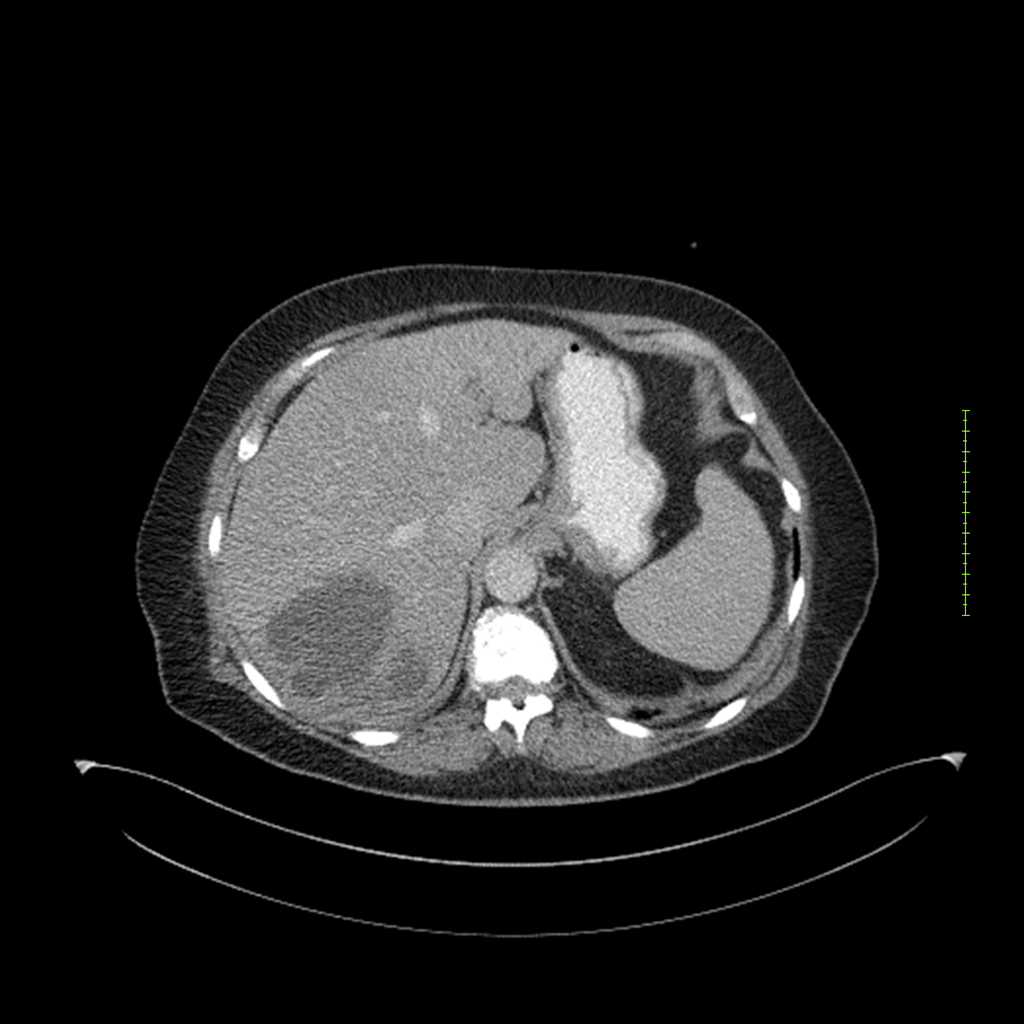
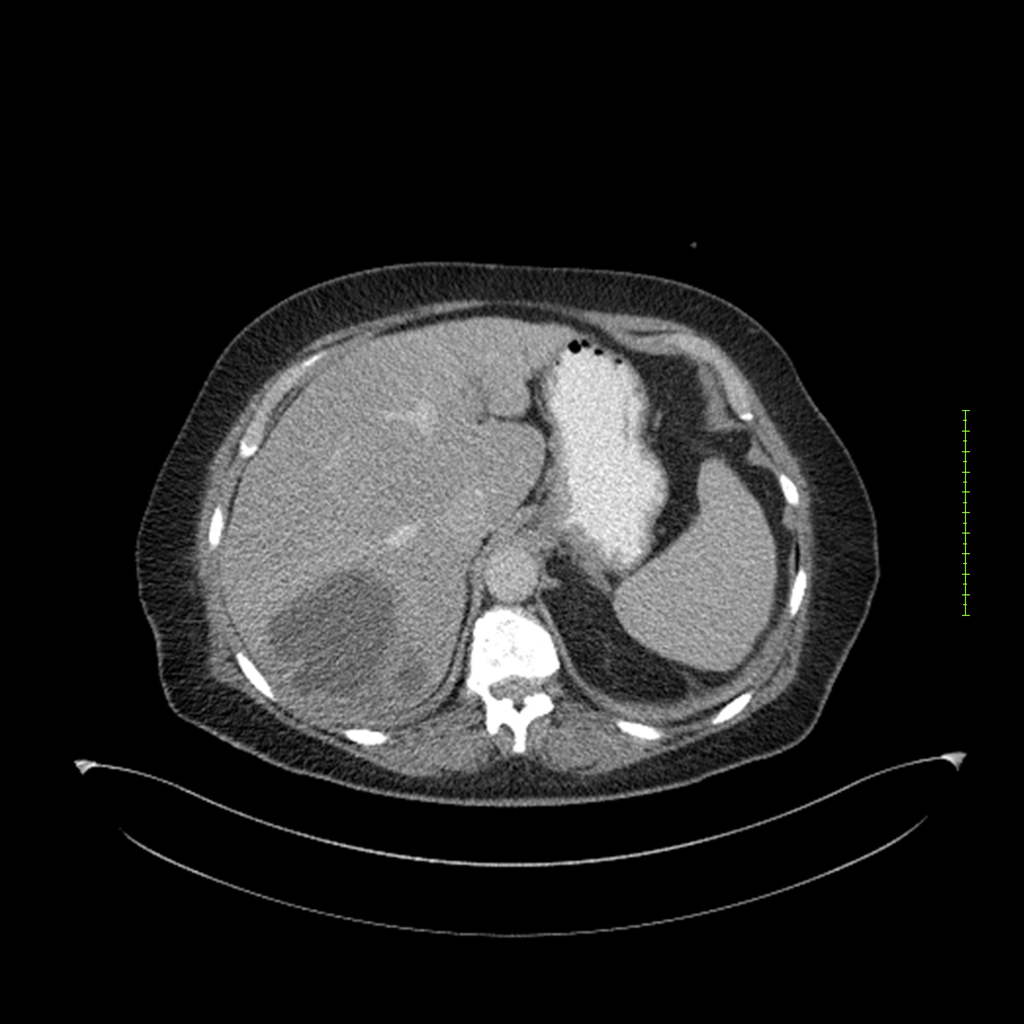
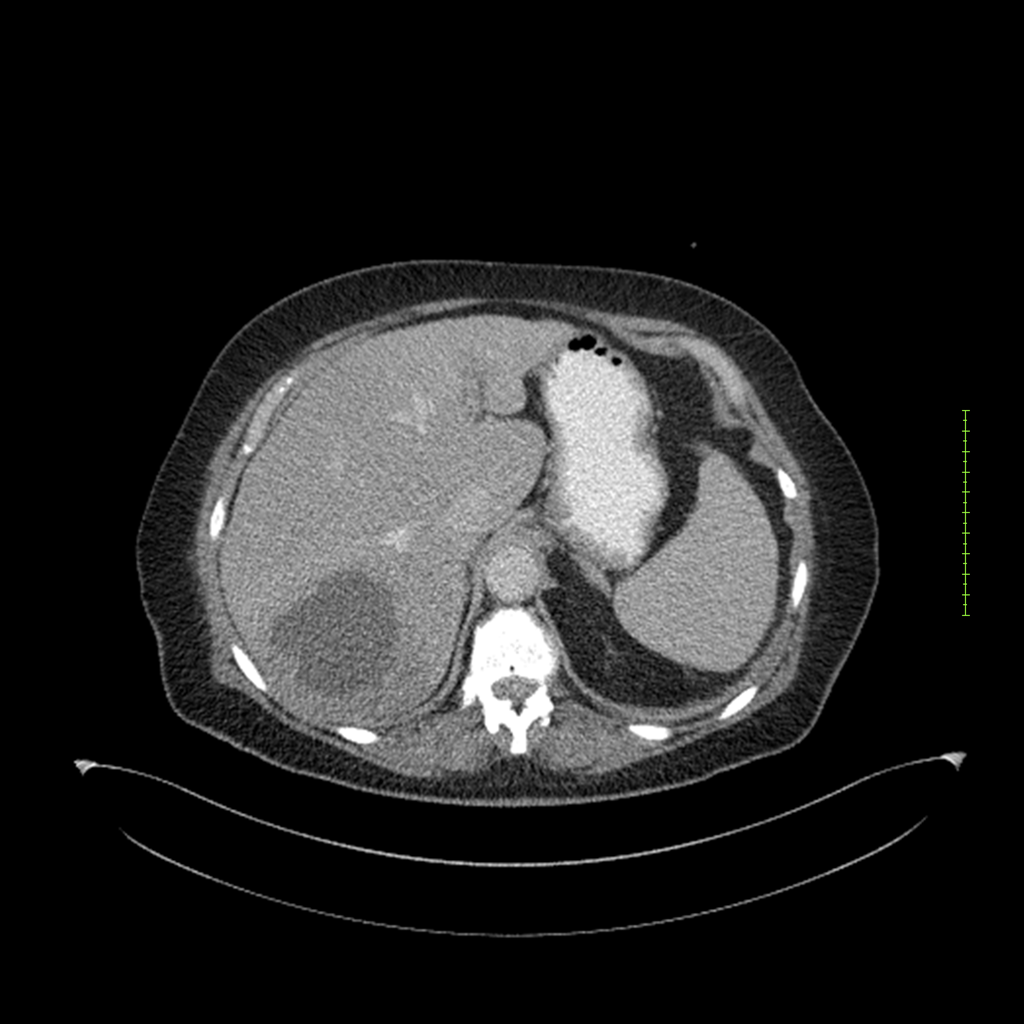
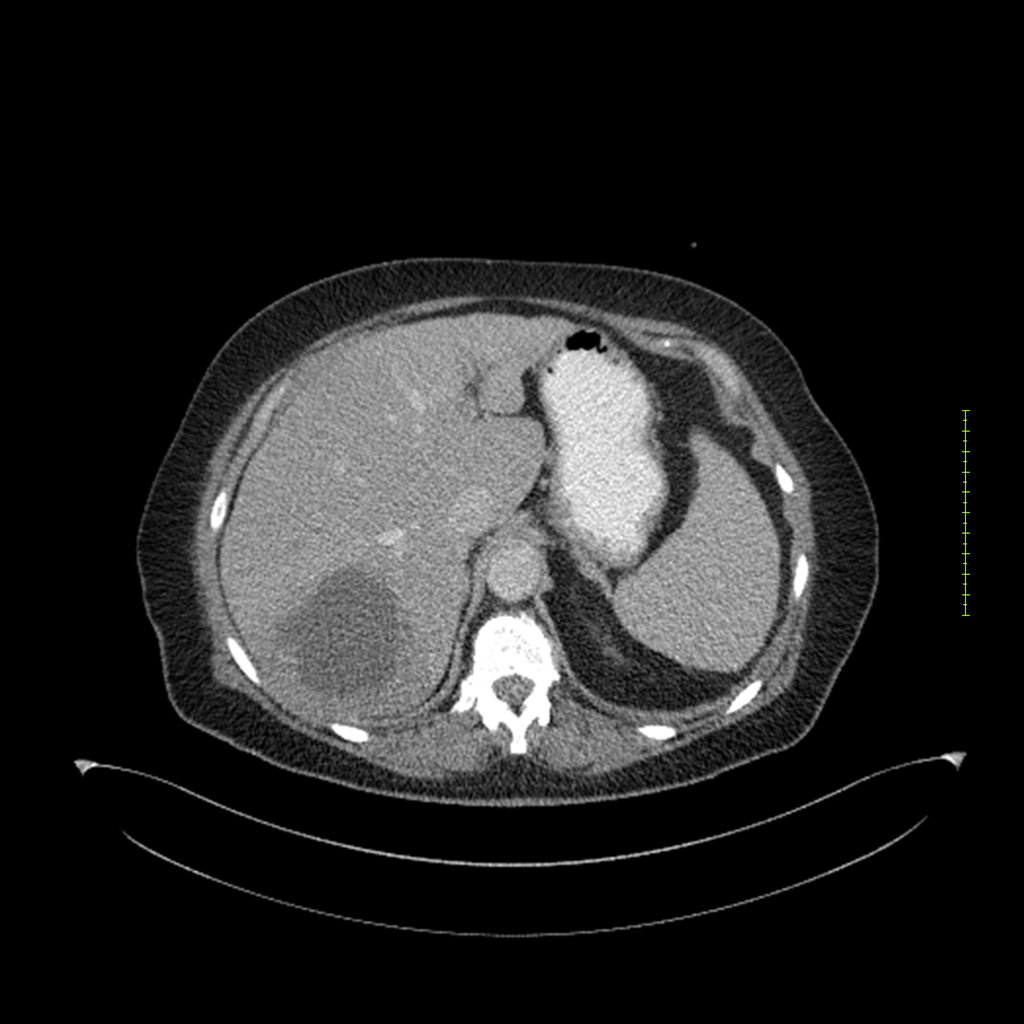
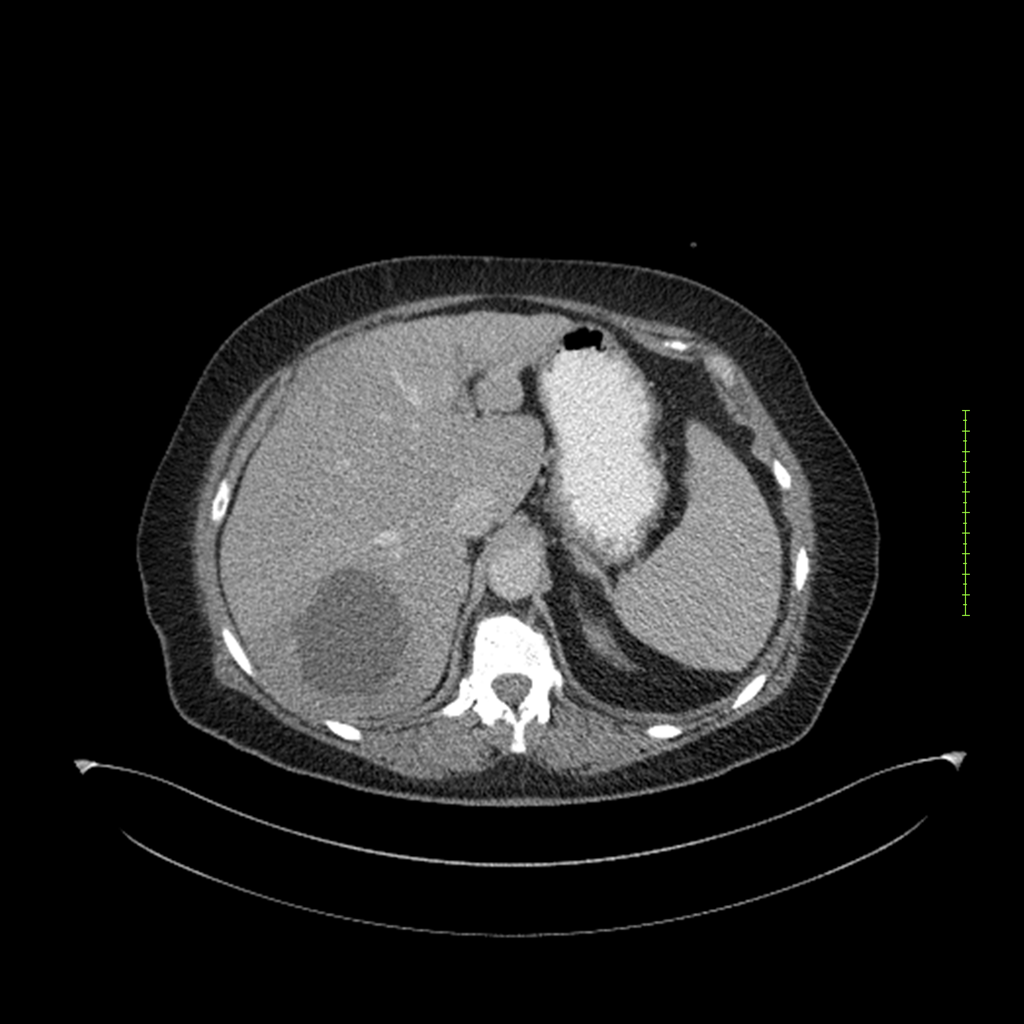
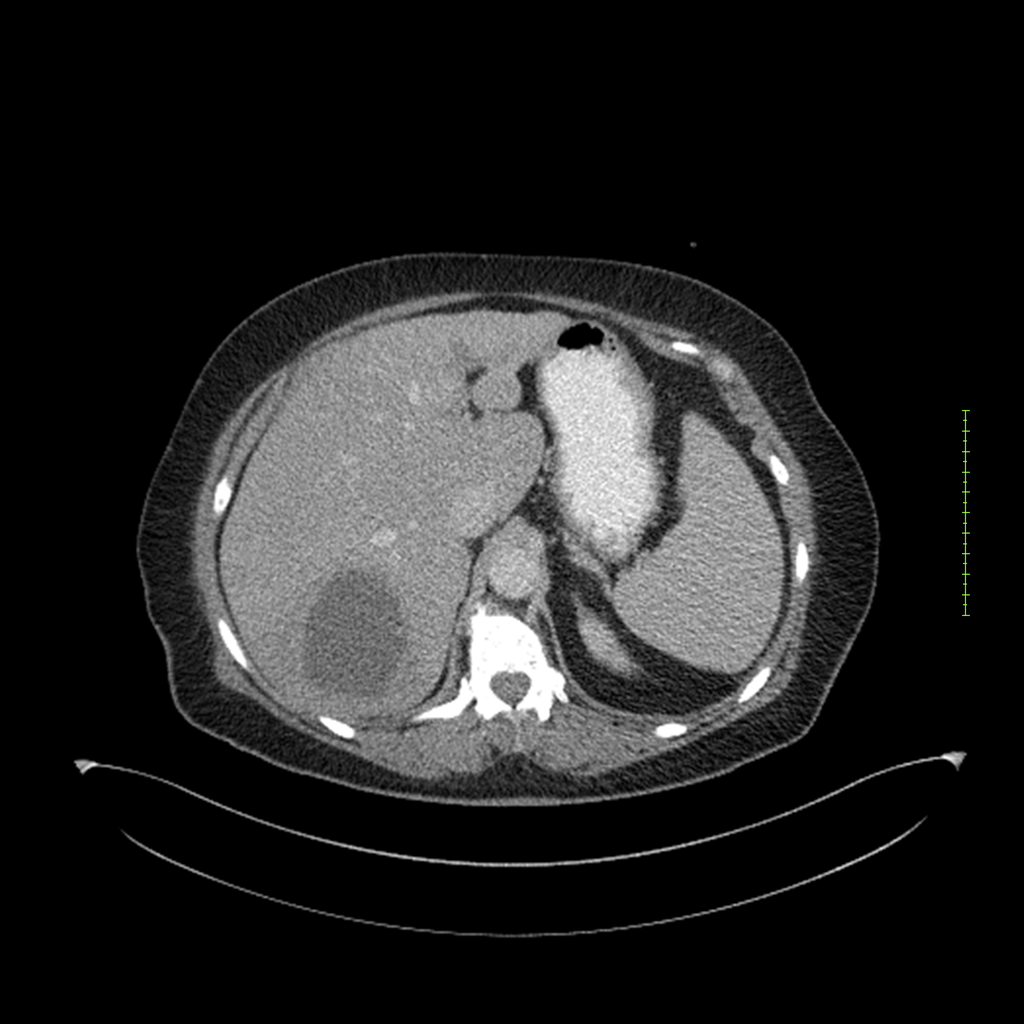
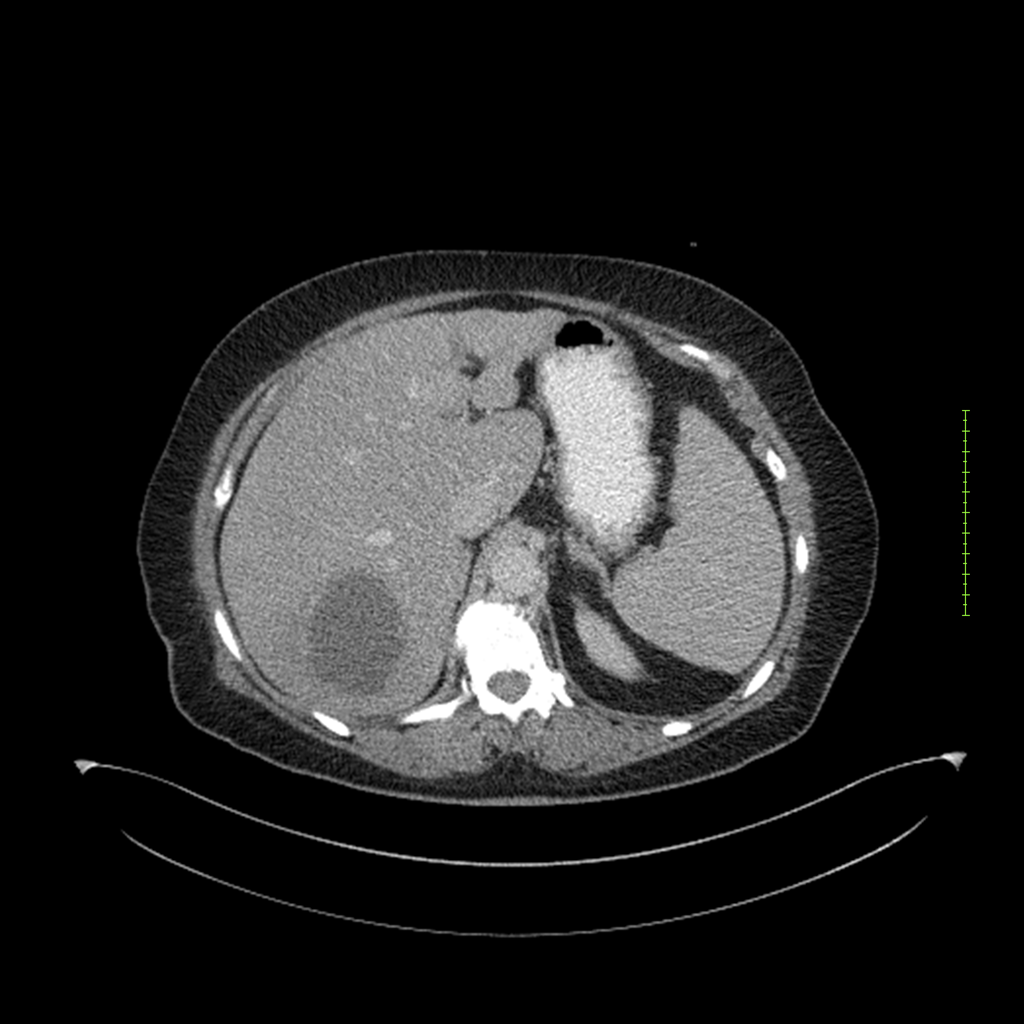
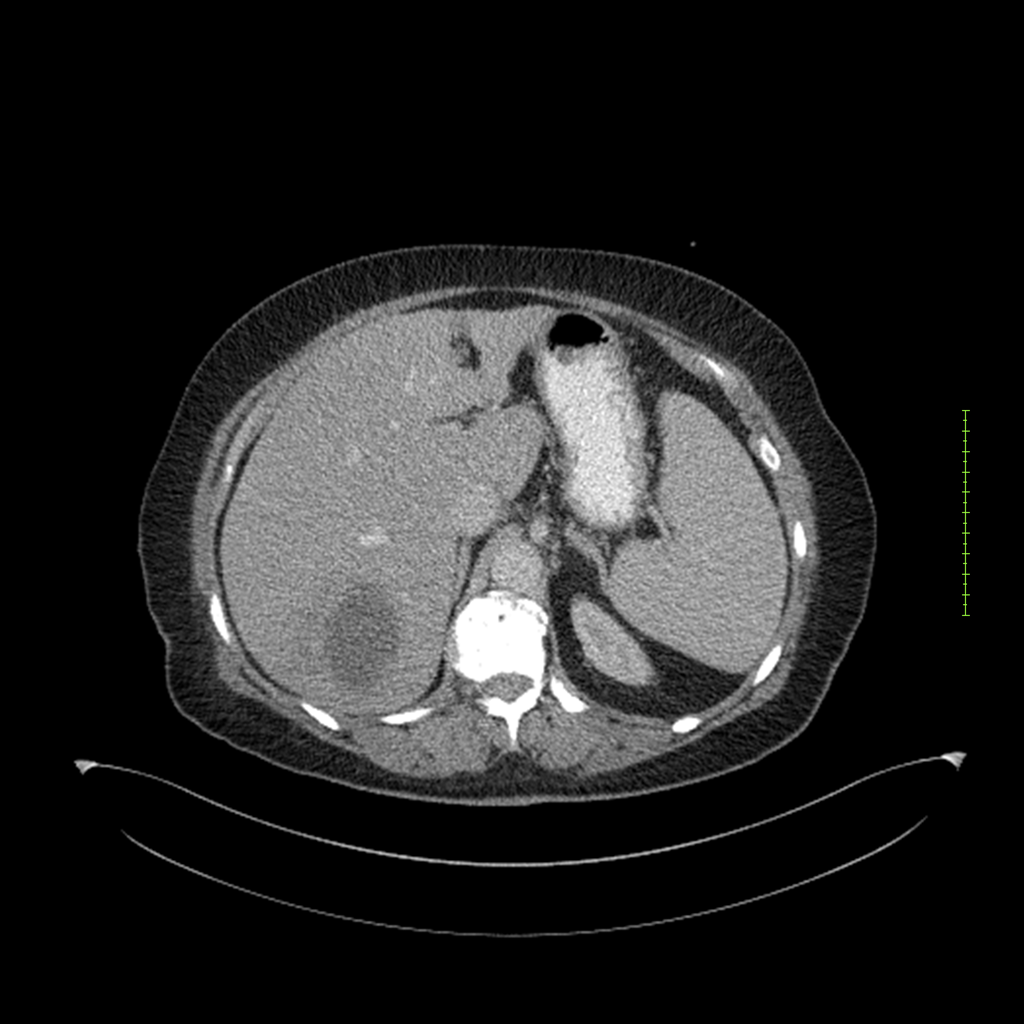
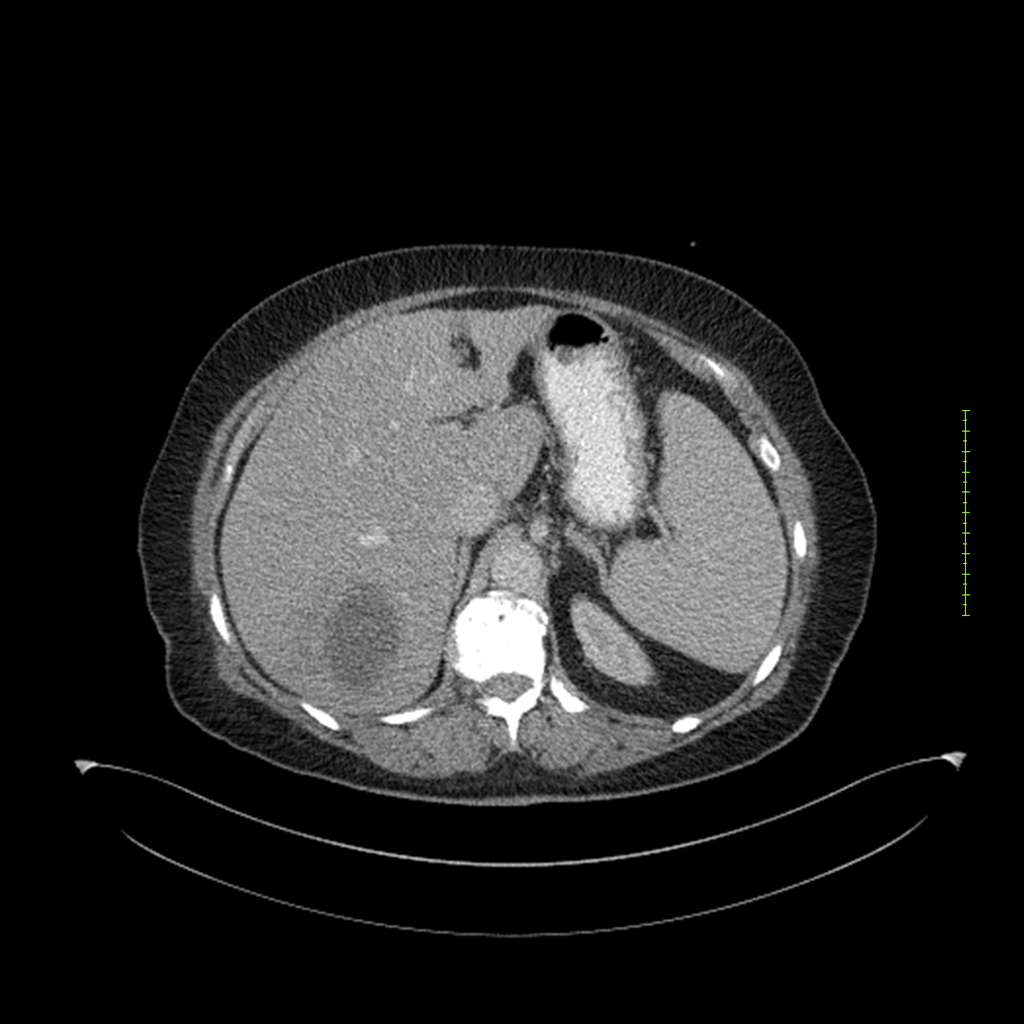
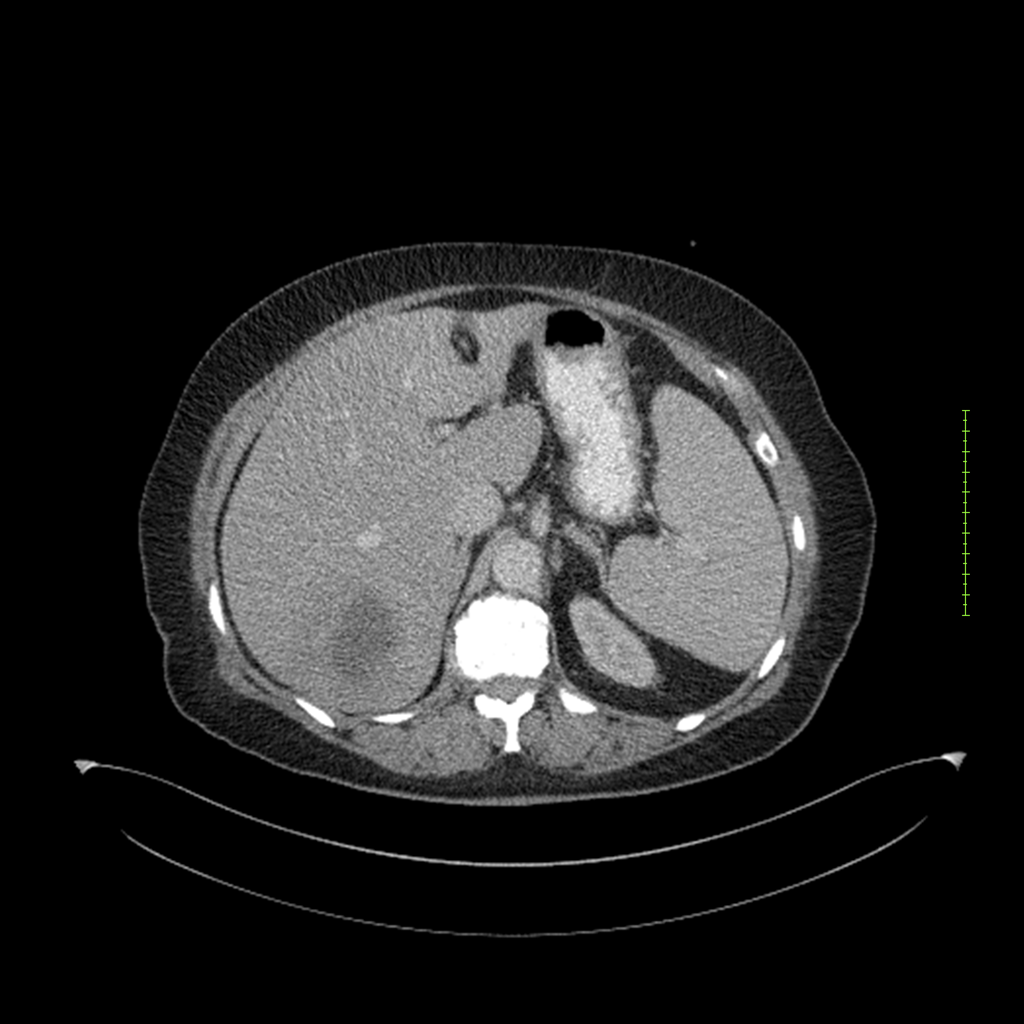
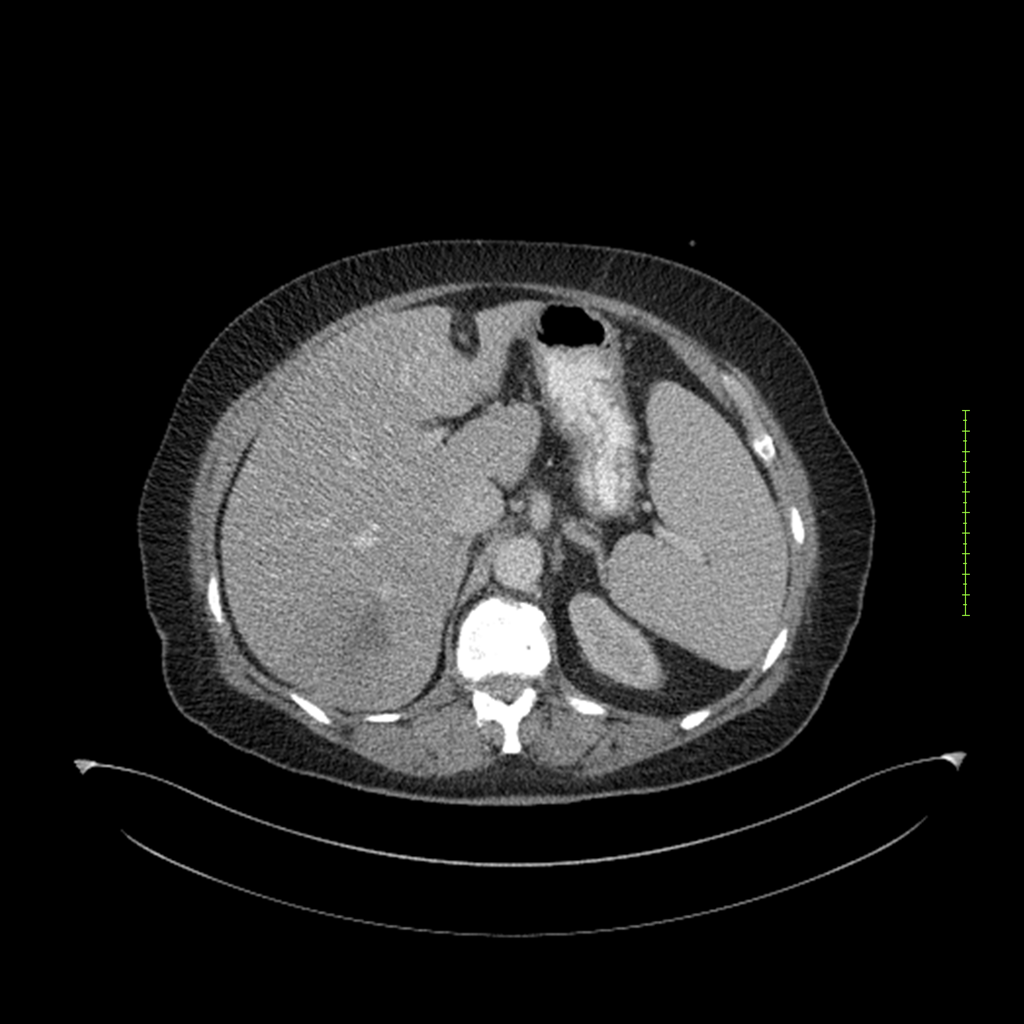
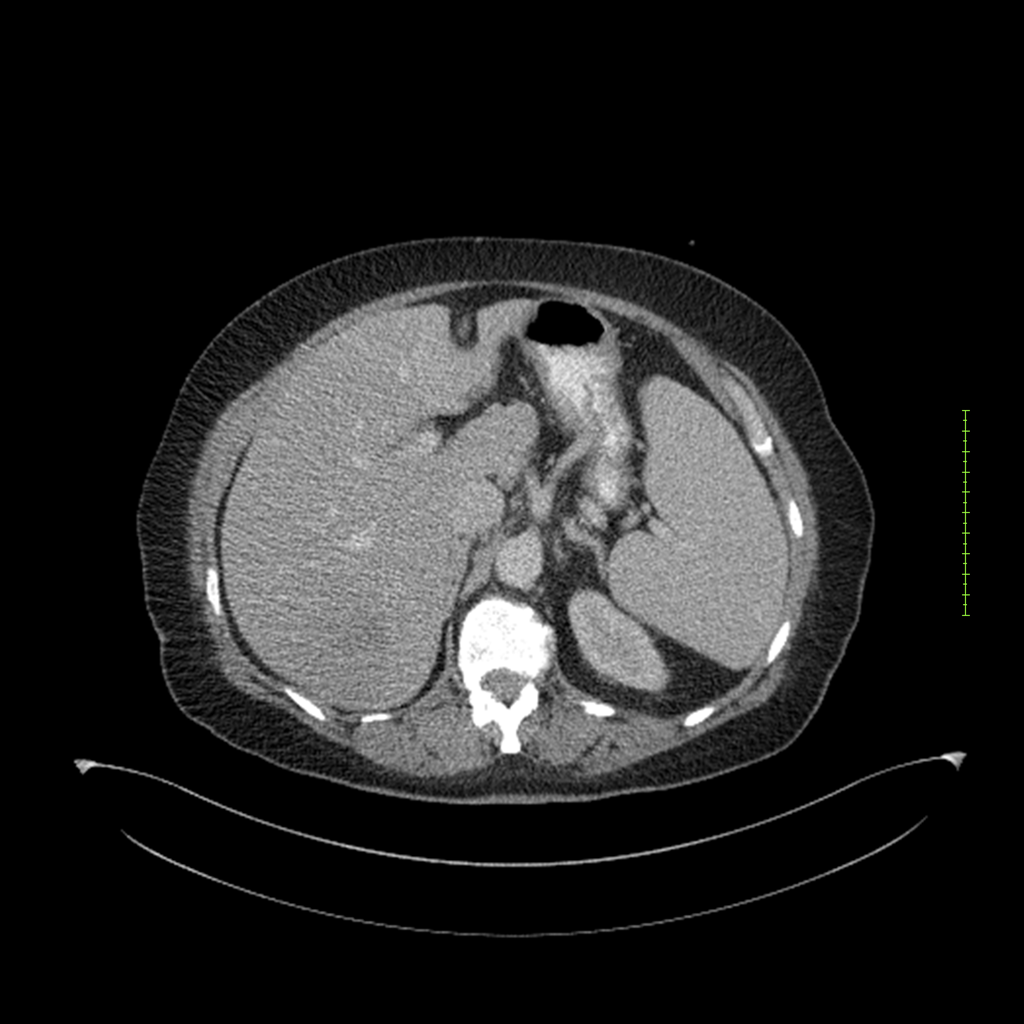
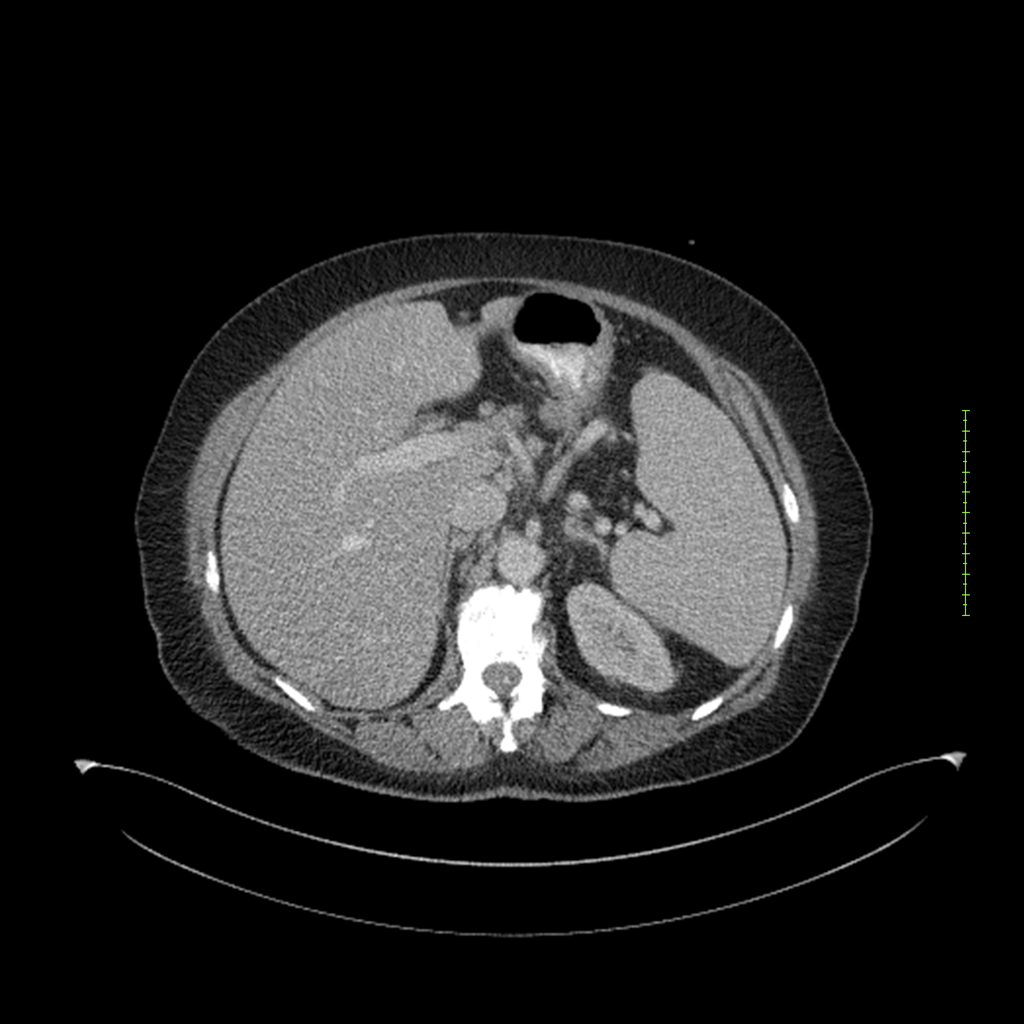
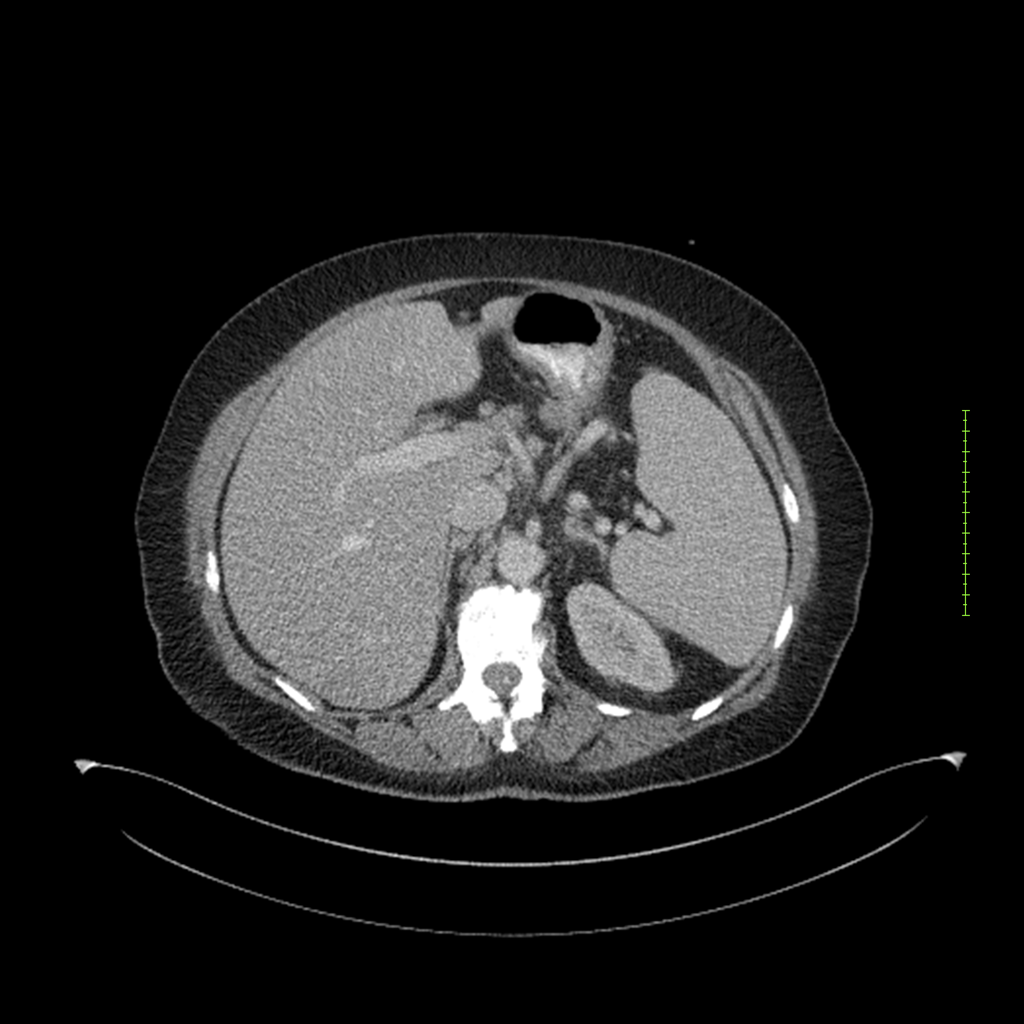
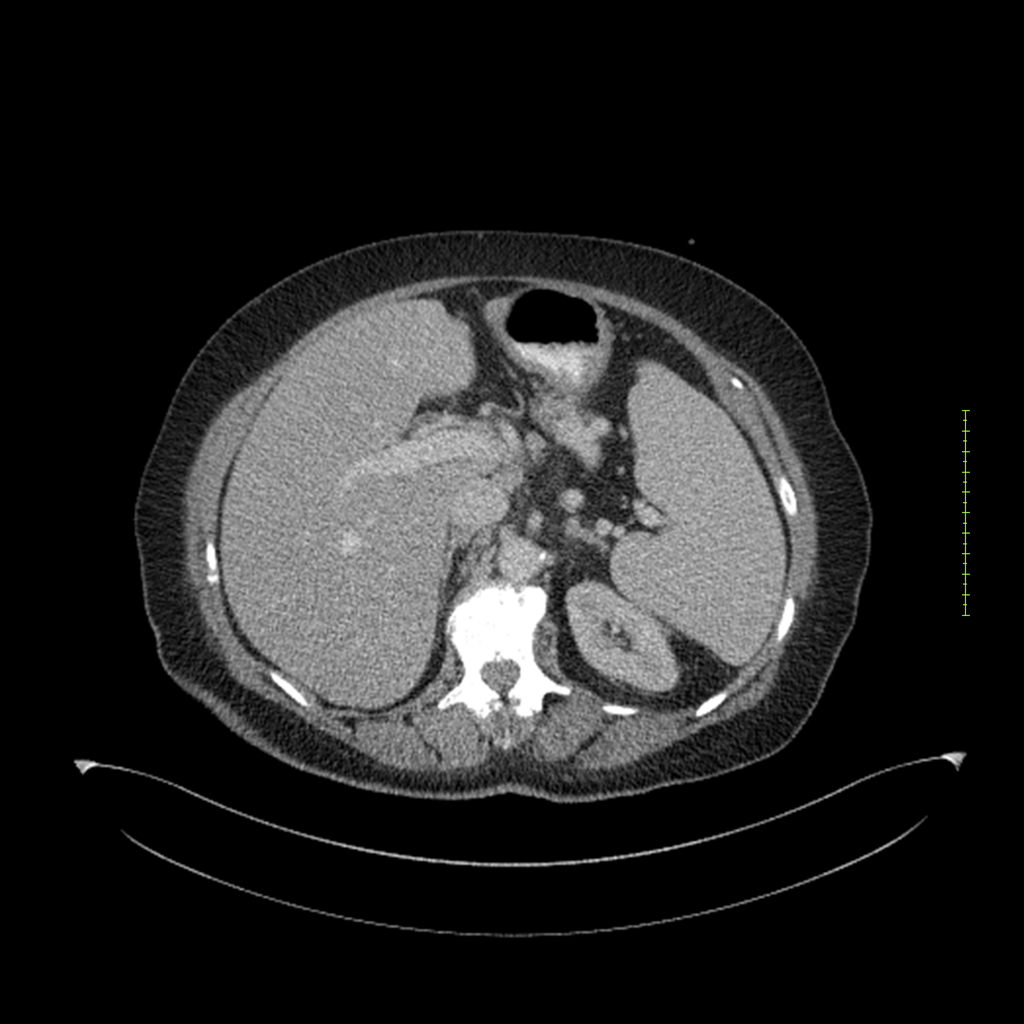
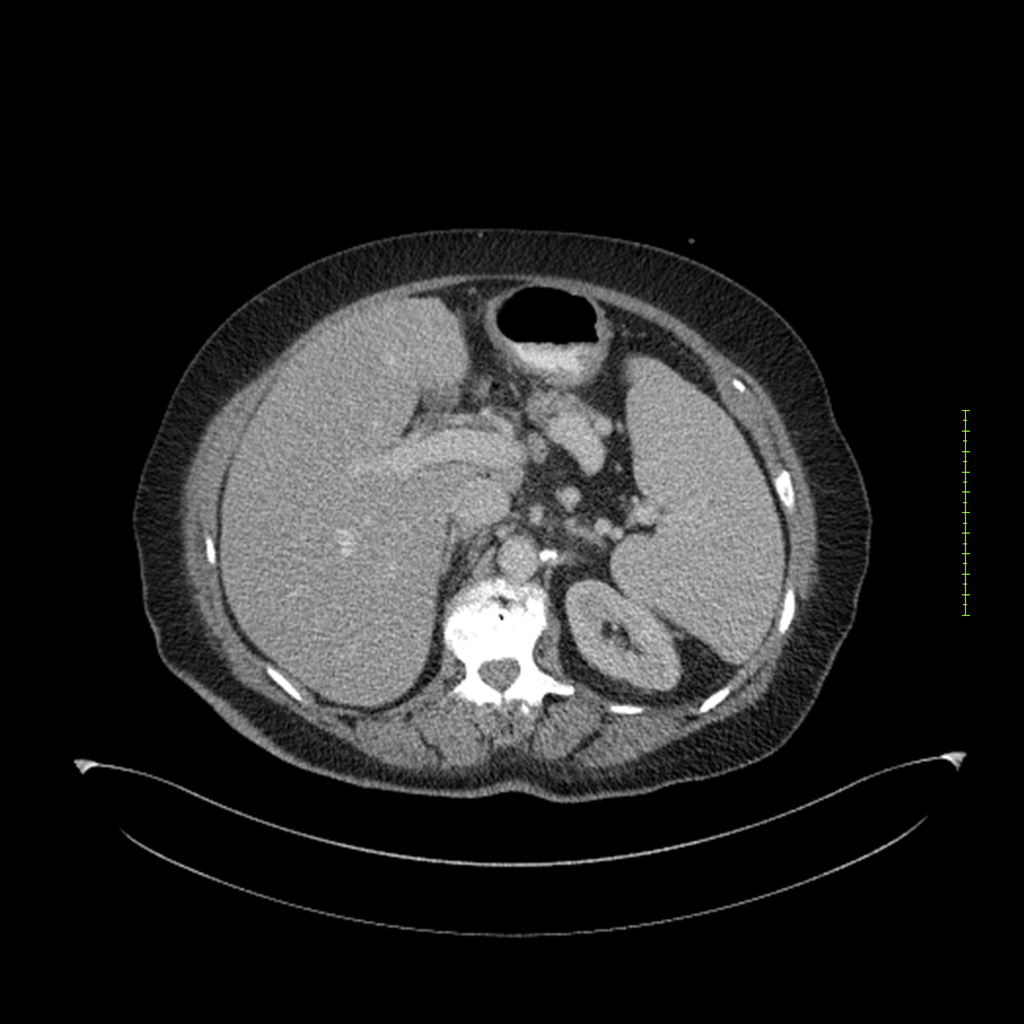
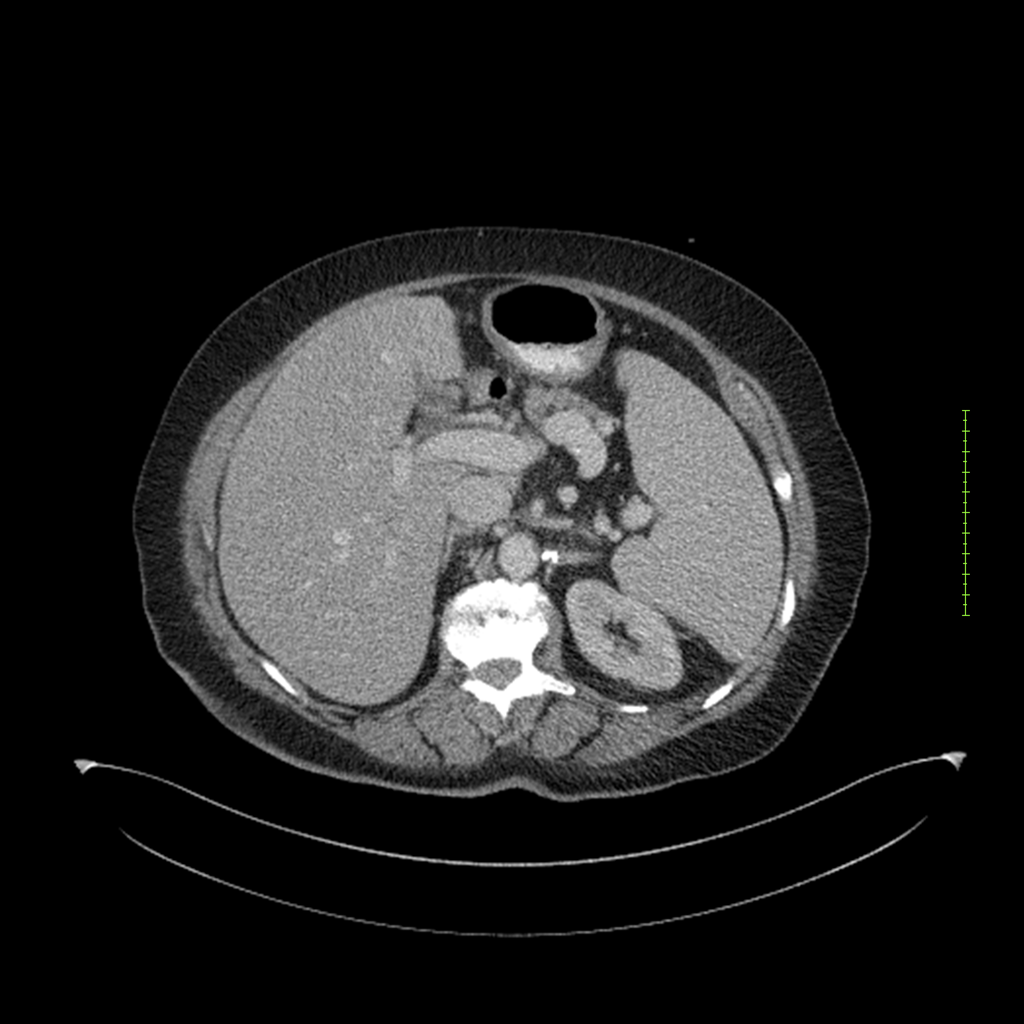
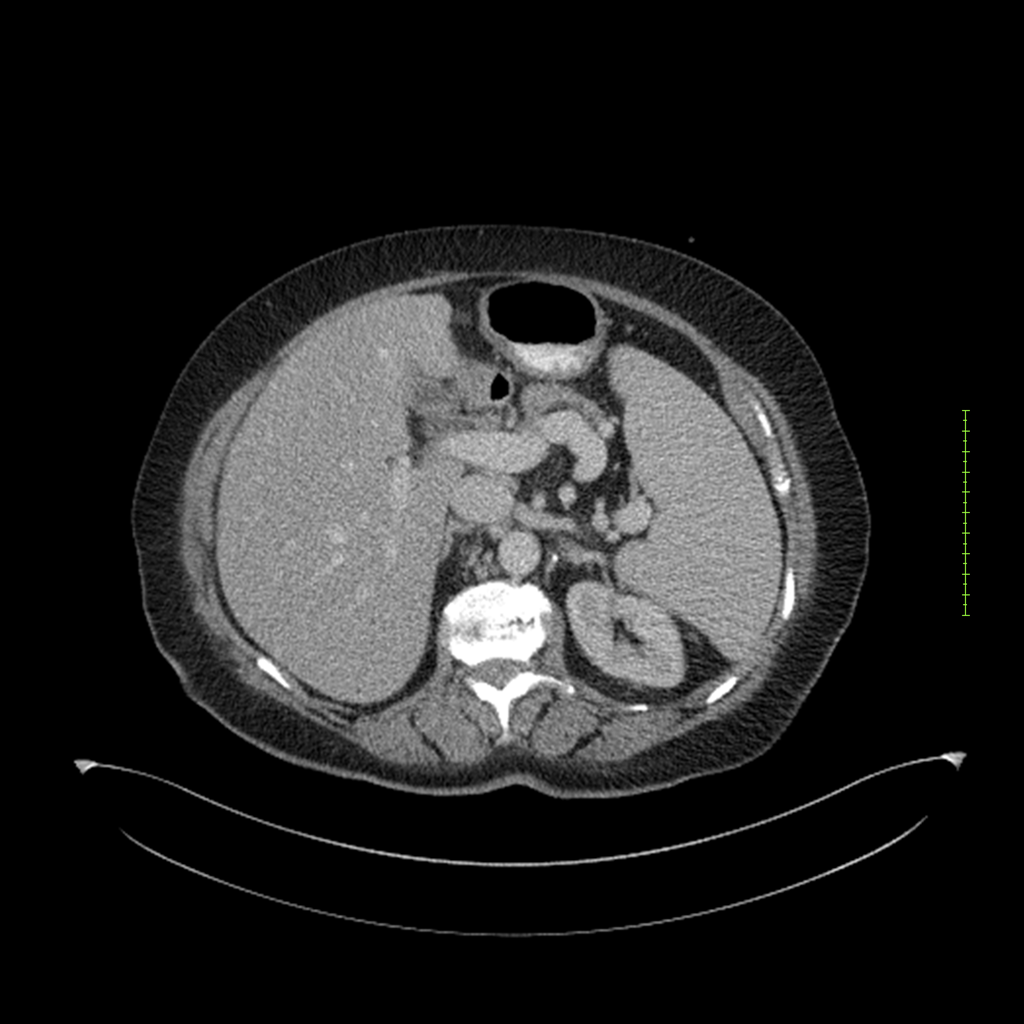
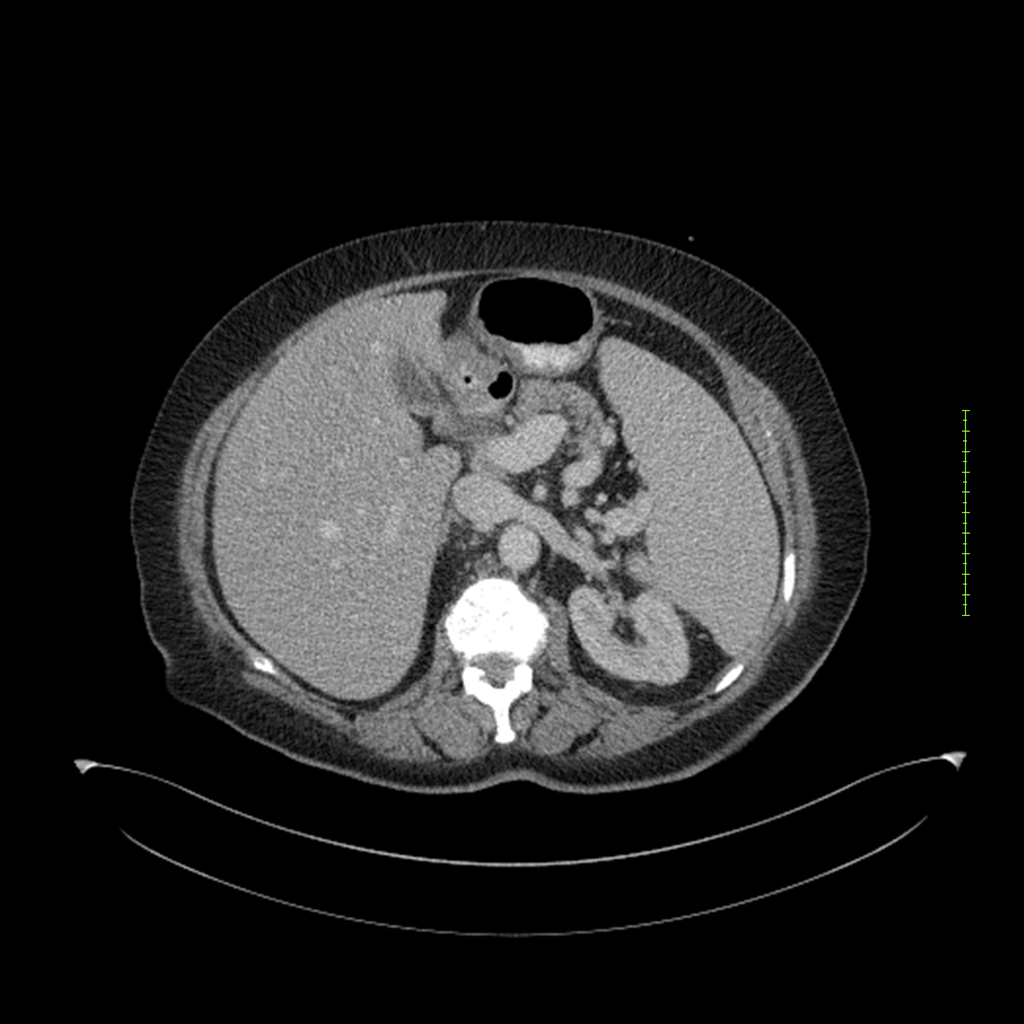
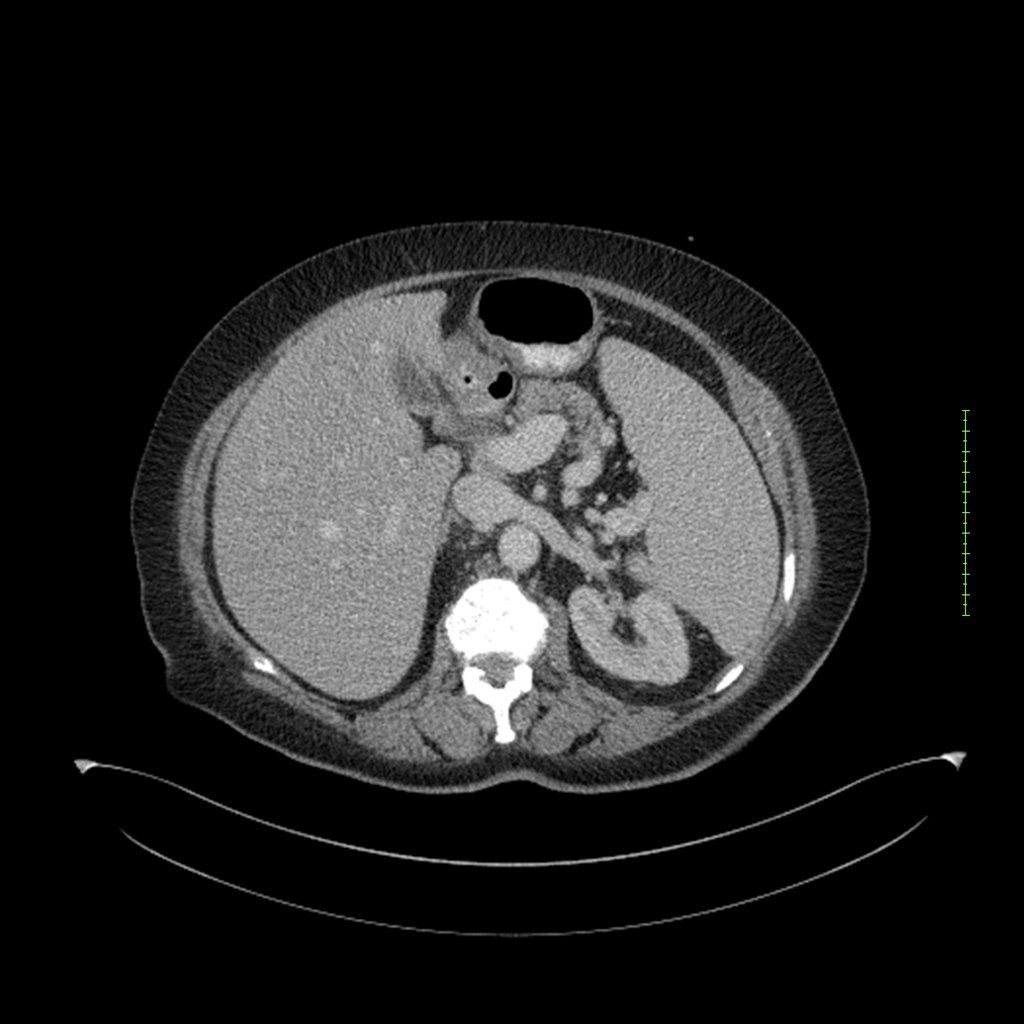
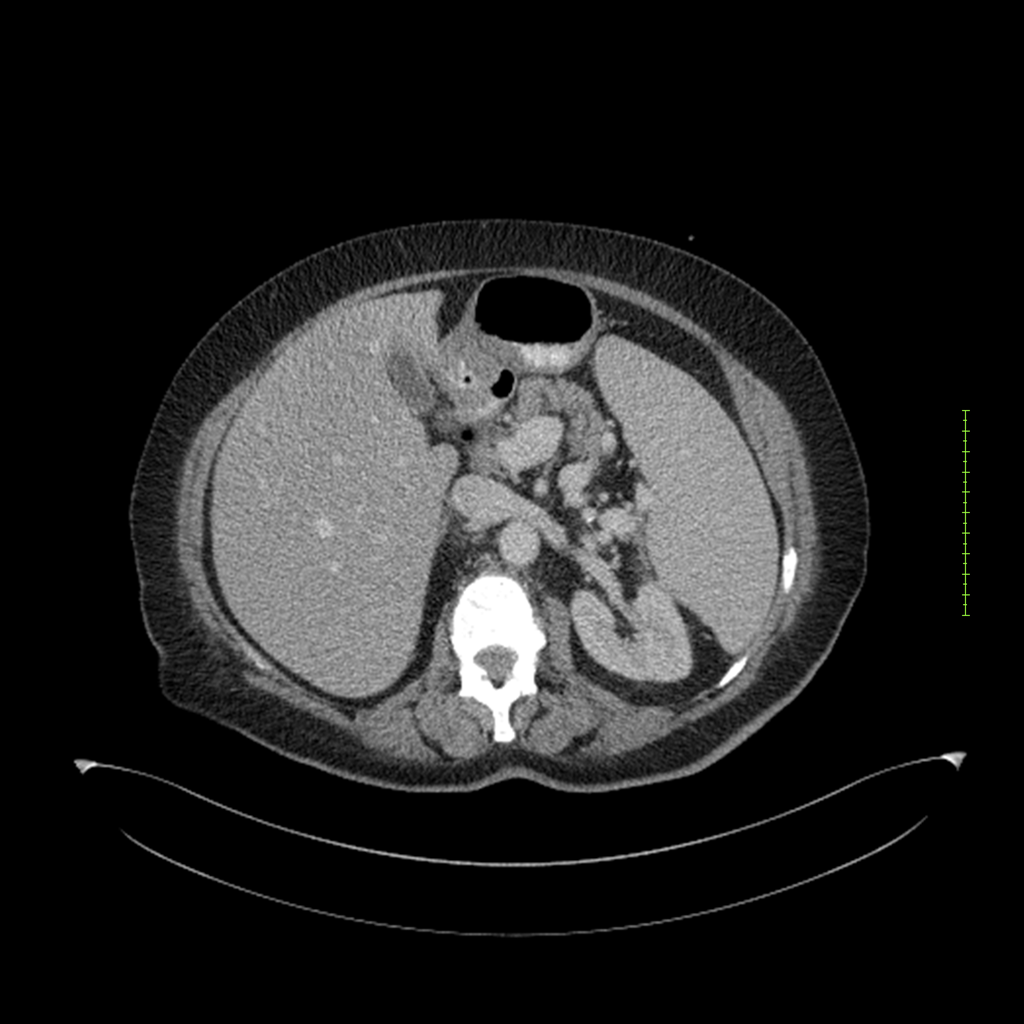
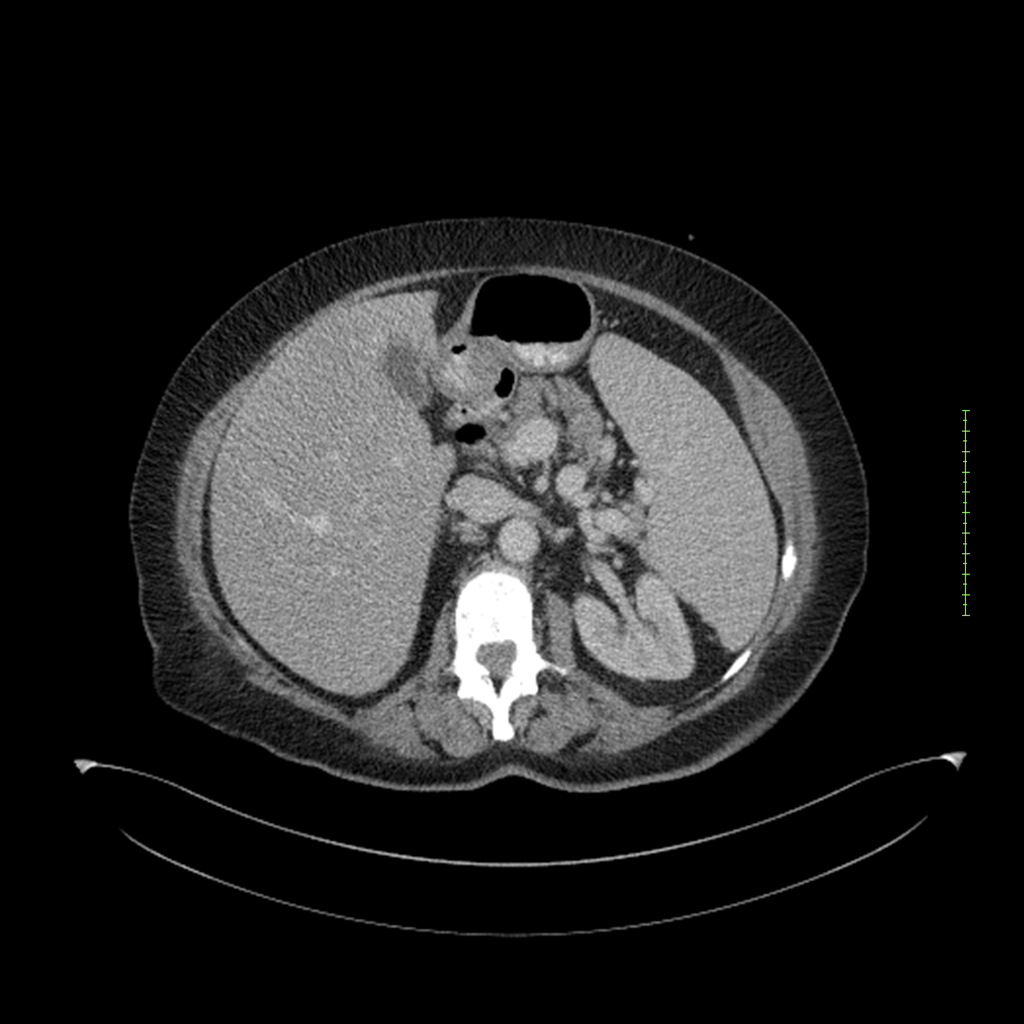
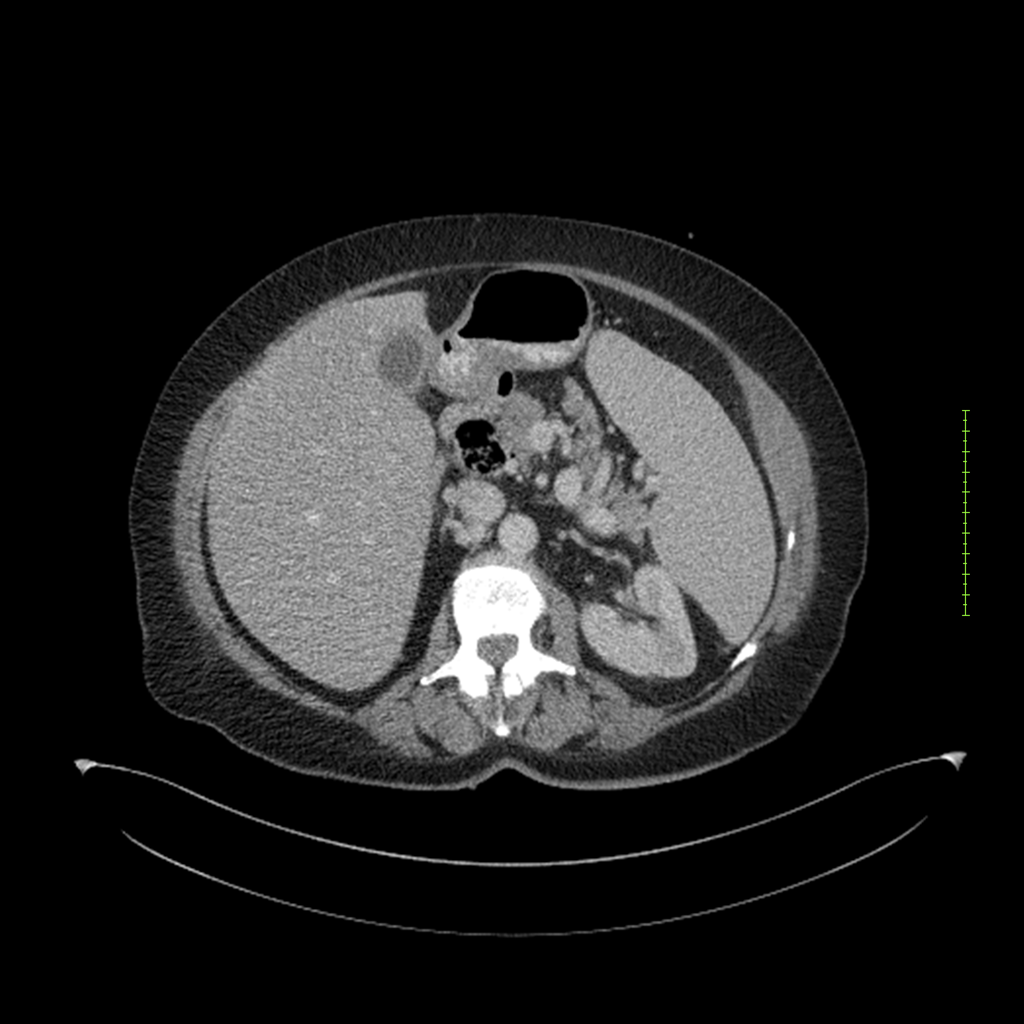
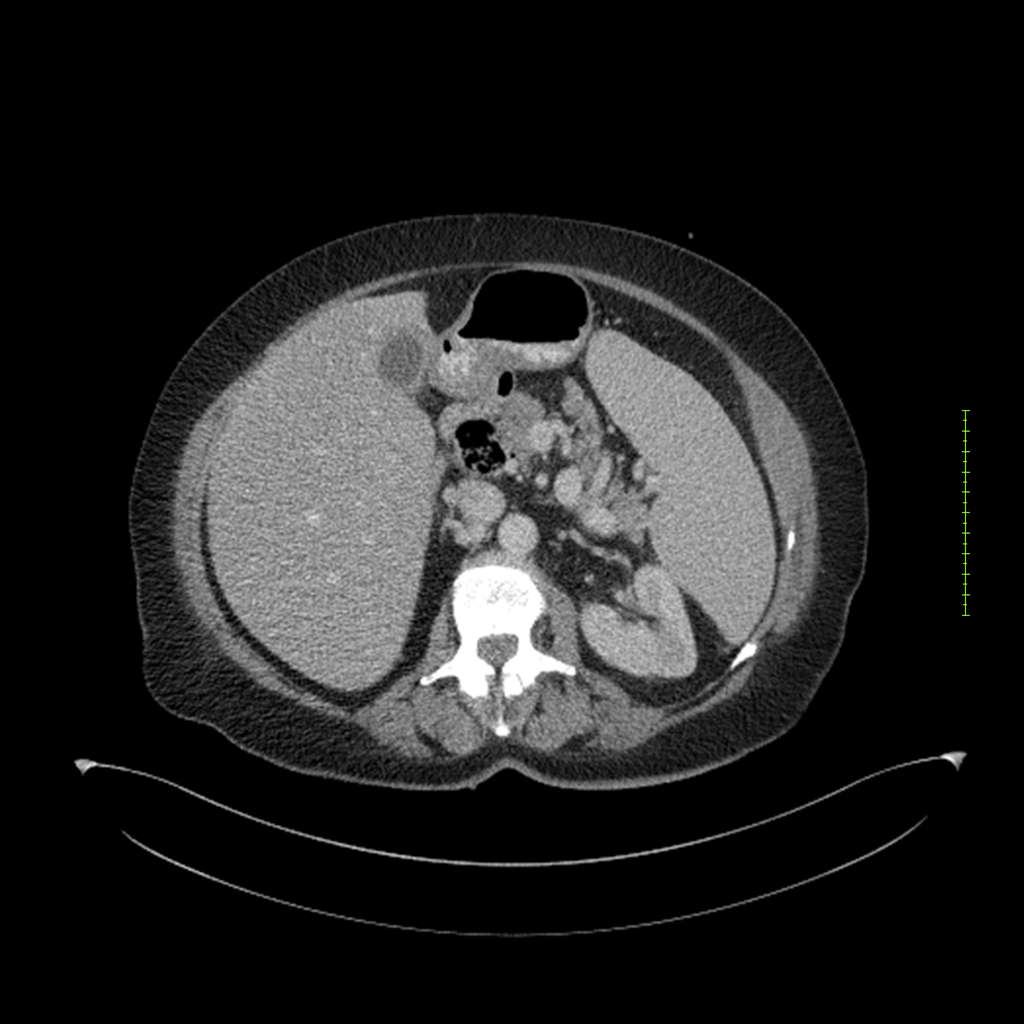
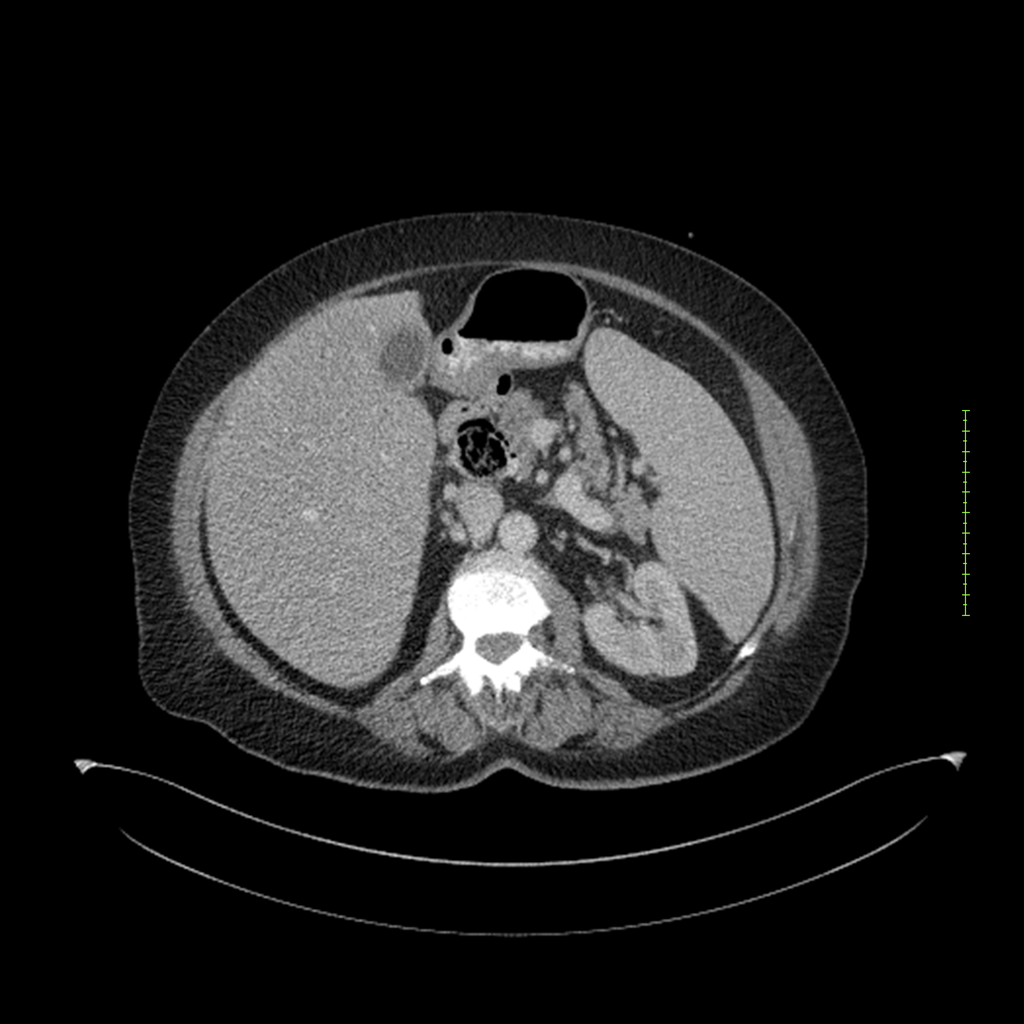
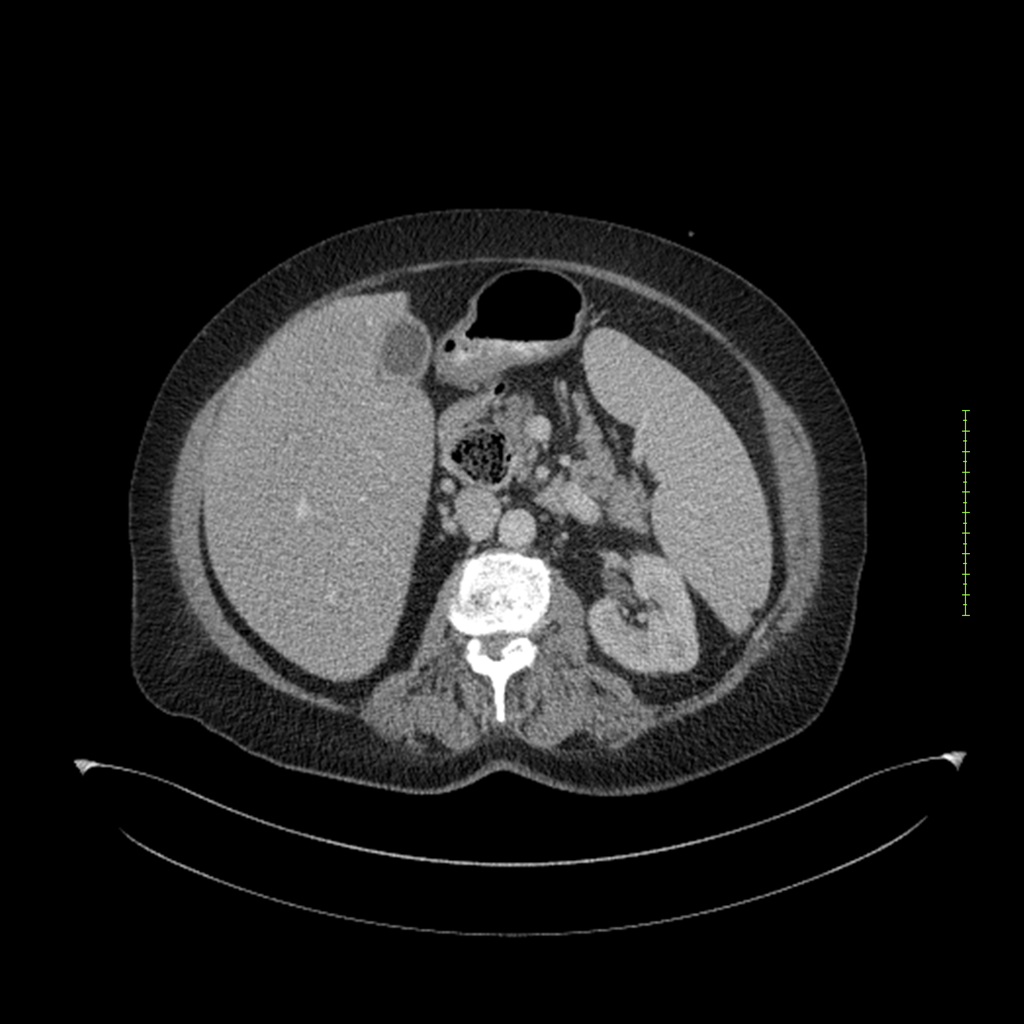
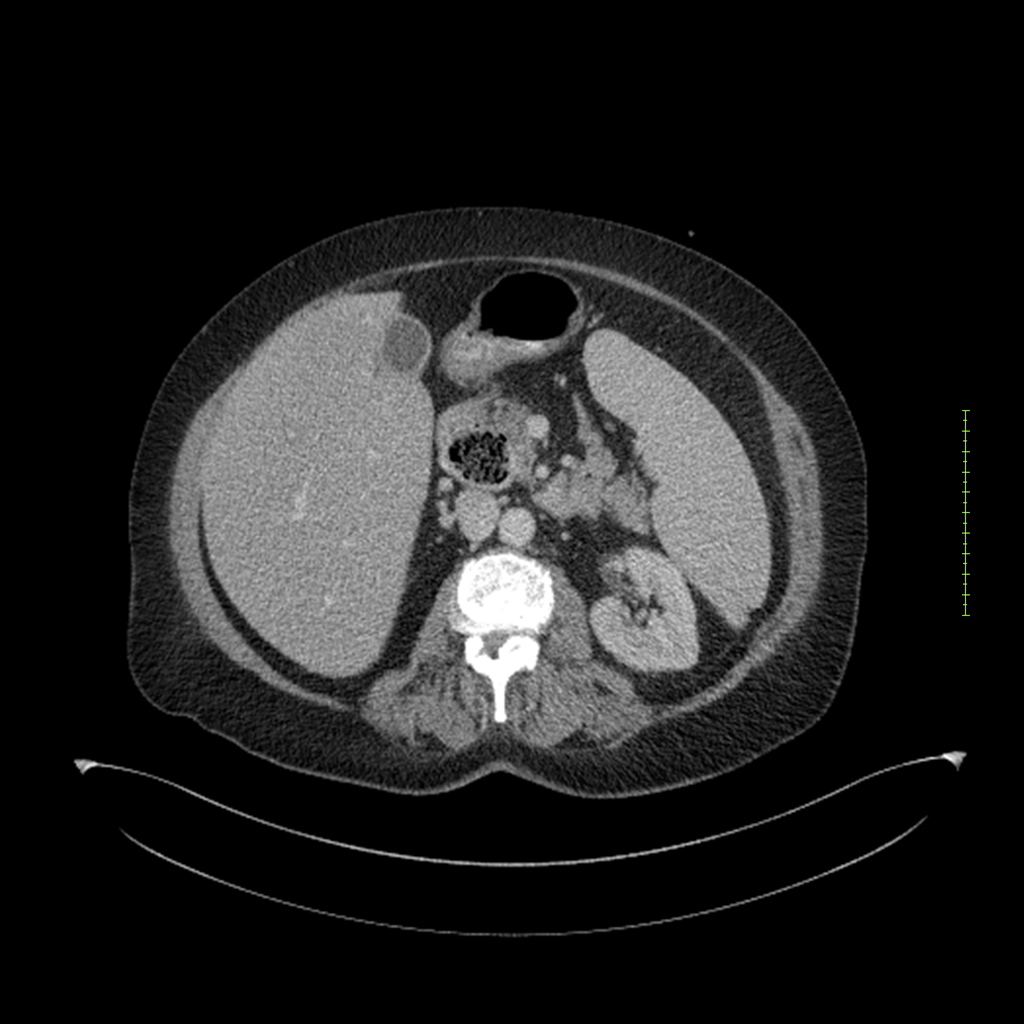
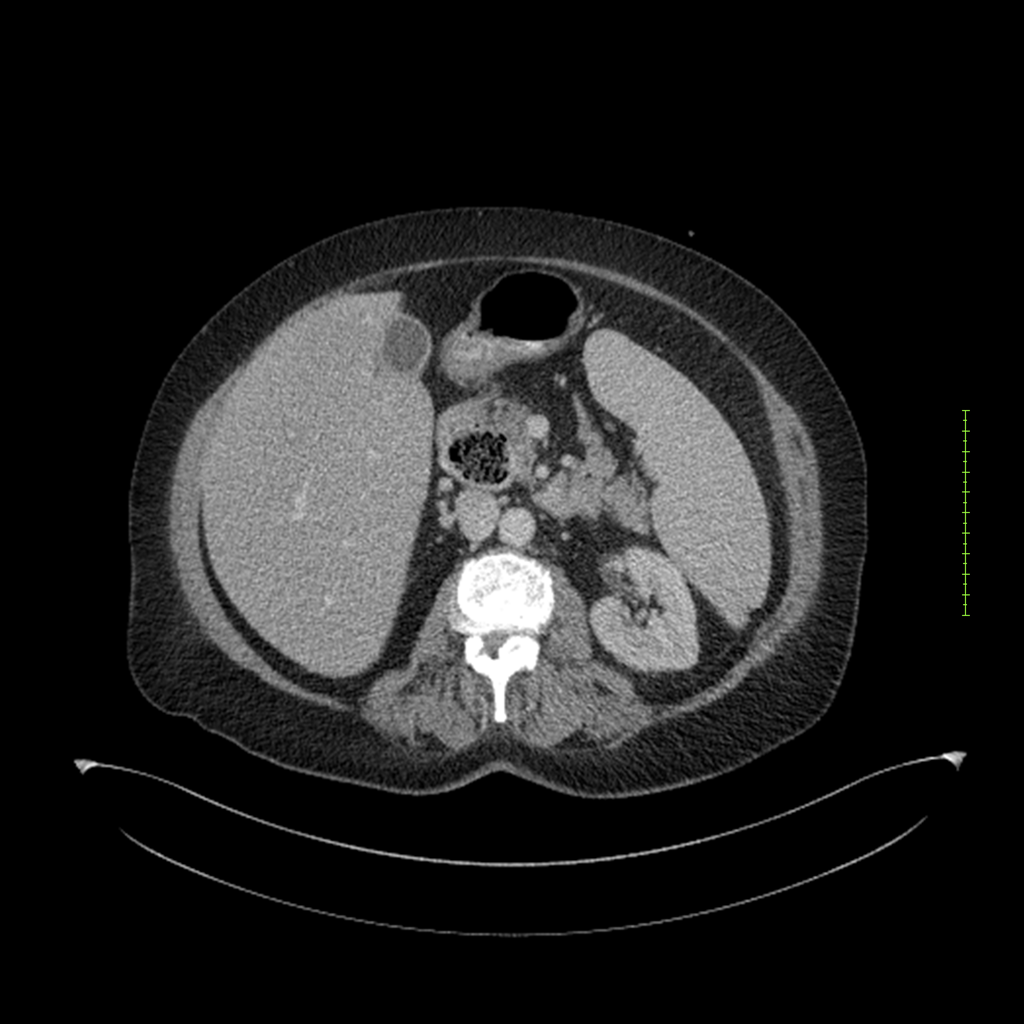
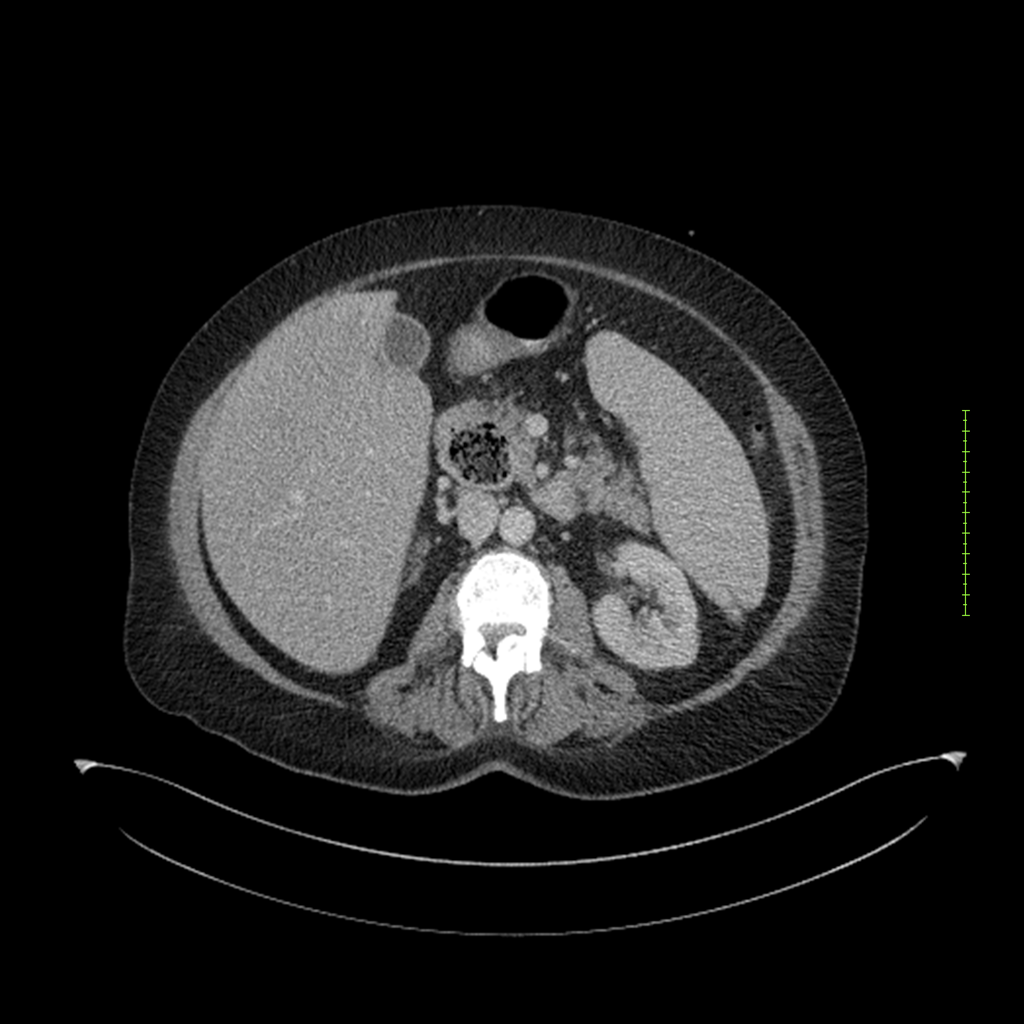
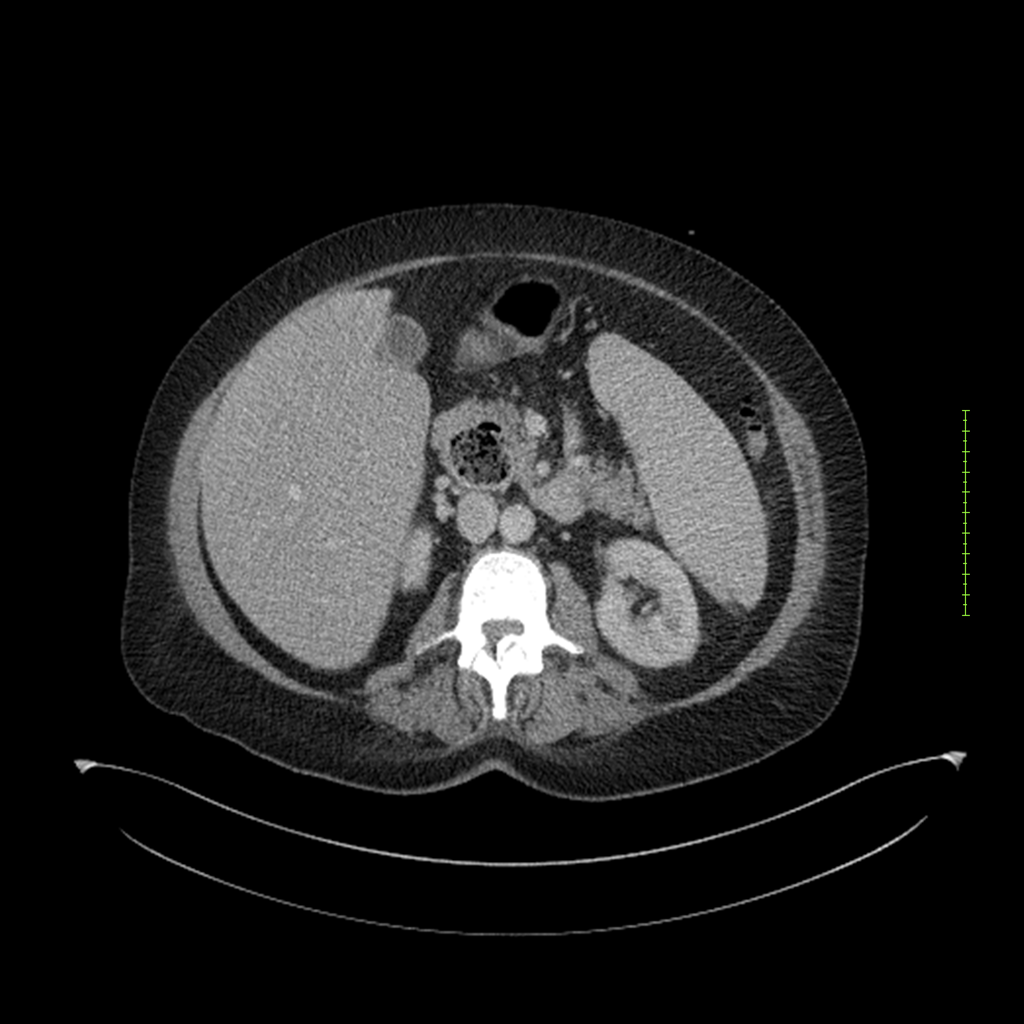
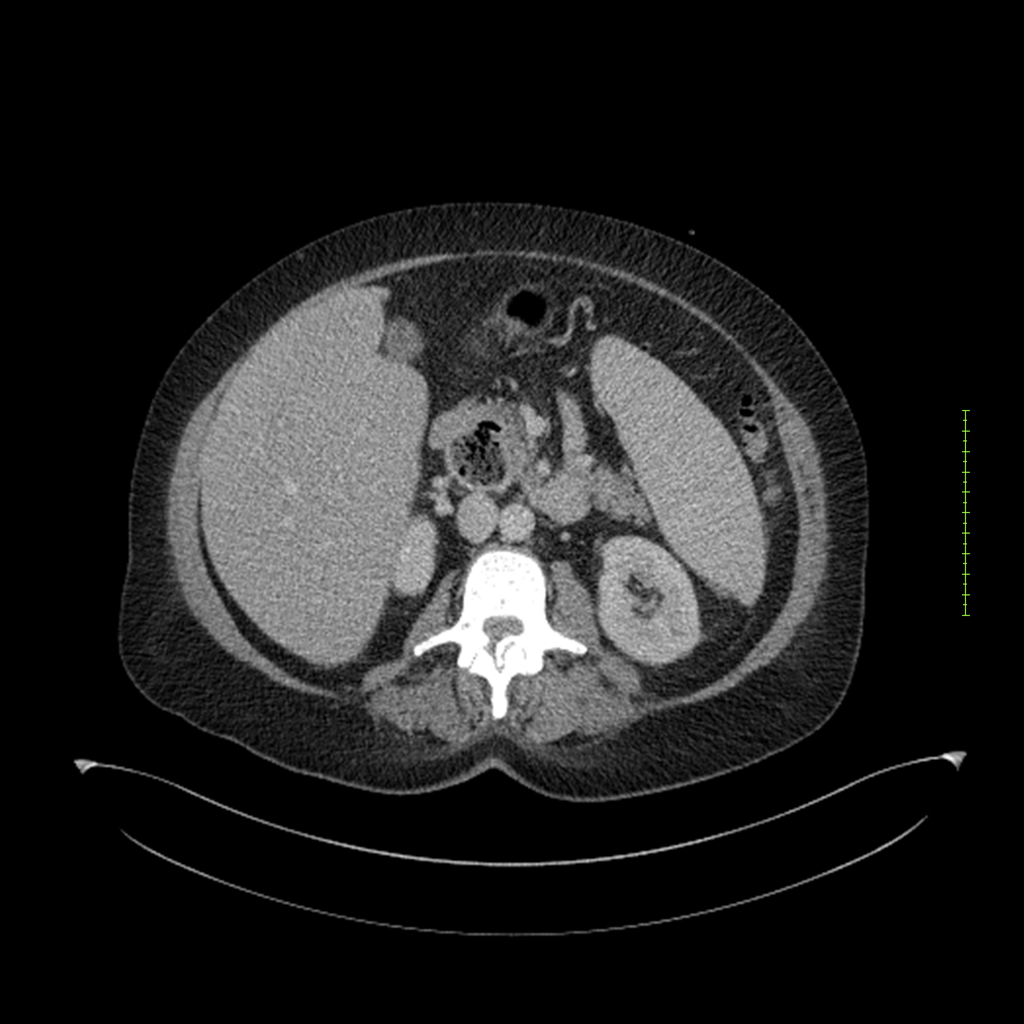
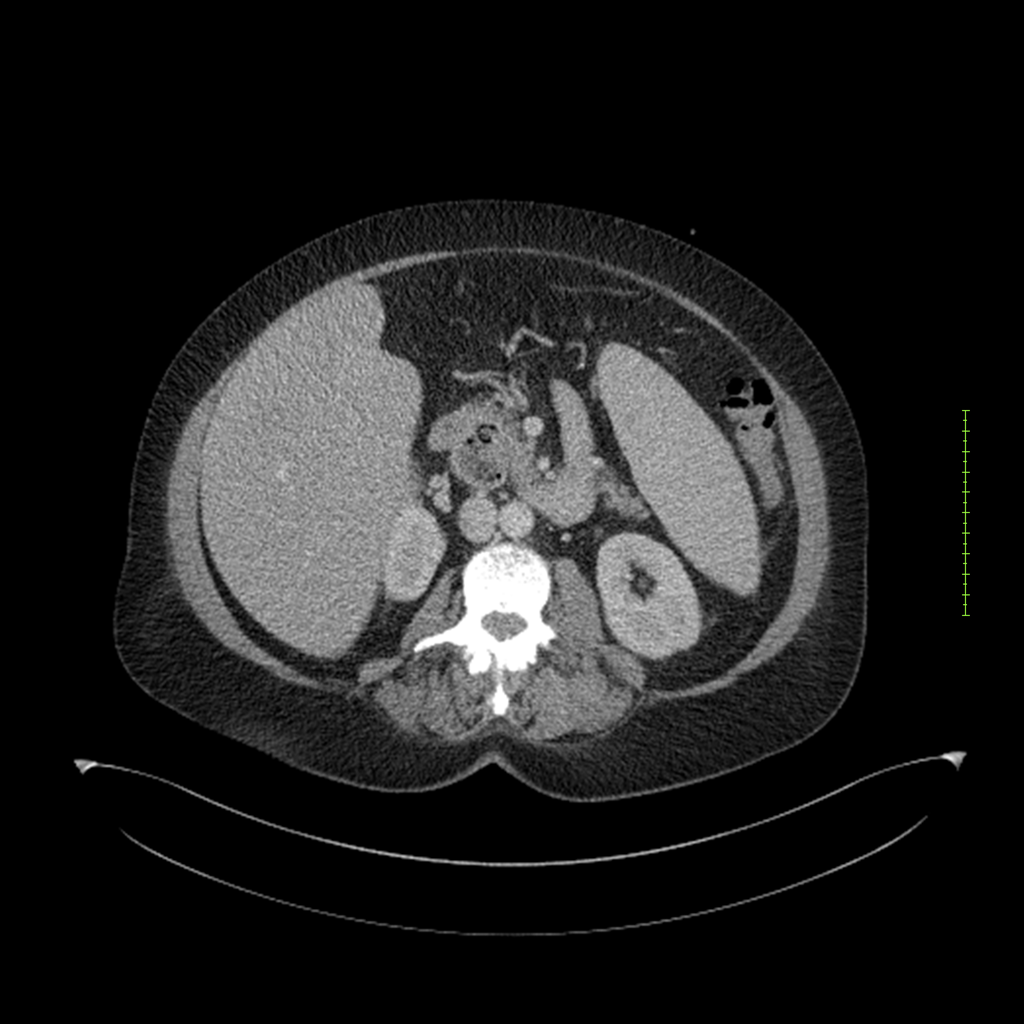
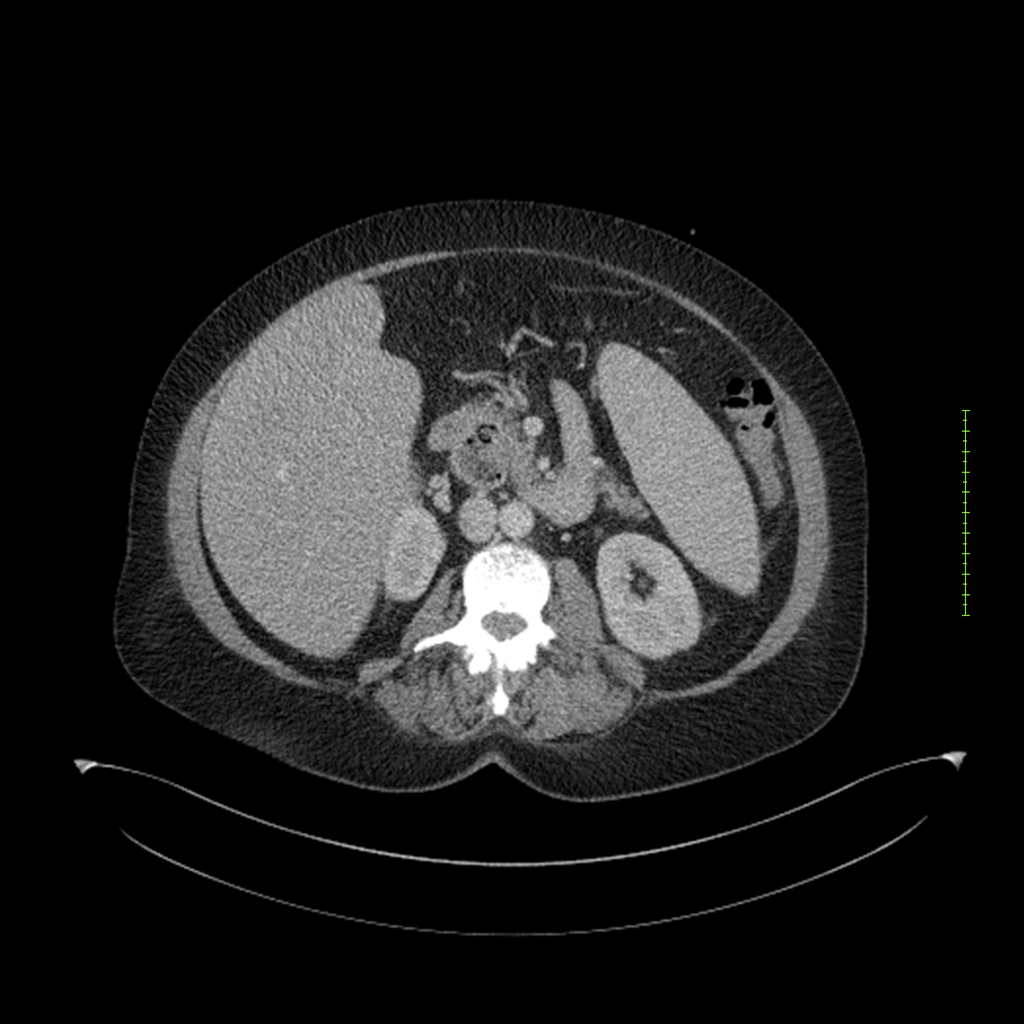
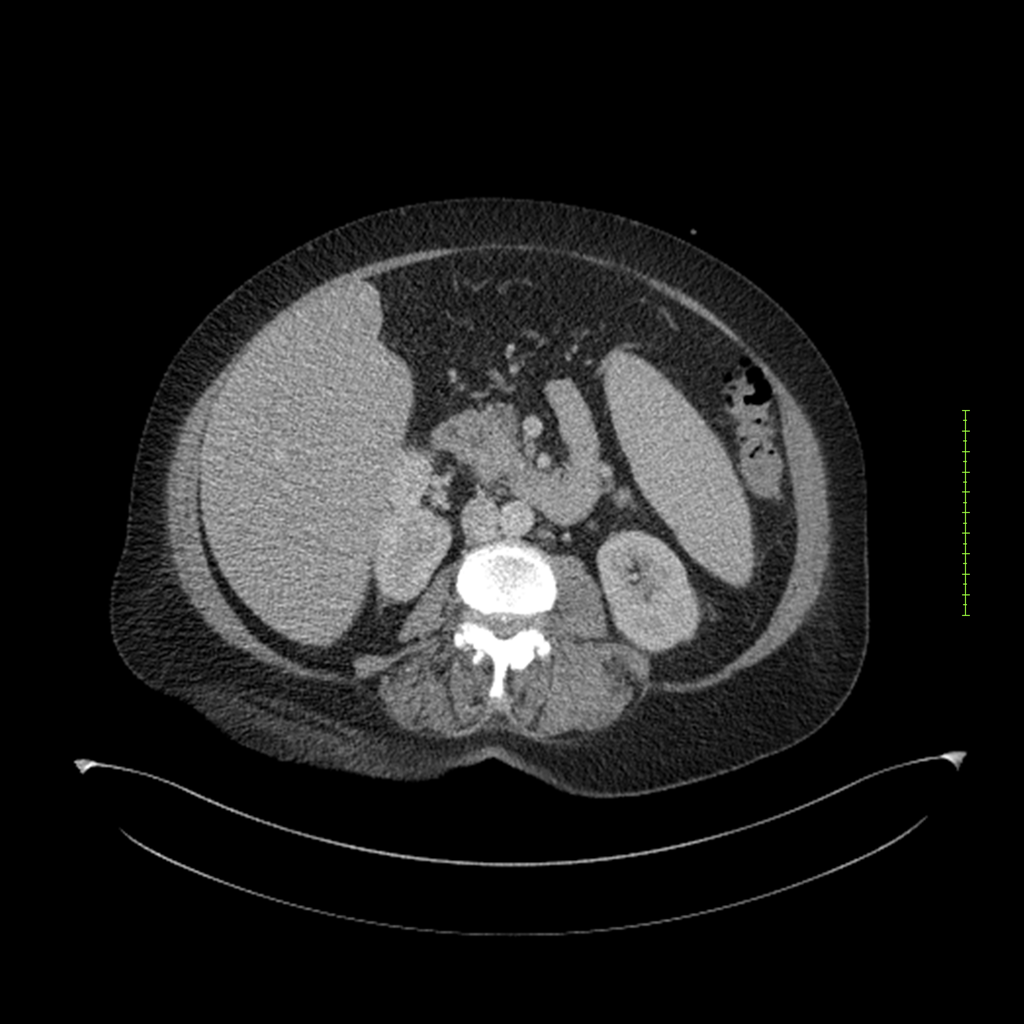
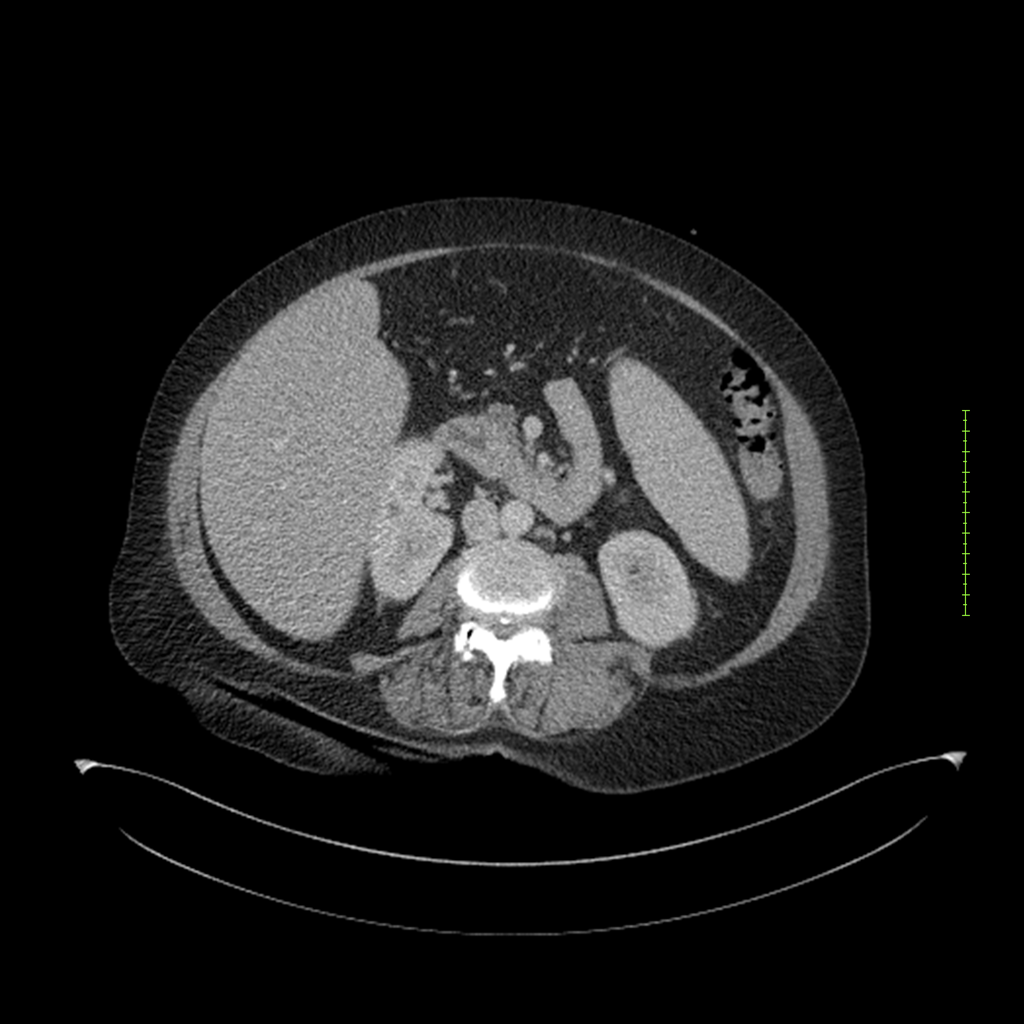
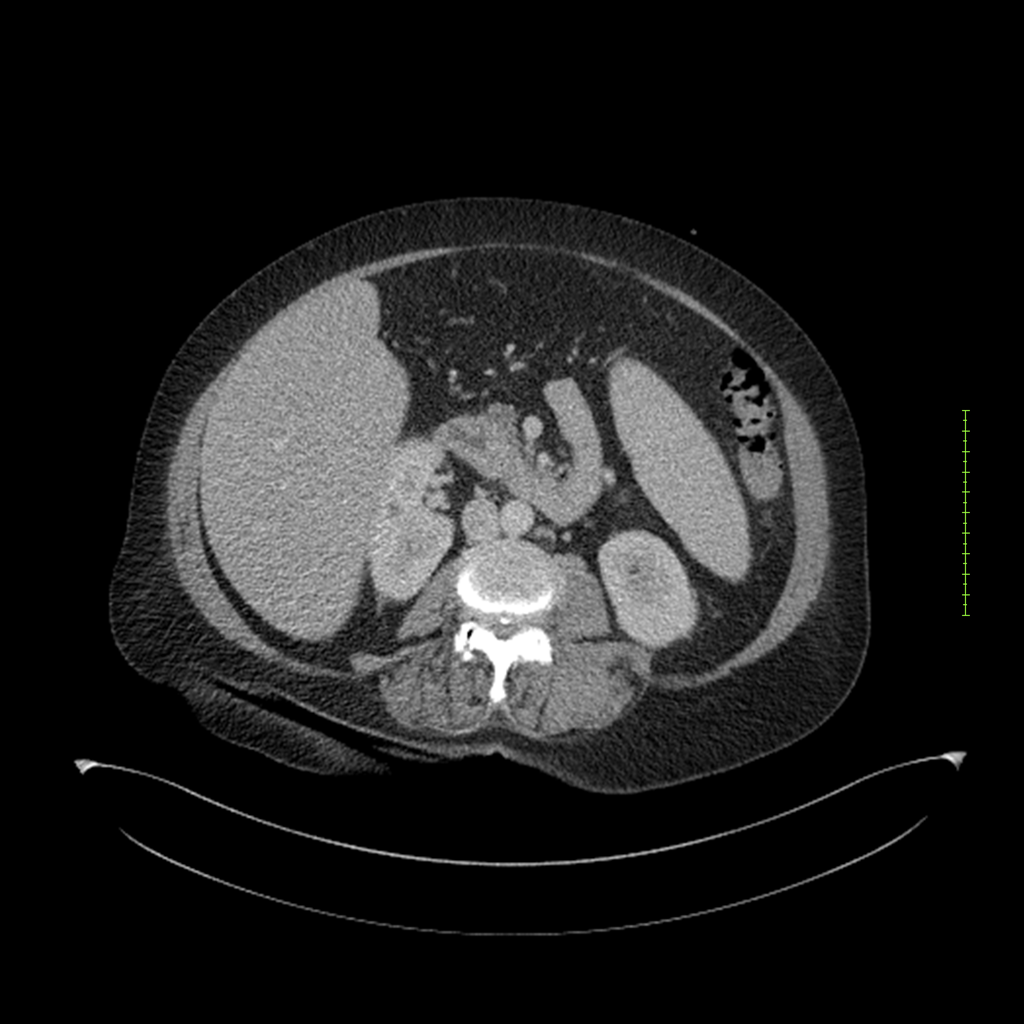
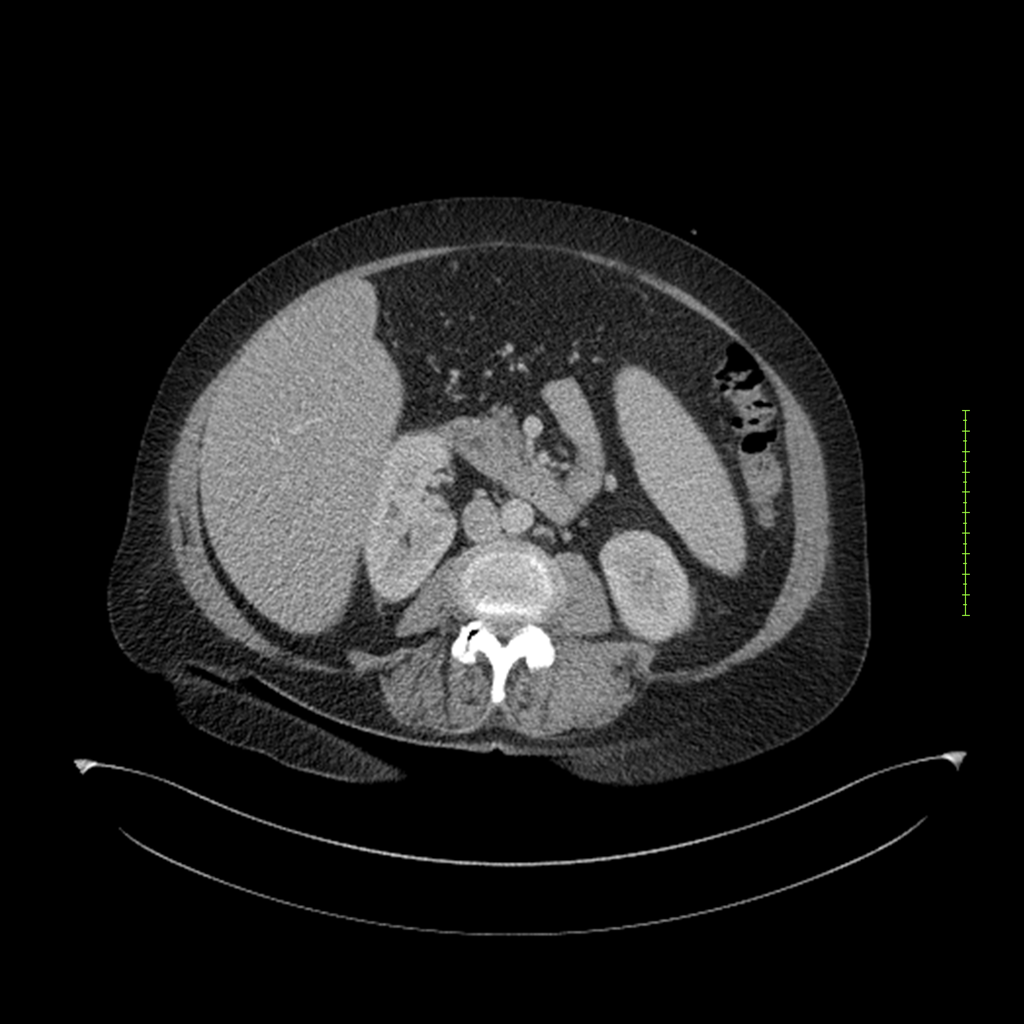
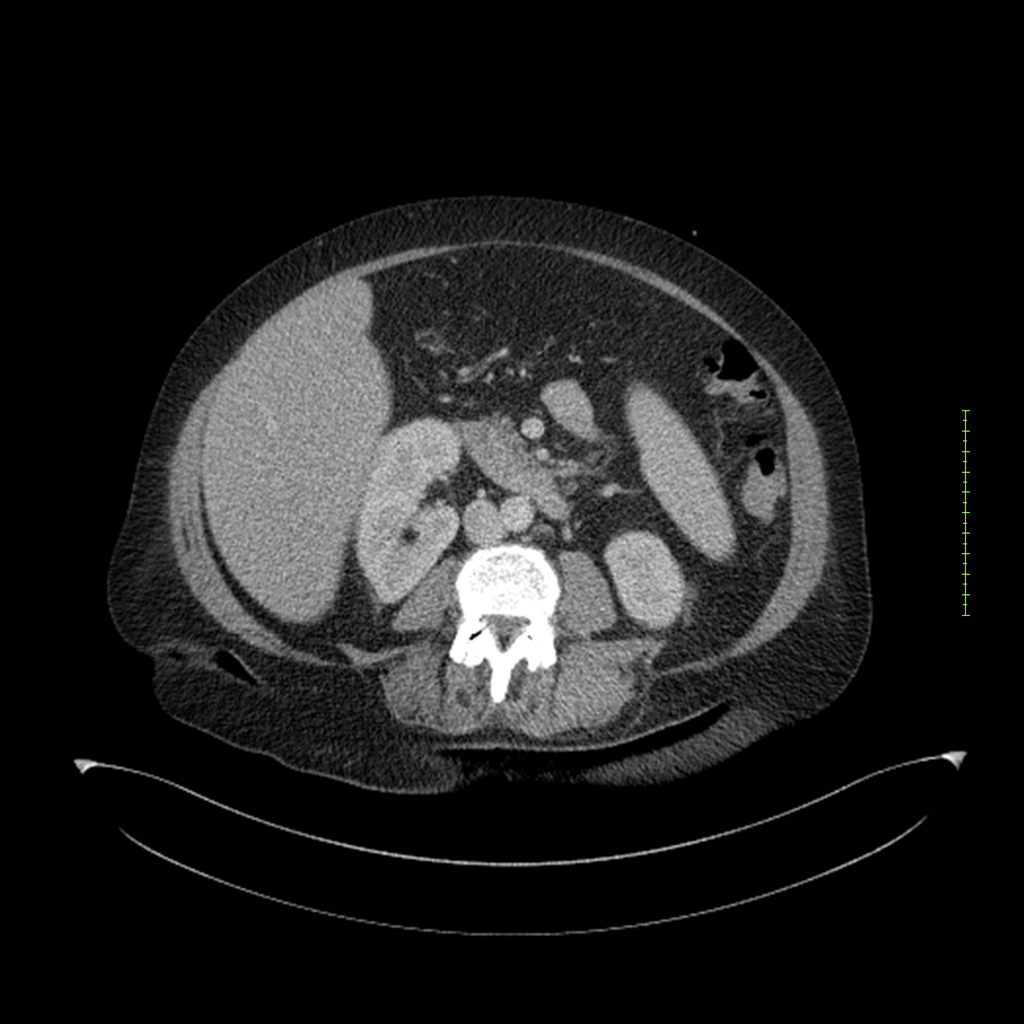
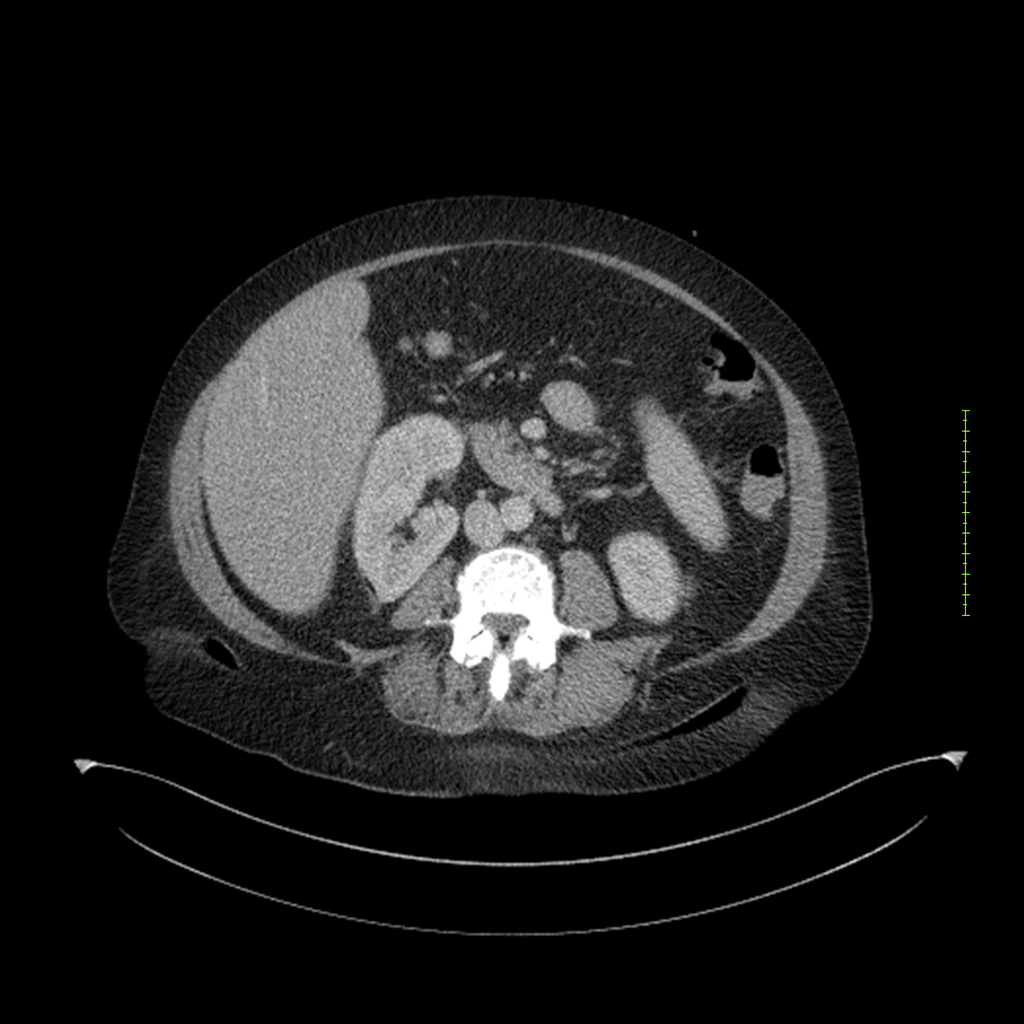
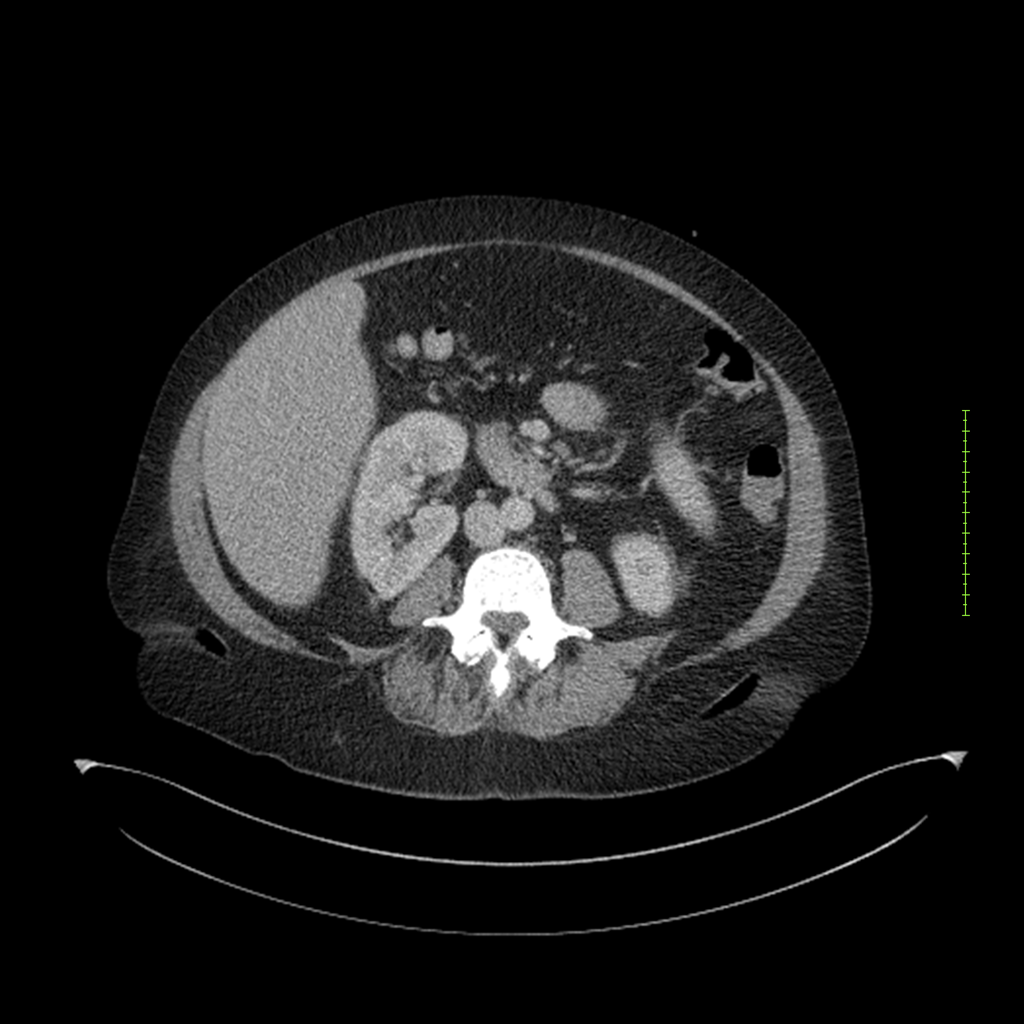
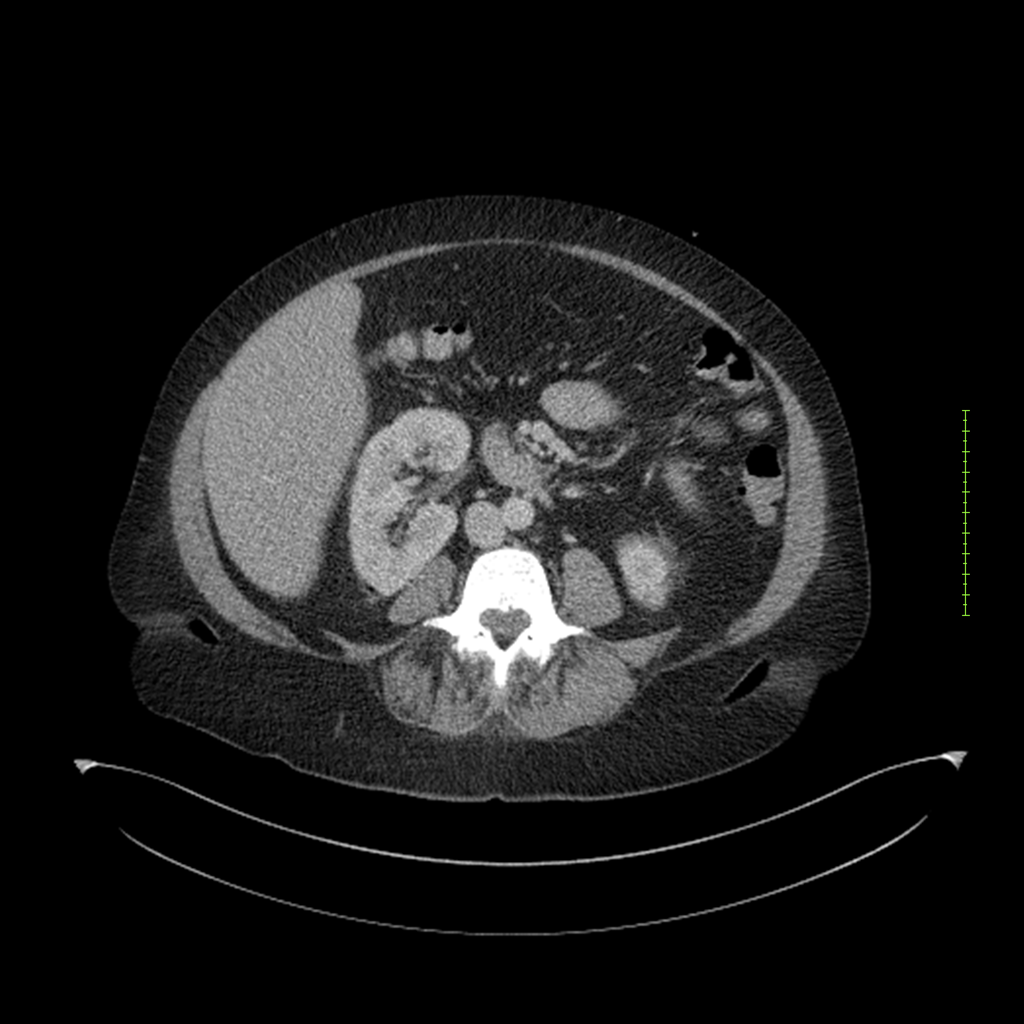
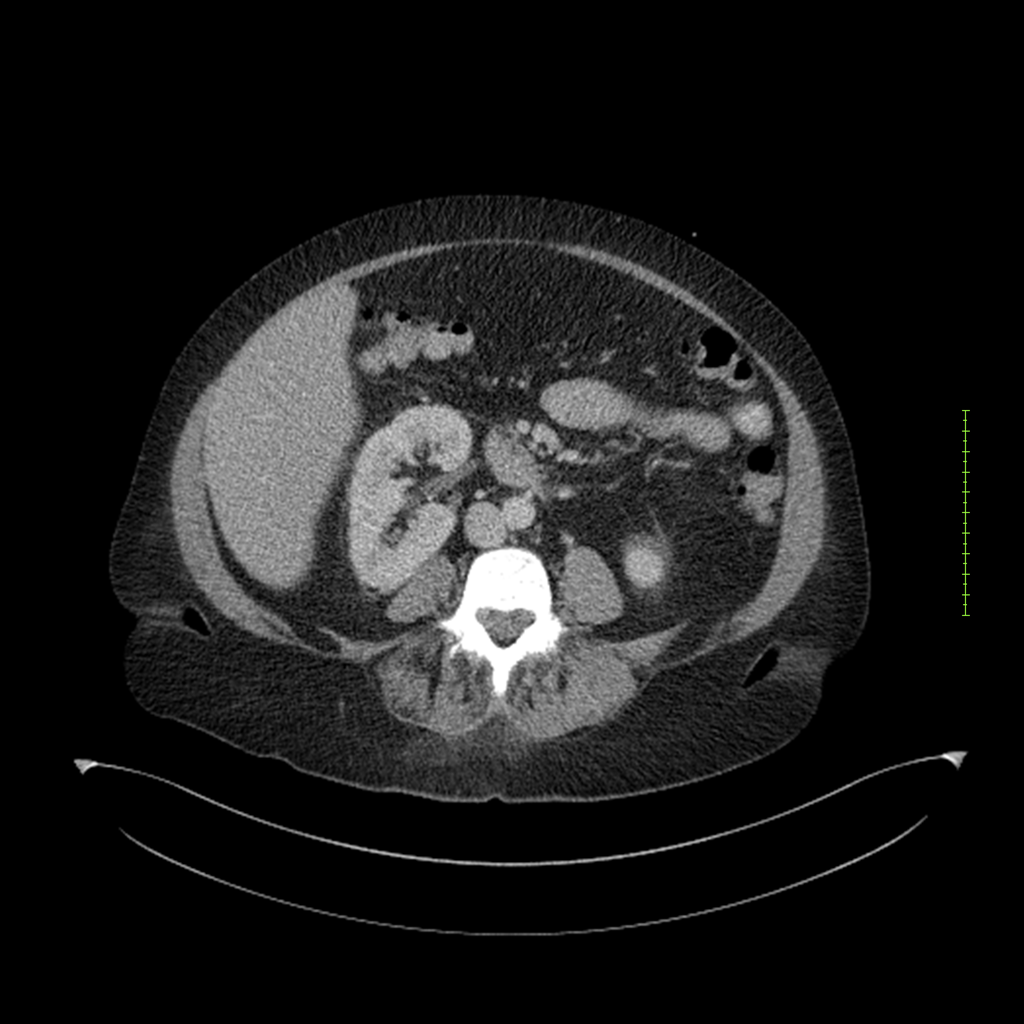
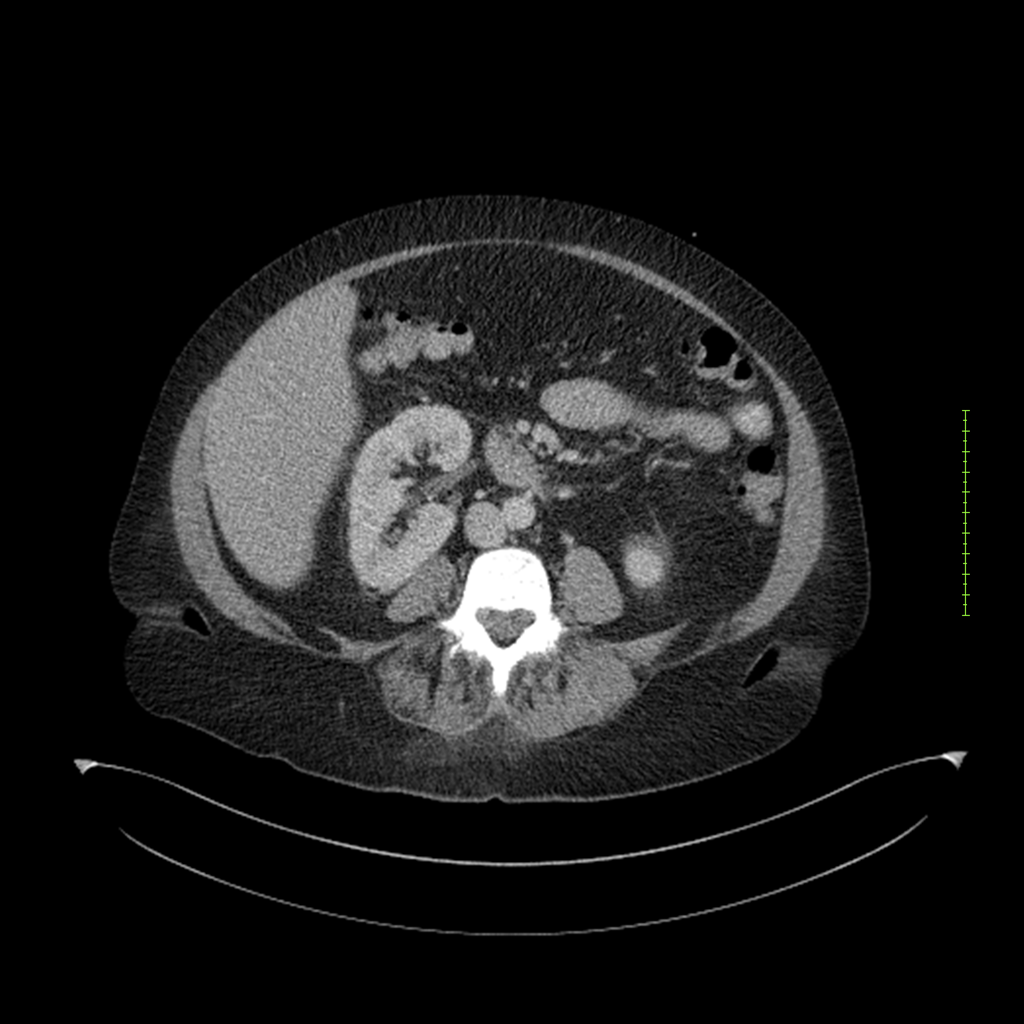
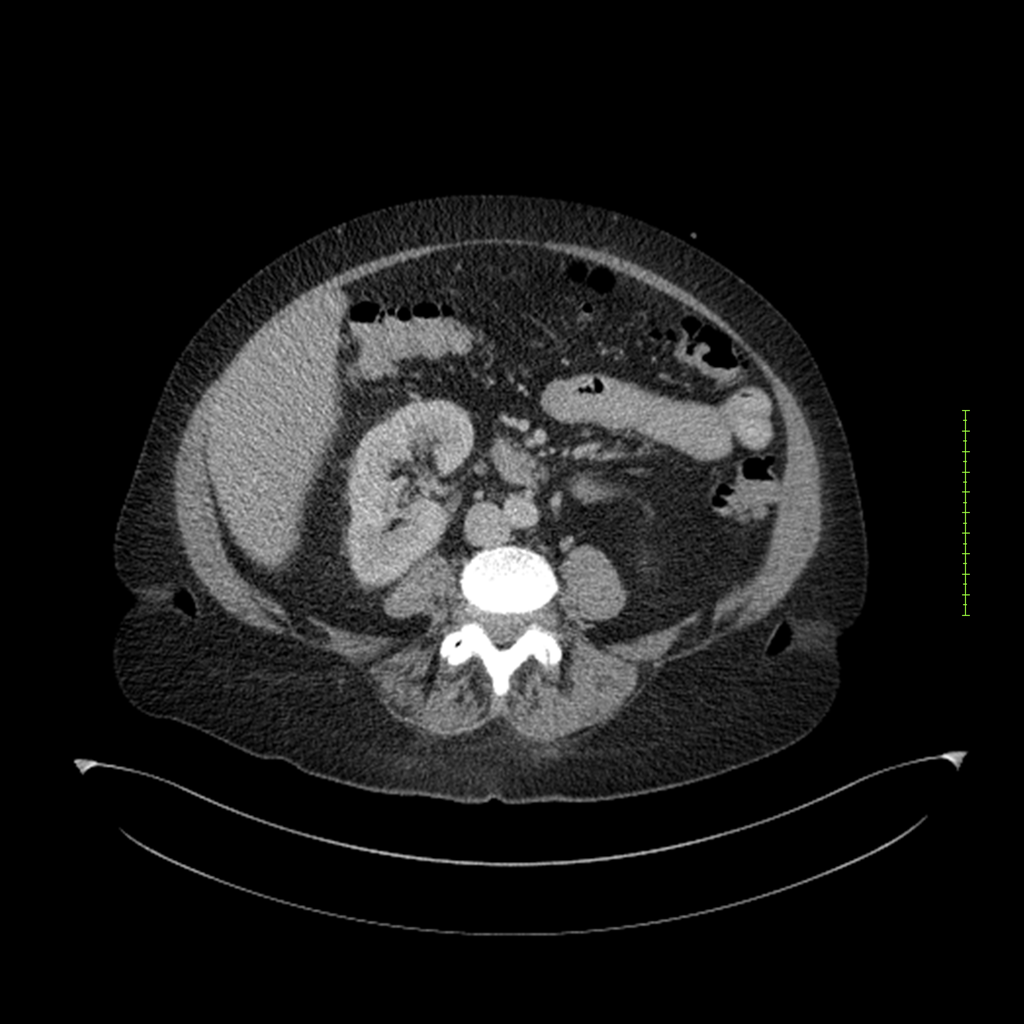
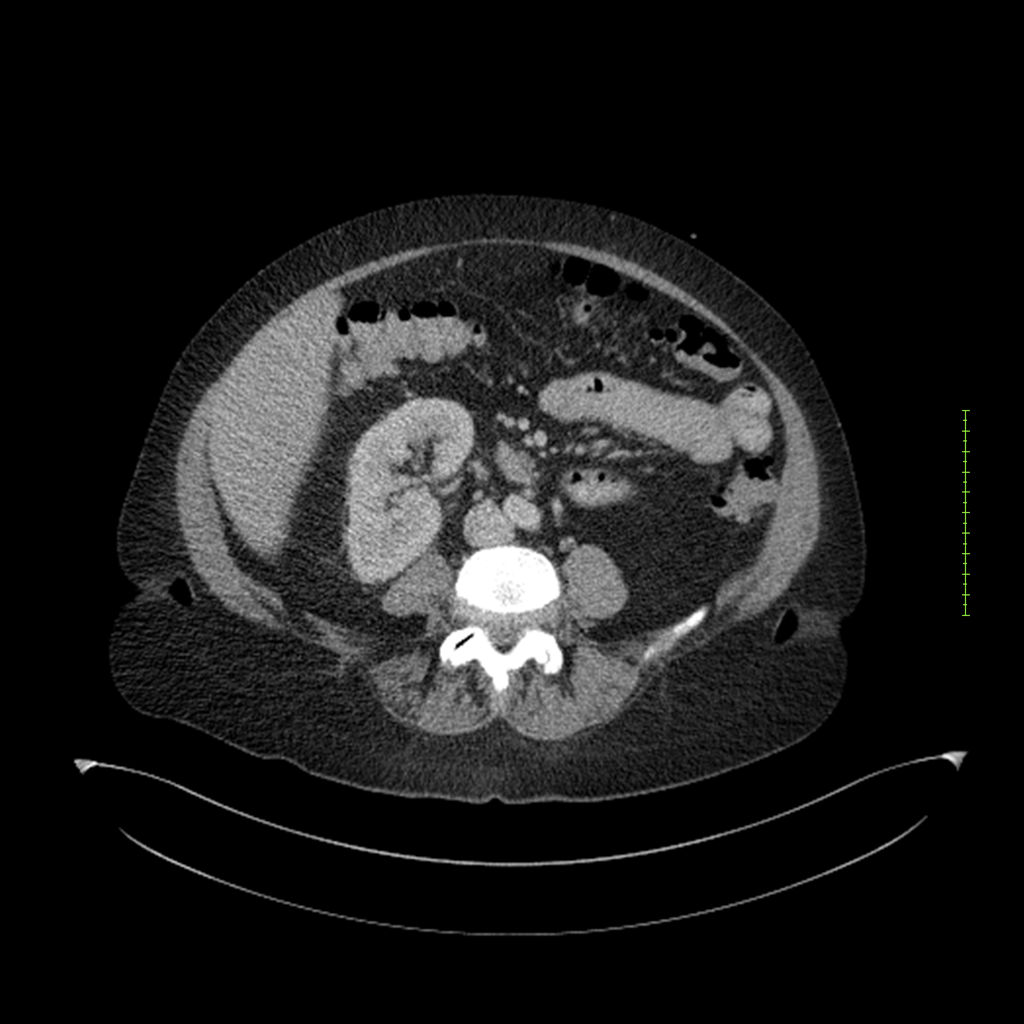
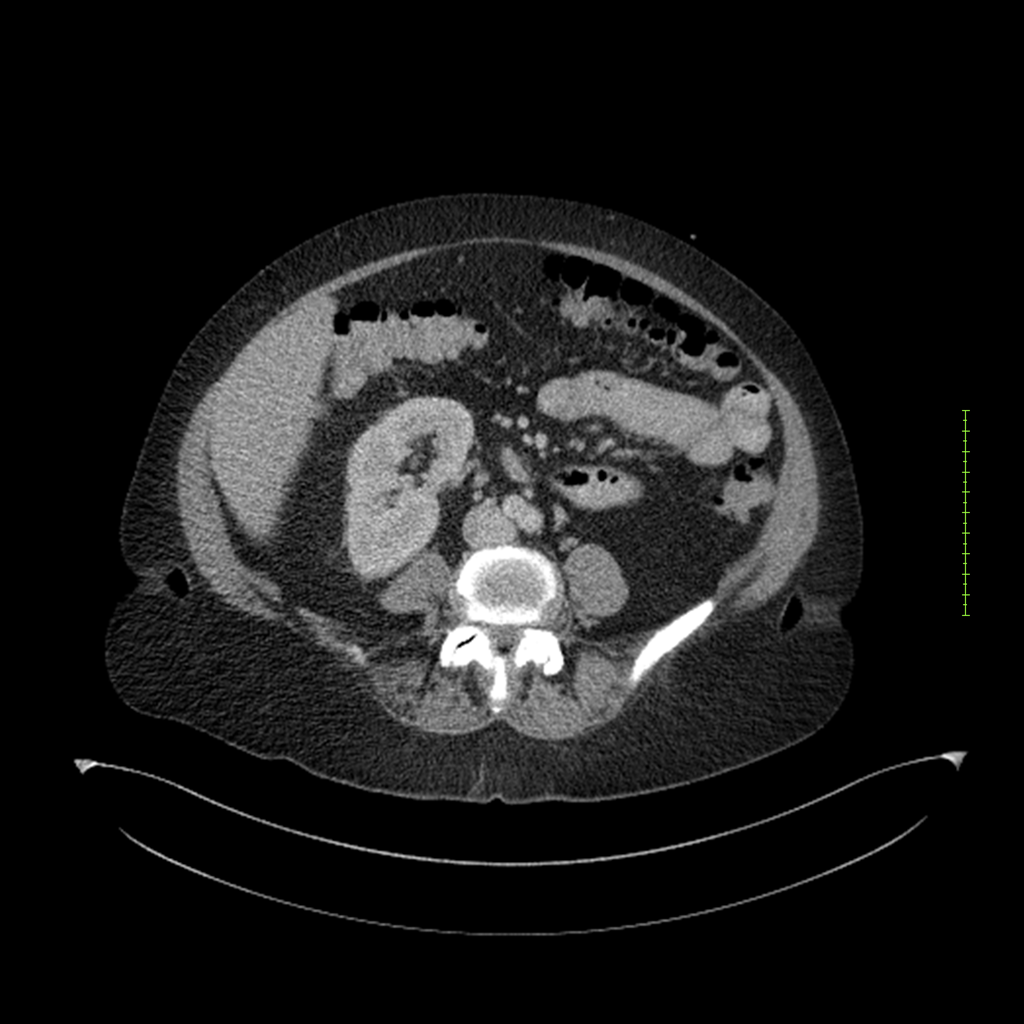
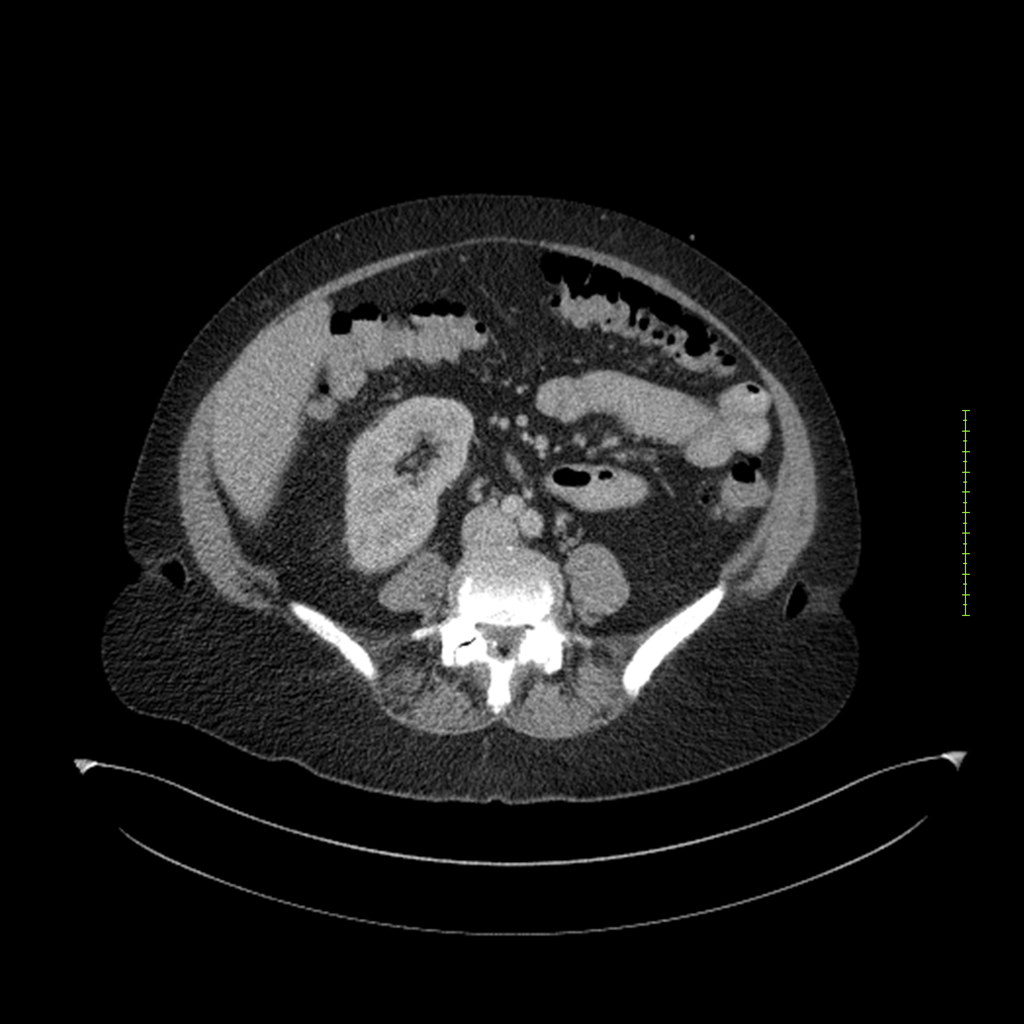
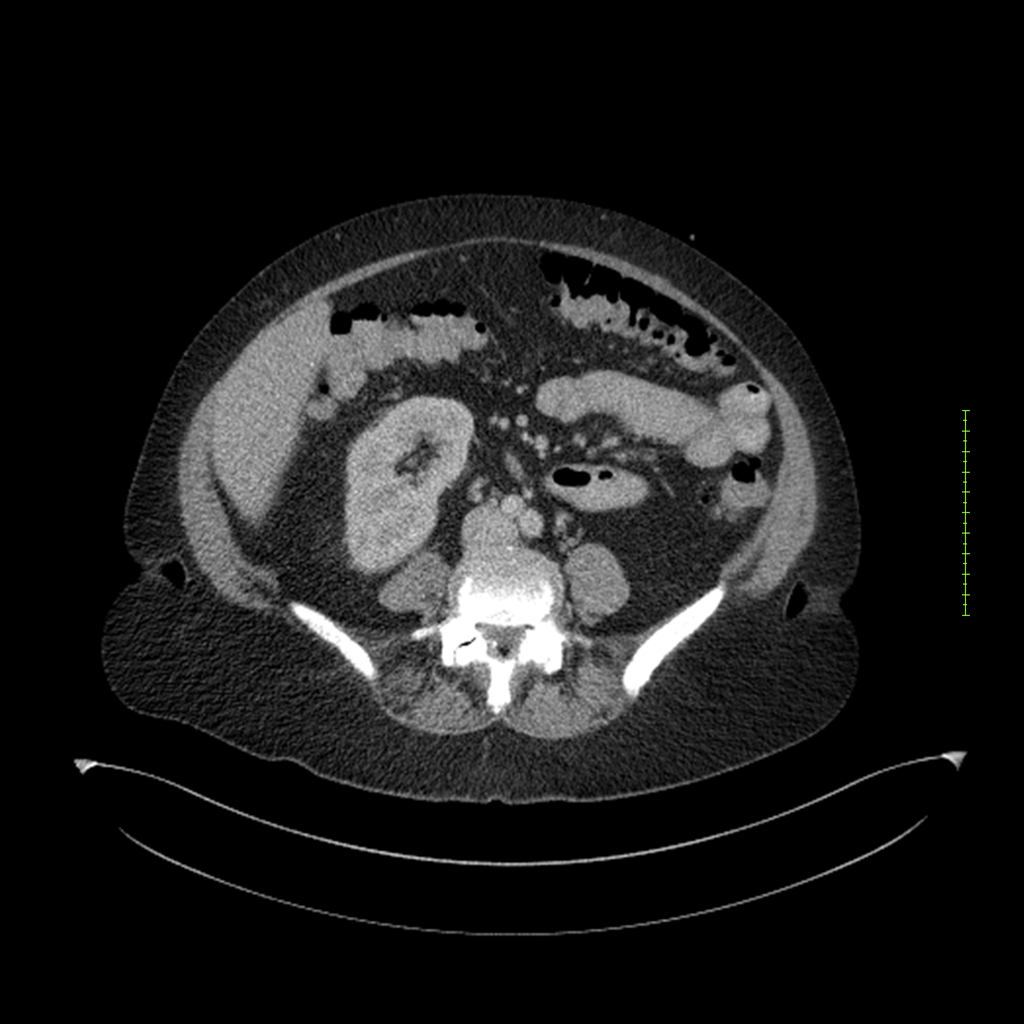
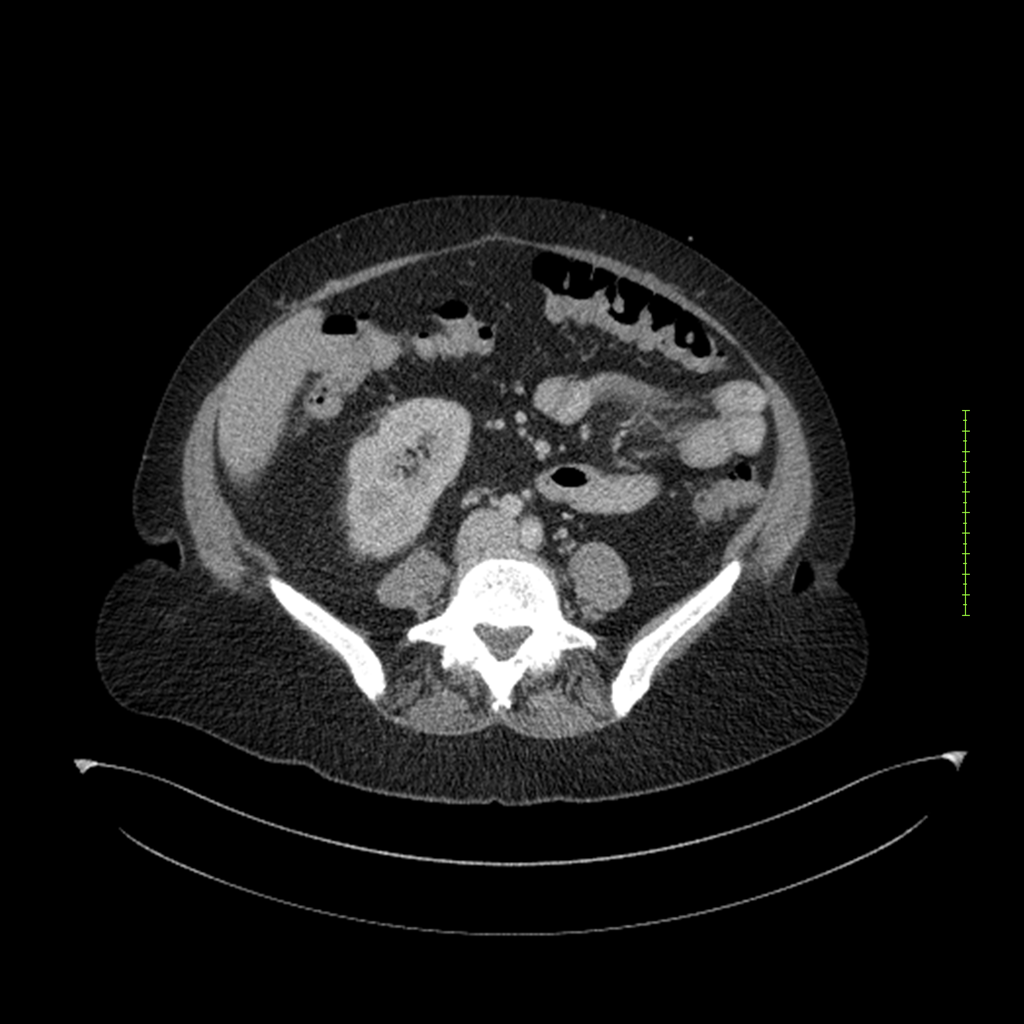
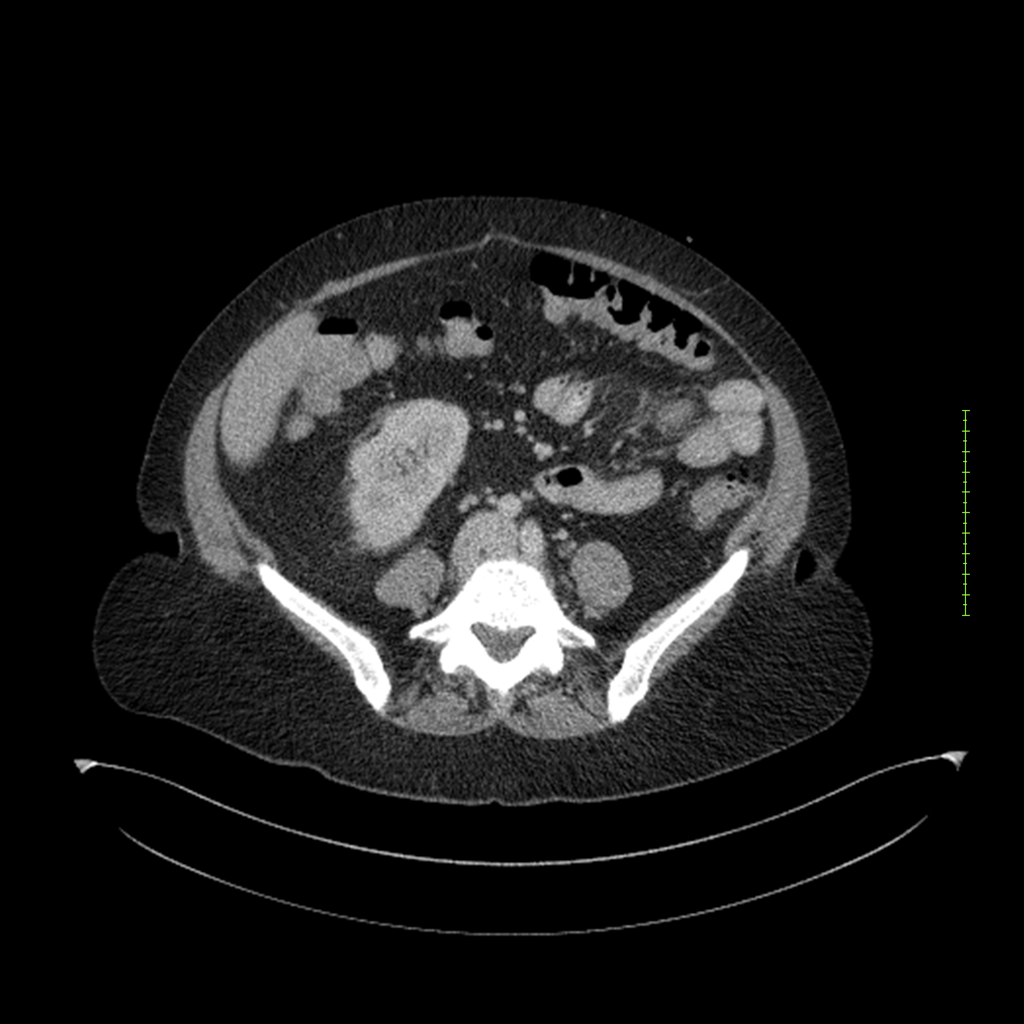
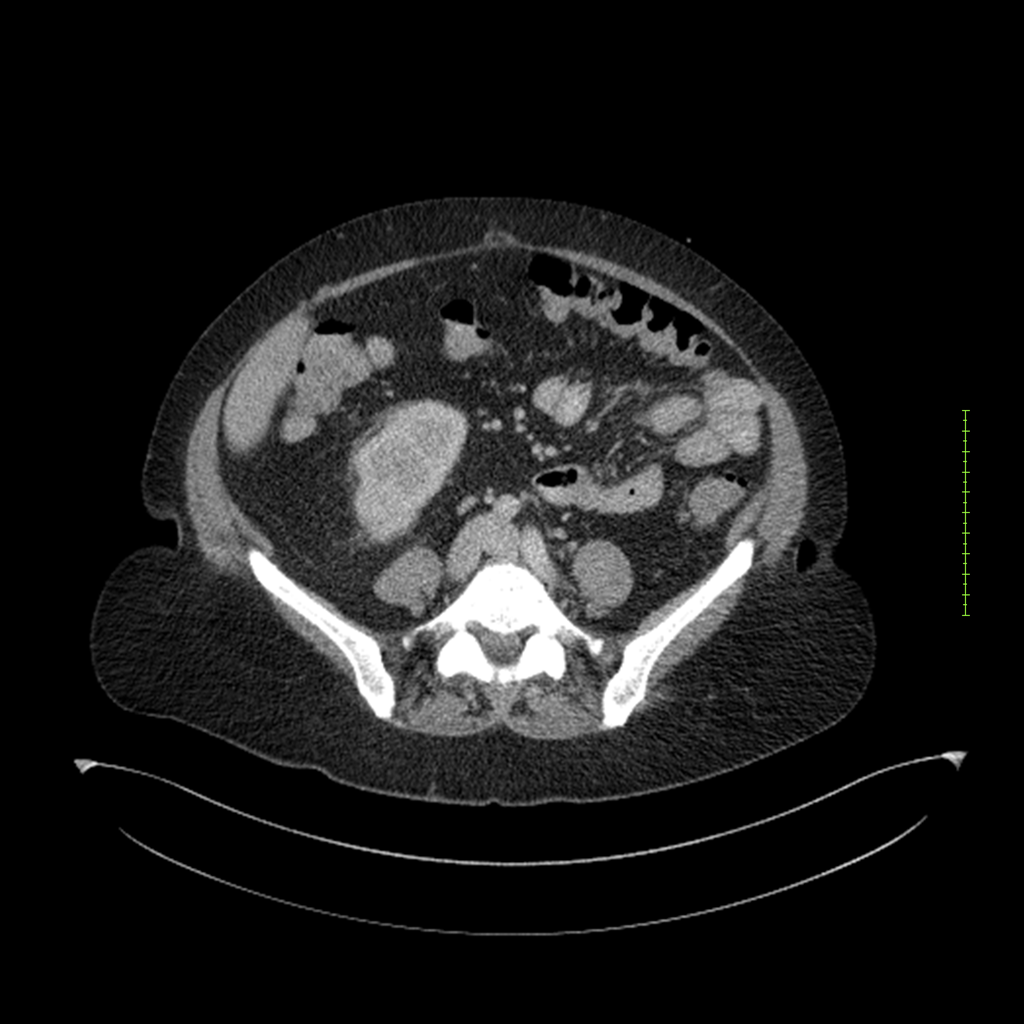
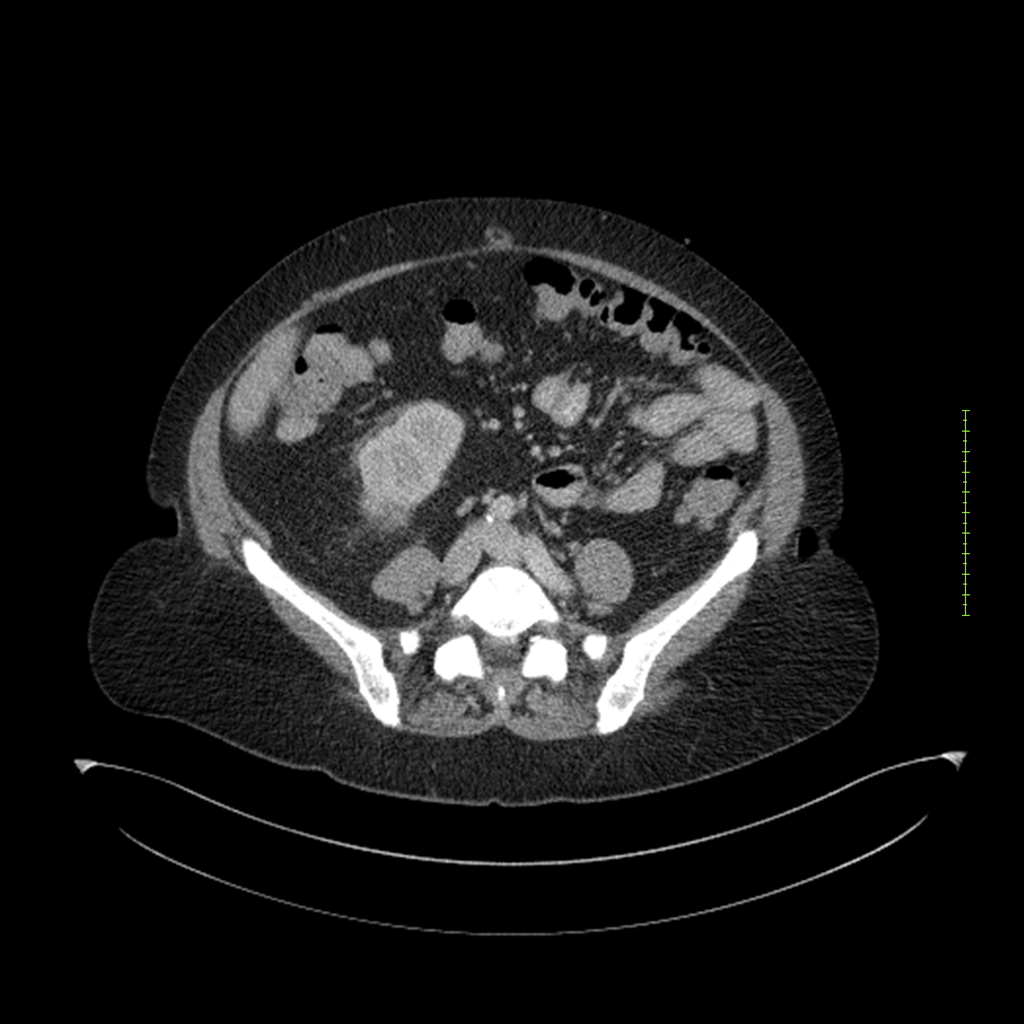
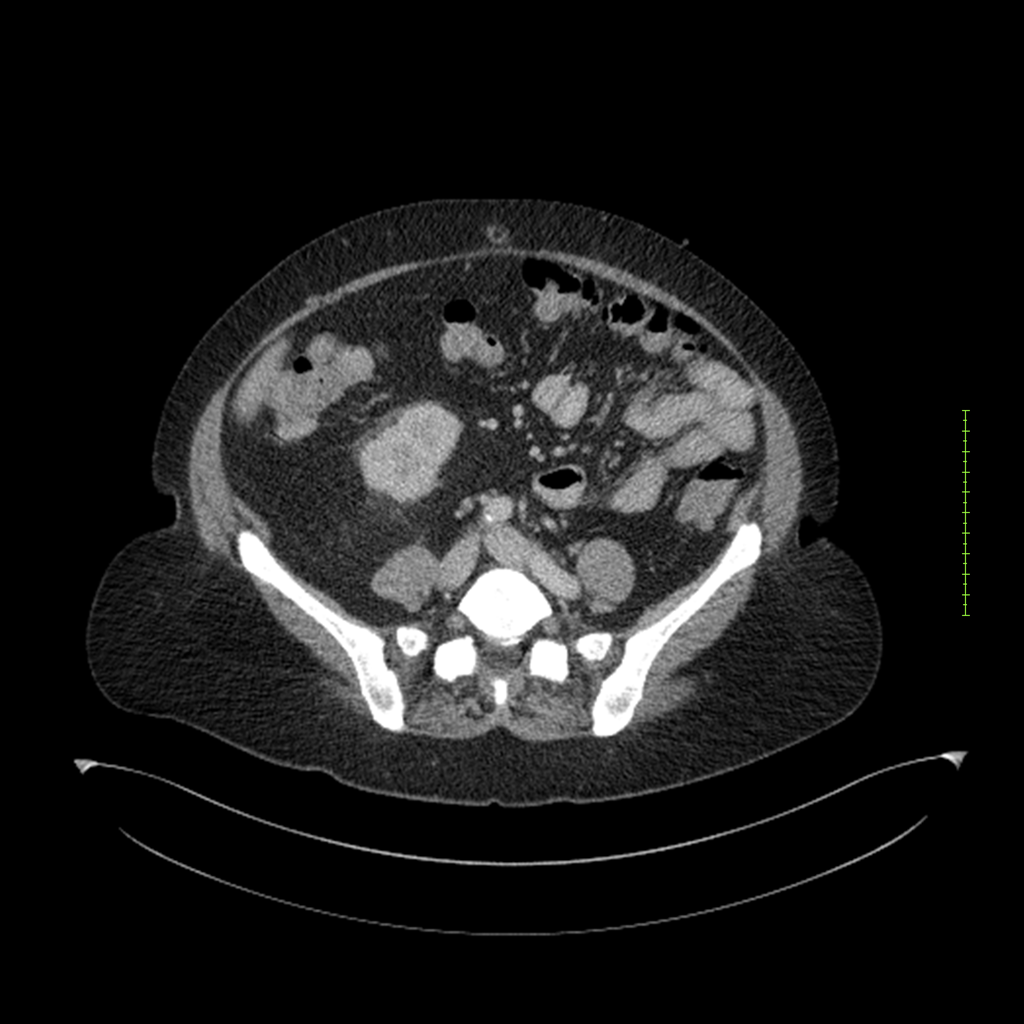
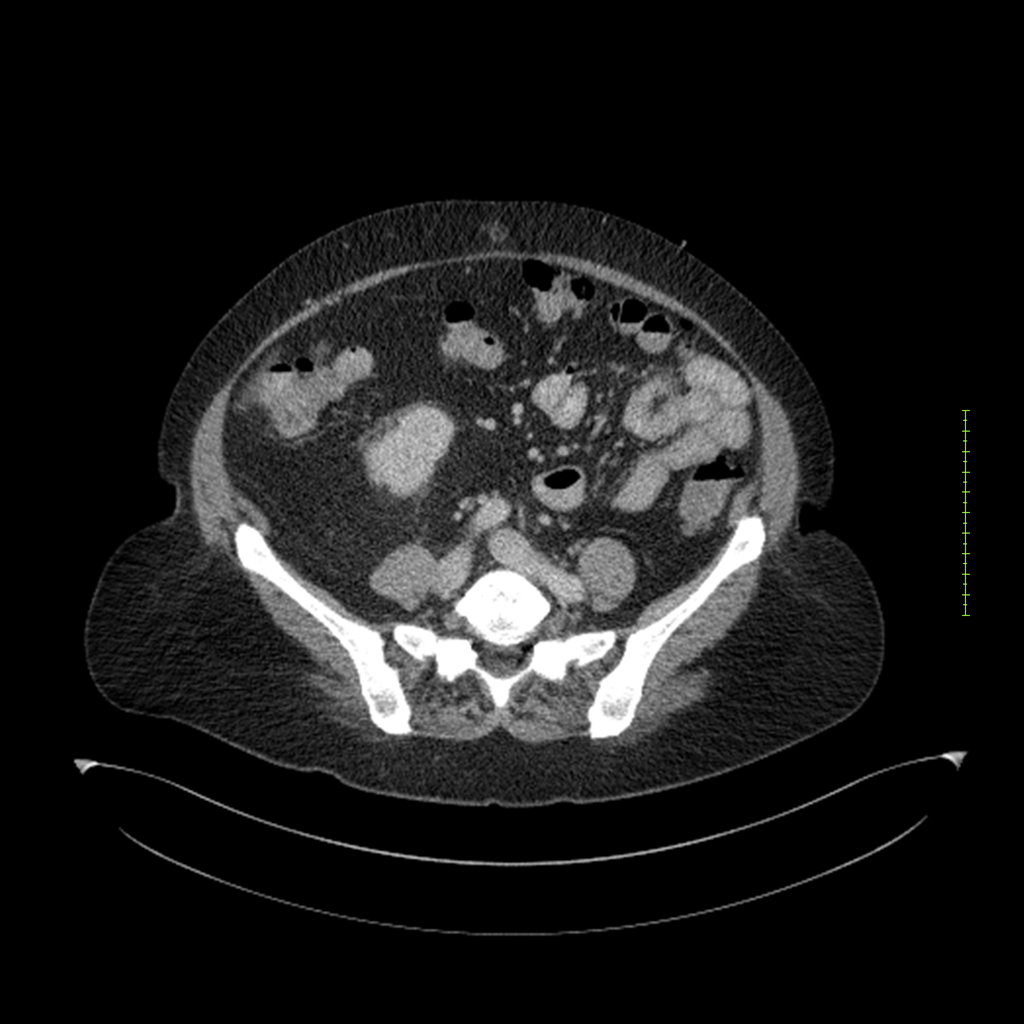
- 4-fase CT-abdomen (sensitiviteit 95-100%)
- - scherp omschreven, hypodense laesie
- - accentuering van de randen op na intraveneuze contrasttoediening
- MRI bij ernstige nierinsufficientie
Conservatieve behandeling
- - Empirische antibiotische therapie (Ceftriaxon iv 2000mg 1dd 6 weken + metronidazol iv 500mg 3dd 2 weken)
- - Diagnostische echogeleide punctie + kweken
- - Primaire percutane drainage bij abcessen >3cm
- - Aanpassing antibitioca vop geleide van kweek en gevoeligheidsbepaling
- - Minimaal 2 weken intraveneus antibitioca (totaal 6 weken) 23-24
Referenties
- 1. Seeto RK, Rockey DC. Pyogenic liver abscess. Changes in etiology, management, and outcome. Medicine (Baltimore) 1996;75:99-113
- 2. Ochsner A, DeBakey M, Murray S. Pyogenic abscess of the liver II. An analysis of forty-seven cases with review of the literature. Am J Surg 1938;XL:292-319.
- 3. Mohsen AH, Green ST, Read RC, McKendrick MW. Liver abscess in adults: ten years experience in a UK centre. QJM 2002;95:797-802.
- 4. Huang CJ, Pitt HA, Lipsett PA, Osterman FA Jr, Lillemoe KD, Cameron JL, et al. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. Changing trends over 42 years. Ann Surg 1996;223:600-7
- 5. Zibari GB, Maguire S, Aultman DF, McMillan RW, McDonald JC. Pyogenic liver abscess. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2000;1:15-21
- 6. Lee KT, Wong SR, Sheen PC. Pyogenic liver abscess: an audit of 10 years experience and analysis of risk factors. Dig Surg 2001;18:459-65.
- 7. Seeto RK, Rockey DC. Amebic liver abscess: epidemiology, clinical features, and outcome. West J Med 1999;170:104-9
- 8. Alvarez JA, Gonzalez JJ, Baldonedo RF, Sanz L, Carreno G, Jorge JI. Single and multiple pyogenic liver abscesses: etiology, clinical course, and outcome. Dig Surg 2001;18:283-8.
- 9. Rahimian J, Wilson T, Oram V, Holzman RS. Pyogenic liver abscess: recent trends in etiology and mortality. Clin Infect Dis 2004;39:1654-9
- 10. Ahmad J, Slivka A. Hepatobiliary disease in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2002;31:329-45
- 11. Alvarez J, Gonzalez J, Baldonedo R, Sanz L, Junco A, Rodriguez J, et al. Pyogenic liver abscesses: a comparison of older and younger patients. HPB (Oxford) 2001;3:201-6.
- 12. Fernandez Ruiz M, Guerra Vales JM, Castelbon Fernandez FJ, Llenas Garcia J. [Pyogenic liver abscess as presenting manifestation of silent colon adenocarcinoma.]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2007;99:303-5
- 13. Chen SC, Yen CH, Lai KC, Tsao SM, Cheng KS, Chen CC, et al. Pyogenic liver abscesses with Escherichia coli: etiology, clinical course, outcome, and prognostic factors. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2005;117:809-15.
- 14. Haque R, Ali IM, Petri WA Jr. Prevalence and immune response to Entamoeba histolytica infection in preschool children in Bangladesh. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;60:1031-4.
- 15. Chung YF. Pyogenic liver abscess--predicting failure to improve outcome. Neth J Med 2008;66:183-4
- 16. Annunziata GM, Blackstone M, Hart J, Piper J, Baker AL. Candida (Torulopsis glabrata) liver abscesses eight years after orthotopic liver transplantation. J Clin Gastroenterol 1997;24:176-9.
- 17. Lai CH, Chen HP, Chen TL, Fung CP, Liu CY, Lee SD. Candidal liver abscesses and cholecystitis in a 37-year-old patient without underlying malignancy. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:1725-7.
- 18. Bernabeu-Wittel M, Villanueva JL, Pachon J, Alarcon A, Lopez-Cortes LF, Viciana P, et al. Etiology, clinical features and outcome of splenic microabscesses in HIV-infected patients with prolonged fever. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1999;18:324-9
- 19. Lodhi S, Sarwari AR, Muzammil M, Salam A, Smego RA. Features distinguishing amoebic from pyogenic liver abscess: a review of 577 adult cases. Trop Med Int Health 2004;9:718-23.
- 20. Van Doorn HR, Hofwegen H, Koelewijn R, Gilis H, Peek R, Wetsteyn JC, et al. Use of rapid dipstick and latex agglutination tests and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serodiagnosis of amebic liver abscess, amebic colitis, and Entamoeba histolytica cyst passage. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:4801-6.
- 21. Robert R, Mahaza C, Bernard C, Buffard C, Senet JM. Evaluation of a new bicolored latex agglutination test for immunological diagnosis of hepatic amoebiasis. J Clin Microbiol 1990;28:1422-4.
- 22. Tanyuksel M, Petri WA Jr. Laboratory diagnosis of amebiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev 2003;16:713-29.
- 23. Chu KM, Fan ST, Lai EC, Lo CM, Wong J. Pyogenic liver abscess. An audit of experience over the past decade. Arch Surg 1996;131:148-52.
- 24. Stichting Werkgroep Antibiotica Beleid. 2017